Page 72
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 6
Research & Reviews: Journal of Material Sciences
ISSN: 2321-6212
Ceramics 2018
May 14-15, 2018
May 14-15, 2018 | Rome, Italy
4
th
International Conference and Expo on
Ceramics and Composite Materials
Hybrid carbaneous nanomaterials composites to enhance the performance of grinding/Cutting fluids
S. Balaji, Ajay Ingle, Swapnil Pawar, N.Natarajan, Yumna Khan, Sharanya Prakash, Dhanashri K. Dhuri, Amit Kalyani
and
Sujatha Pushpakanth
Kalyani Centre For Technology And Innovation, Bharat Forge Limited, India
T
he rapid developments in nanotechnology has led to the emergence of a relatively new class of fluids called nano-
fluids, which could offer enhanced thermal conductivity and reducing the surface tension of the base fluid. Neat oil is
traditionally and commonly used in many fields such as cutting, grinding and machining applications. Different nanoparticles
exhibit various physicochemical properties (e.g., structure and shape), which can influence their lubricating properties. In
this work, we have engineered colloidal suspensions of nano composite with an average size of 30 to 50 nm of functionalized
graphene was covalently bonded to boron nitride by a microwave process, the nanocomposite was dispersed with base fluid
concentration ranging from 0.1 to 0.01% , by ultrasonication method. To obtain a uniform distribution of the nanocomposite
in the fluid matrix, with the purpose of filling the research gap in the literatures, this paper presents experimental data of
thermal conductivity and viscosity properties of hybrid graphene based nanocomposite in the nano fluids for effective grinding
applications. The FTIR spectroscopy further confirmed the presence of pyrophosphate and metal-oxygen bonding with O-H
stretching and existence of nitride bonds in the composites which reveal the existence of boron group and carbon particles
in the composite nano-fluid. Machining parameters are measured during grinding applications using nano composite fluid.
It is observed that properties such as surface roughness, temperature stability, cylindrical and chips morphology, and cutting
efficiency drastically improved with increased tool life exhibiting better machining performance compared to base fluid.
The grinding chips morphology observed in the scanning electron microscope revealed less shearing with improved martial
cutting. The results showed that the type of nano-composite and its concentration in base fluid play a significant role in
reducing friction.
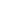
Figure 1:
Schematic representation of preparation and application of nano-fluids
Recent Publications:
1. Padmini R, Vamsi Krishna P, Krishna Mohana Rao G (2016) Effectiveness of vegetable oil based nanofluids as potential
cutting fluids in turning AISI 1040 steel. Tribology International 94:490-501.
2. Baldev Raj, Angayarkanni S.A, John Phlip(2017) Nanofluids for Efficient Heat Transfer Applications.Nanotechnology
for Energy Sustainability 40
3. Sheikholeslamia M, Hayat T, Alsaedic A, Abelmand SNumerical analysis of EHD nanofluid force convective heat
transfer considering electric field dependent viscosity.International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 108:2558-2565.
4. Dinesh Setti, Manoj Kumar Sinha, Sudarsan Ghosh, Venkateswara Rao P(2014) Performance evaluation of Ti–6Al–
4V grinding using chip formation and coefficient of friction under the influence of nanofluids International Journal of
Machine Tools & Manufacture 88 : 237–248.
Biography
Dr. S. Balaji obtained his doctoral degree in the field of Material and Biomaterial science. His additional expertise is in the synthesis of nanoparticles and composite
fabrications. His current research is focused towards the development of nano-biomaterials and metal matrix composite and improving their performance in
applications such as Automobile & Health Care. He also holds five Indian patents & 16 International publications.
Balaji.Srinivas@Bharatforge.comS. Balaji et al., Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C1-015