ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
Adinath D. Gade1, Sagar P. Mali2 , Yogesh A. Mane3
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
Economic development is happening due to rapid rate of industrialization and urbanization in India. The growth and development of the urban area largely depend on proper urban planning and provision of urban utility services for urban wellbeing. Good quality road network, electricity, water supply, proper urban land use and sanitation planning are major urban service and School, Banks, Hospital, Fire and Police station, Market and Entertainment are major utility service which indication of the quality of city. Technology plays vital role in urban utility services, urban monitoring, planning and decision making. The aim of this present study is to find out various utility services with respect to road network and find the optimal path and service area of urban resources in Solapur city. Google earth data and Survey of India (SOI) toposheets were used for base map. GPS survey carried out for collected the various utility services within city. In analysis, satellite image used for study the land use / land cover pattern of the city, network analysis used for find out the optimal path for rapidly accessible utilities and service area demarcated for the identification of zones of the specific utility service. Analysis resulted that, there is lack of major utility services in the city periphery and need to more services establish in city periphery. Geoinformatic techniques has powerful source for real time data and helpful in utility planning and monitoring urban environment.
Keywords |
| GPS, Service Area, Optimal Path |
I. INTRODUCTION |
| In 2001, about 286 million persons were living in urban areas of India and it was the second largest urban population in the world. The 74th Constitution Amendment Act (CAA) came into force in June, 1993 which sought to improve strengthen urban governance and management of services. The traditional role of Municipal Corporation had been one of providing basic Utilities of civilian for their happy social life. Service includes water supply, sanitation, roads, street-lights, health service and maintenance of public places. In addition, they performed certain regulatory functions relating construction of buildings, public areas and commercial places for public wellbeing like Banks, ATM centers, Fire stations, Ambulance, School and Colleges, Hospitals and Blood banks, Police station and shopping malls, Entertainment locations establishments in a proper place in city. In addition, as each element plays its own role in the formation of urban structure, every city possesses a unique structure with its own momentum, presenting entities that are occasionally regarded as too diverse for a single topical study. Nevertheless, “geography is not about the precise analysis of particular service areas. it is more concerned with the ways in which these relationships are reflected in the functional and physical structure of the town” (Dickinson, 1959). |
II. STUDY AREA |
| Solapur is situated on the south-eastern border of Maharashtra State adjoining Karnataka. The city is located on the East side of Maharashtra between 170 40â N Latitude and 750 54â E Longitude. The city covers an area of 180.33 sq km. |
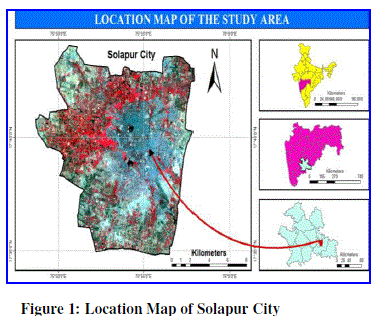 |
III. DATA & METHODOLOGY |
 |
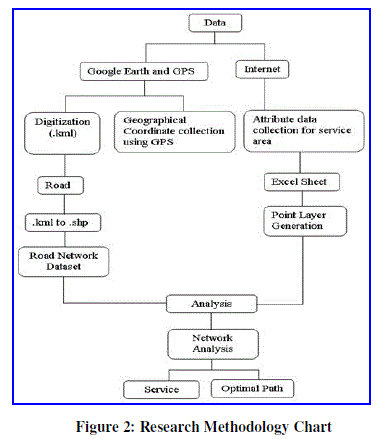
| In the present research methodology, both spatial and non-spatial data integrated in GIS environment. First road network map prepared on Google Earth and GPS survey carried out for collection of utility services in the city. Both Google map and GPS survey data convert into shape file using Global Mapper 12 software and bring these file into ArcGIS 9.3 desktop application. Final analysis carried out using Network Analysis tool in ArcGIS 9.3 and calculate Optimal path and service area of various utility services in the city with respect to time and speed of vehicle. Figure 3. highlight the general research methodology. |
 |
IV. RESULT AND DISCUSSION |
 |
| With the use of remote sensing & GIS technology we can calculate accurate distance & time from incident to facility. Here calculate distance (meter) & time (minute) from incident( Bus Stop) to facility(Hospital). Here we consider the average speed of vehicle have 30Km./hr . In Solapur city Shivaji Chowk Bus Stop is main Bus Stop from this incident Dr. Chidgupkar Hospital is very nearest. The distance between this two place is 747.401694 meter & 1.494803 minute time necessary for cover this distance. Then, Sidheshwar Cancer Hospital is far way from facility (Hospital) The distance between this two place is 4778.255535meter & 9.556511minute time necessary for cover this distance. Table No: 3 calculate the distance (meter) & time (minute) from incident( Bus Stop) to facility(Hospital) in Solapur city. |
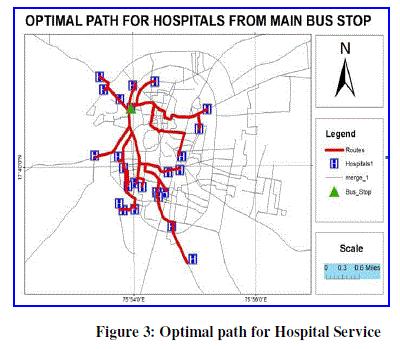 |
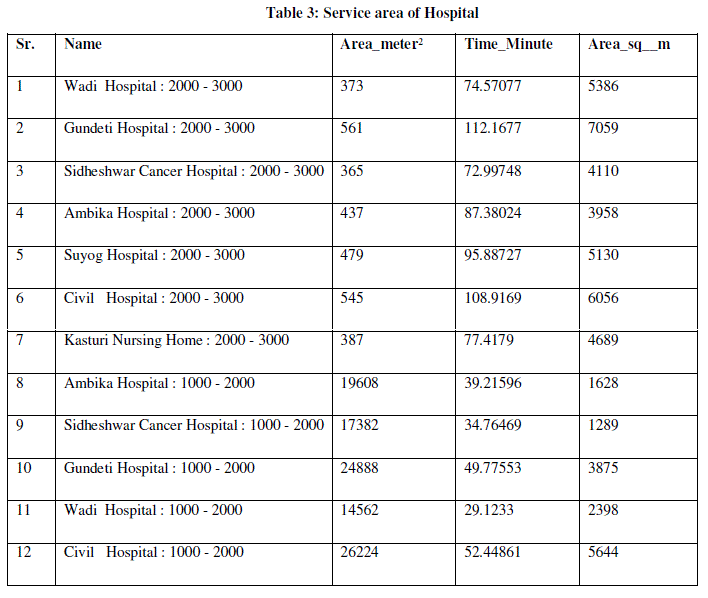
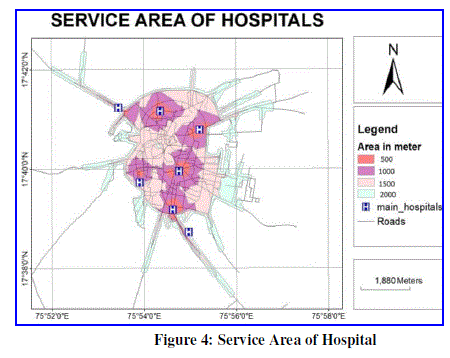
| Here calculate the service area of hospitals with using remate sensing & GIS technology. Service area divided in to four categories (0-500, 500-1000, 1000-2000 & 2000-3000 meter ) & calculate total area & time distance. |
 |
 |
| Nearly, 18995 sq km. area cover in 0-500 meter service area zone , 5658 sq km. area cover in 0-500 meter service area zone . 4140 sq m. area cover in 500-1000 meter service area zone & 57426 sq km. area cover in 1000-2000 meter service area zone. |
| 3. Optimal path for Fire Brigade: |
| Here draw optimal path from fire brigade to main chowk . The distance between Saraswati chowk Bus Stop to first fire brigade is very optimal or short compare to other that is 445.296254 meter distance & want 0.890593 minute time for cover this distance. The distance between Ashok Nagar Bus Stop is mutch away from second fire brigade compare to other that is 2060.44582 meter distance & want 4.120892 minute time for cover this distance. |
 |
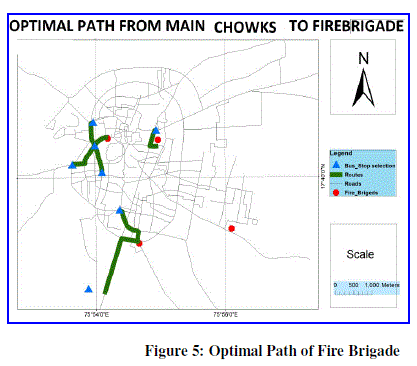 |
| In Solapur four area found. Here we calculate the service area of fire brigade with breakage 1000, 2000, 3000 & 4000 meter. As well as calculate the time in meter for cover this particular area. Table 4 show the zone wise service area & time. For 1000 meter area travelling wants two minute time. In Solapur city want 12 to 14 minute’s time for provide fire brigade service to outer side of city. Then 6 to 8 minute’s time want for middle area of city. |
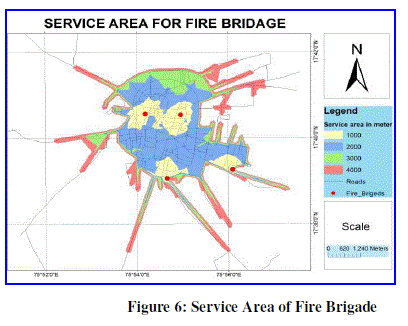 |
| Nearly 942 sq. km. area cover under 0-5 minute time service area zone of school & colleges,3452 sq. km. area cover under 5-10 minute time service area zone, then 6795 sq. km. area cover under 10-15 minute time service area zone. |
V. CONCLUSION & DISCUSSION |
| In Solapur city several emergency services like blood banks, hospitals and fire brigades etc. mainly found in the very few in number and concentrated at city core area which took more time for providing emergency services. |
| Dr. Chidgupkar Hospital is very nearest from CBD. The distance between this two place is 747.401694 meter & 1.494803 minute time necessary for cover this distance. Then, Sidheshwar Cancer Hospital is far way from facility (Hospital) The distance between this two place is 4778.255535meter & 9.556511minute time necessary for cover this distance. Most hospitals lie within 1000-2000 meter i.e. 57426 sq m. |
| In the service area of School & colleges very mutch area cover within 0-1000 meter service zone ie 775 km² area cover. In time analysis of service area nearly 942 sq. km. area cover under 0-5 minute time service area zone of school & colleges,3452 sq. km. area cover under 5-10 minute time service area zone, then 6795 sq. km. area cover under 10-15 minute time service area zone. . In Solapur city want 12 to 14 minute’s time for provide fire brigade service to outer side of city. Then 6 to 8 minute’s time want for middle area of city. |
| In Suggestion, there is needed more emergency services such as hospitals, fire stations and blood banks at the peripheral region of the Solapur city for providing better accessibility in very short time. The other utility services like schools and colleges and mainly concentrated in city core area which need to decentralize towards the city outskirt or can be established such a new services towards city periphery for reduce the imbalance in utility services in the Solapur city. |
References |
|