
Volume 6
Research & Reviews: Journal of Material Sciences
ISSN: 2321-6212
Ceramics 2018
May 14-15, 2018
Page 38
conference
series
.com
May 14-15, 2018 | Rome, Italy
4
th
International Conference and Expo on
Ceramics and Composite Materials
J J Reinosa, Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C1-013
Effectiveness in UV absorption of hierarchical nano ZnO-microTiO
2
composites with photodegradation
inhibition
N
owadays, sunscreens are formulated by using TiO
2
and ZnO nanoparticles because they are efficient inorganic UV filters. In
fact microsized TiO
2
and ZnO have been increasingly replaced by TiO
2
and ZnO nanoparticles in order to solve the cosmetic
drawback of the white opaque sunscreens apart from the higher yield that nanoparticles suppose. Also the aggregation state of the
particles in sunscreens is related to the solar protection factor (SPF) of the final emulsion. In this sense, dispersed nanoparticles into
sunscreens increase the SPF value, but it means a possible leading to their incorporation into the stratum cornea, the outer layer of
the skin. Moreover, when TiO
2
is irradiated produces free radicals which are implicated in a number of potential health issues such
as skin aging because of the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). In this work, composites combining TiO
2
microparticles
and ZnO nanoparticles have been achieved by using several synthesis and dispersion methods. It has been demonstrated by the
incorporation of the different composites into sunscreens that the presence of nanoparticles anchored over TiO
2
microparticles
allows increasing the efficiency of nanoparticles but decreases the possible health problems by their absorption as nanoparticles.
The aim of these new composites is to gain the advantages of inorganic nanoparticles avoiding their potential drawbacks. Hence,
the combination of both oxides provokes higher SPF value and lower photodegradation, in comparison with TiO
2
microparticles.
Moreover, the disposition of ZnO and TiO
2
particles means a positive synergy by the recombination of photo induced electrons
holes, which decreases the formation of free radicals.
J J Reinosa
Institute of Ceramics and Glass (CSIC), Spain
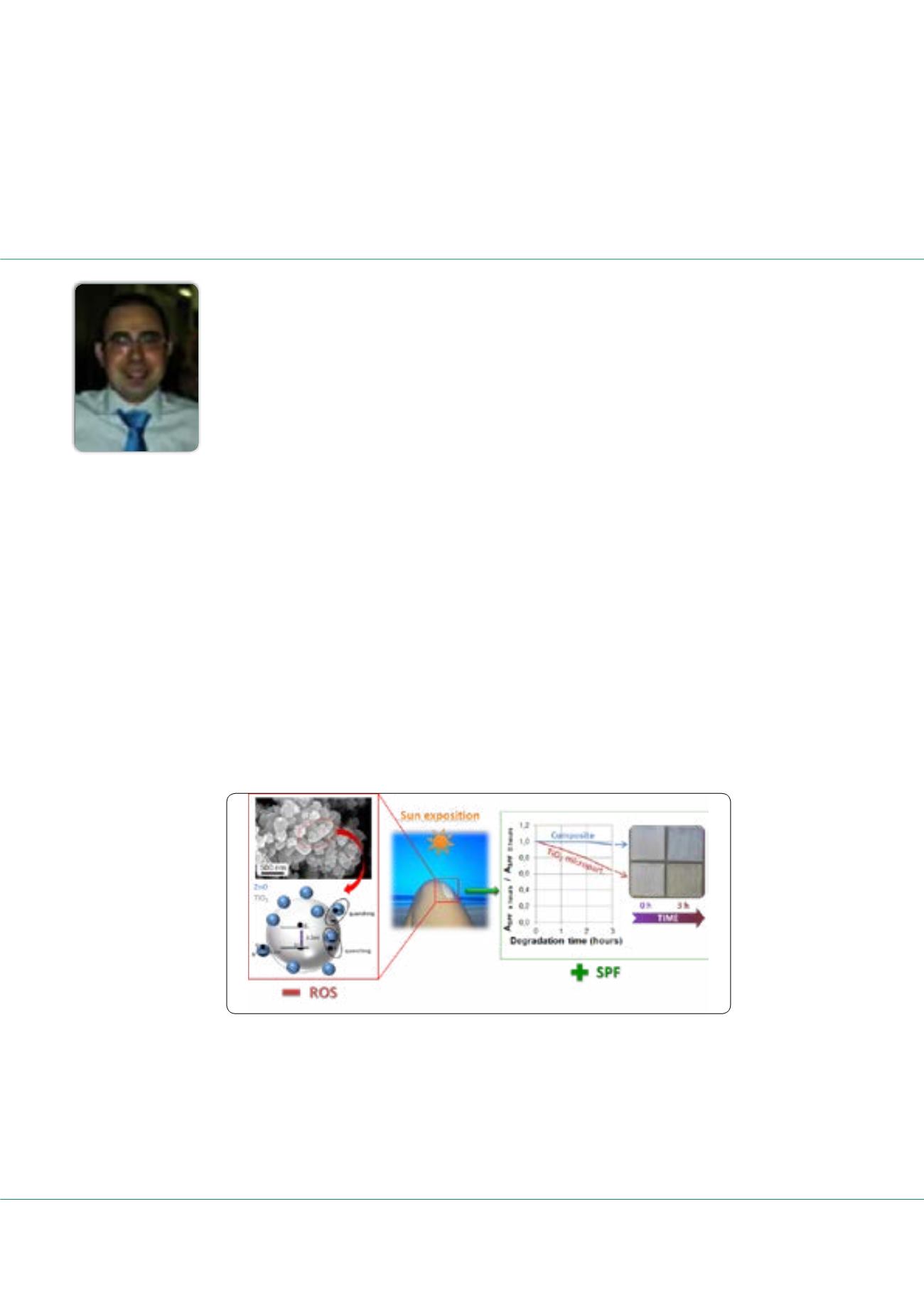
Figure 1: TiO2 and ZnO semiconductor oxides with high absorption in the UV-range; nevertheless in this study it was
observed the quenching of free radicals by recombination of electronic carriers. The hierarchical composite presents a
higher UV-absorption than the pure TiO2 counterpart. The functional stability study on standard sunscreen reveals a 50%
high UV-absorption over time for the hierarchical composite without organic photodegradation of the formulation
















