ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
Dr. P.Sireesha1,Dr.B.Sudhakar Rao2 and Dr.D.Thammi Raju3
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
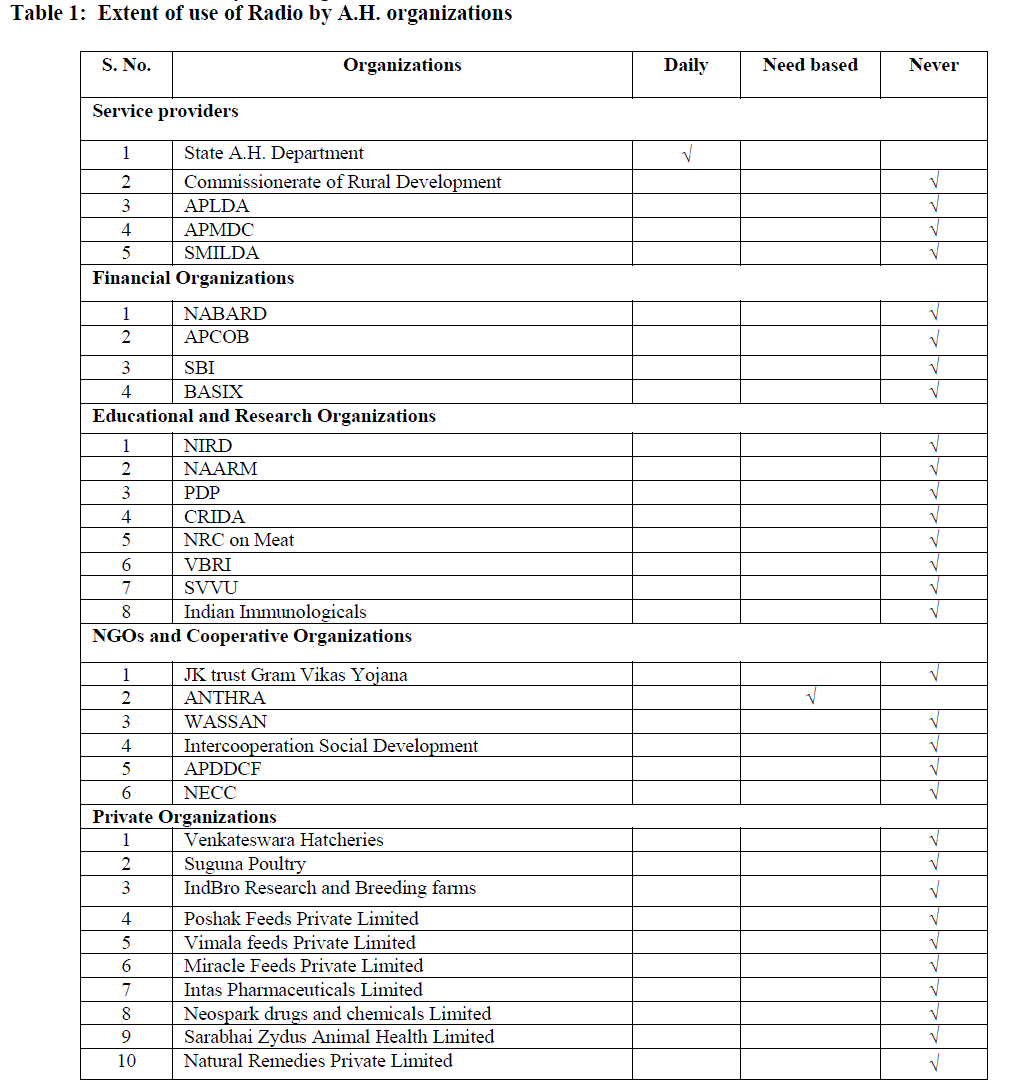
Data was collected from 33 organizations which were actively involved in Animal Husbandry activities and elicited through a questionnaire following an exploratory research design on “Utilization of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) tools by various organizations in Animal Husbandry – A study in Andhra Pradesh.” The findings on the extent of use of ICT tools revealed that Radio was utilized by State A.H. Department and ANTHRA. Further analysis on the extent of ICT tools by organizations revealed that TV was utilized by NIRD, NAARM, State A.H. Department, APLDA, SMILDA, BASIX, PDP, CRIDA, and NRC on Meat, VBRI, SVVU, JK trust Gram Vikas Yojana, NECC and ANTHRA. Video Conferencing was used by State A.H. Department, Commissionerate of Rural Development, APCOB, SBI, NIRD, NAARM, CRIDA, Venkateswara Hatcheries, Sarabhai Zydus Animal Health Limited and Natural Remedies Private Limited. Tele conferencing was used by APCOB, BASIX, NAARM, Suguna Poultry, IndBro Research and Breeding farms, Intas Pharmaceuticals Limited and Sarabhai Zydus Animal Health Private Limited. Multimedia CDs were found to be used by SMILDA, APLDA, NABARD, BASIX, NIRD, NAARM, NRC on Meat, Indian Immunologicals, CRIDA, SVVU, VBRI ANTHRA, Intercooperation Social Development, WASSAN, NECC, Suguna Poultry, IndBro Research and Breeding farms, Intas Pharmaceuticals Limited and Natural Remedies Private Limited. Information kiosk was utilized by only NAARM and BASIX. The other ICT tools utilized by the different organizations were wireless set conferencing by State A.H. Department and Local Area Network by PDP and Poshak Feeds Private Limited.
Keywords |
| ICT, extent of use, Animal Husbandry organizations. |
INTRODUCTION |
| India is a country in which agriculture occupies a central position in the socioeconomic milieu of the rural people. Despite the growth of the other areas of the economy, Agriculture still provides livelihood for approximately 60% of the population dwelling in the rural areas and its contribution to GDP is approximately 22% (Kumar, 2005). Livestock sector is one of the allied sectors which has proved to be an integral part of livelihood system of rural families and continues to be a major source of rural economy. There is rapid growth in the overall livestock production of our country which can be attributed to the technological revolution in A.H. and the successful adoption of recommended technologies by the rural farmers through different channels of information dissemination by the extension agencies. Apart from the conventional methods of information dissemination like traditional extension methods, electronic and print media, the recent foray into information gateway is the initiative of ICT tools in Agriculture and allied sectors. Agriculture and Animal husbandry has also been influenced by IT in the present scenario of IT revolution although the share of IT in agriculture is only 1.3% (Chargotra, 2006). |
| Information technology has demonstrated its utility and advantages in all elements of human life and especially in vocations of agriculture and allied sectors enhancing the productivity either directly or indirectly. The extension activities in Indian scenario are traditional in nature and suffer from certain drawbacks such as expensive in nature, irrelevancy of the content, inadequate coverage, one way information system, erosion of messages in passing through different layers, extension personnelâÃâ¬ÃŸs ineffective communication, neglect of extension in livestock development etc. (Sasidhar and Sharma, 2006). Information technology can help to overcome the barriers of traditional extension system to a greater extent. Earlier the mindset of extension system is of transferring technology packages, now with the initiation of ICT tools, the mindset has changed to transferring knowledge or information packages. By this, extension system will become more knowledge intensive and demand driven, and thus more effective in meeting farmerâÃâ¬ÃŸs information needs. |
| The emergence of Rural Knowledge Centers and information kiosk in our country, promoted by NGOs and corporate sector, have demonstrated that the local Panchayats and self-help groups can take advantage of appropriate information and communication technologies and with this facility, they can easily access the scientific and technical knowledge they need, to solve the problems with greater precision. Keeping the enormous contribution of livestock to the GDP and the scope of livestock sector in employment generation and improving the living standards of the farmers as well as irreplaceable role of Information and Communication technology tools in livestock sector, the stake holders have paved the way to utilize ICT tools in livestock sector. |
OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY |
| 1. To delineate the various ICT tools utilized by Animal Husbandry organizations and their extent of use by them. |
METHODOLOGY |
| The study was purposively conducted in Hyderabad and Rangareddy districts of Andhra Pradesh as most of the Animal Husbandry organizations are located in these two districts. A total of 33 organizations which are actively involved in Animal Husbandry activities were selected for the purpose of study. Several organizations involved in the livestock development either directly or indirectly in Andhra Pradesh were ascertained in consultation with various sources viz. consultation with experts, secondary sources such as reports, literature, documents etc. The questionnaire for the organizations was developed in consultation with experts in the field of Animal Husbandry extension and those involved in computer applications. Rapport with the representatives of organizations is very essential so as to get accurate responses. In the present study the investigator established initial rapport with the organizations selected for the study and got acquainted with the officials personally. Later after the development of the questionnaire the investigator handed over the questionnaire to the concerned officials of the selected organizations and elicited their responses through the questionnaire. Questionnaire was prepared in English and data was collected from 33 organizations. It was made sure that all the questions in the questionnaire were self explanatory. Statistical tools used for analysis of data included frequency and percentages. |
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION |
| A total of 33 organizations which are actively involved in Animal Husbandry activities were selected for the purpose of study. Based on the nature of work, functions, type of administration, the organizations considered for the study were grouped into five categories for better presentation of the results and subsequent discussion. They are: |
| 1. Service Providers |
| 2. Financial Organizations |
| 3. Educational and Research Organizations |
| 4. Non Governmental Organizations and Cooperative Organizations |
| 5. Private Organizations |
I. Service Providers: |
| 1. State Animal Husbandry Department |
| 2. Commissionerate of Rural Development -Rural Livelihood project |
| 3. Andhra Pradesh Livestock Development Agency (APLDA) |
| 4. Andhra Pradesh Meat Development Corporation (APMDC) |
| 5. State Management Institute for Livestock Development in Andhra Pradesh (SMILDA) |
II. Financial Organizations: |
| 1. National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) |
| 2. Andhra Pradesh Cooperative Bank (APCOB) |
| 3. State Bank of India -Agri business unit (SBI) |
| 4. Bharatiya Samruddhi Investments and Consulting Services Limited (BASIX) |
III. Educational and Research Organizations: |
| 1. National Institute of Rural Development (NIRD) |
| 2. National Academy of Agricultural Research Management (NAARM) |
| 3. Project Directorate on Poultry (PDP) |
| 4. Central Research Institute for Dryland Agriculture (CRIDA) |
| 5. National Research Centre on Meat N(NRC on Meat) |
| 6. Sri Venkateswara Veterinary University -College of Veterinary Science, Hyderabad (SVVU) |
| 7. Veterinary Biologicals Research Institute (VBRI) |
| 8. Indian Immunologicals |
IV. Non Governmental Organizations and Cooperative Organizations: |
| 1. JK Trust Gram Vikas Yojana |
| 2. ANTHRA |
| 3. Watershed Support Services and Activities Network |
| 4. InterCooperation Social Development |
| 5. Andhra Pradesh Dairy Development Cooperative Federation (APDDCF) |
| 6. National Egg Coordination Committee (NECC) |
V. Private Organizations: |
| 1. Venkateswara Hatcheries |
| 2. Suguna Poultry |
| 3. IndBro Research and Breeding farms |
| 4. Poshak Feeds Private Limited |
| 5. Vimala feeds Private Limited |
| 6. Miracle Feeds Private Limited |
| 7. Intas Pharmaceuticals Limited |
| 8. Neospark drugs and chemicals Limited |
| 9. Sarabhai Zydus Animal Health Limited |
| 10. Natural Remedies Private Limited |
11. EXTENT OF USE OF VARIOUS ICT TOOLS BY THE ORGANIZATIONS IN ANIMAL HUSBANDRY |
| Extent of use was operationally defined for the purpose of investigation as the frequency of use of ICT tools in acquiring information on Animal Husbandry through ICT tools. Various ICT tools i.e. Radio, TV, Mobile Phone, Internet, Video conference, Teleconference, Personal computers, Fax, Information kiosks, multimedia compact disks and other ICT tools were utilized by various organizations. The details of „extent of useâÃâ¬ÃŸ of above ICT tools are presented below. |
Extent of use of Radio by A.H. organizations |
 |
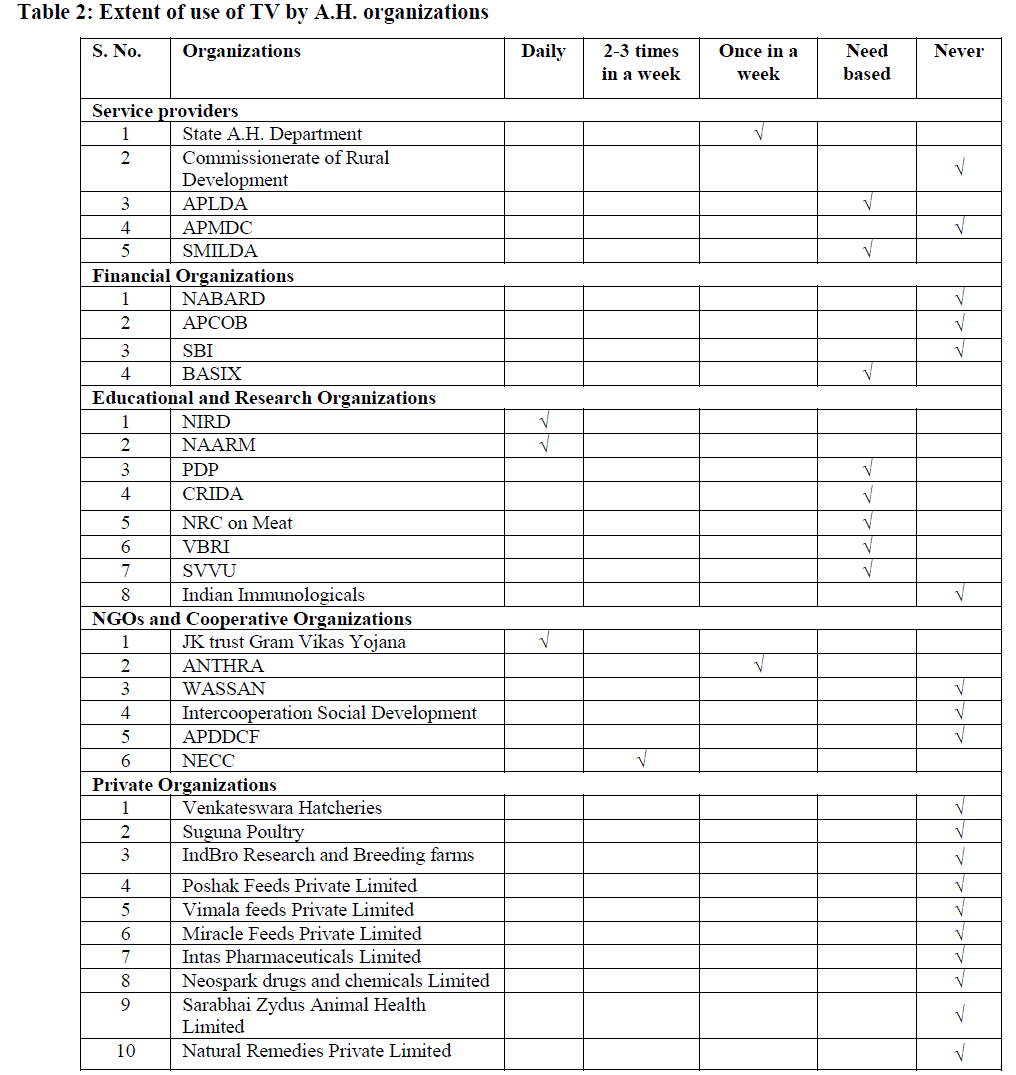 |
| From Table 2 it is evident that among Service Providers, State A.H. Department was utilizing TV once in a week over Doordarshan through a programme called Grama Darshini, because of its involvement in mass media programmes in A.H. topics for the benefit of farmers. Apart from this, it is also utilizing TV more widely for viewing the films on various aspects of livestock farming to farmers during extension activities and training programmes. APLDA reported to be using TV need based and used for training programmes to Gopalamitras and farmers. SMILDA are using TV as an ICT on need basis for training purpose to personnel. Among the Financial Organizations, TV is used mostly for training purpose to personnel and farmers in BASIX. It was observed that NIRD and NAARM were found to be using TV daily among the Educational and Research Organizations regularly for their institutional programmes. PDP, NRC on Meat, VBRI have reported to be using TV need based for training purposes to personnel while CRIDA also utilizing TV for training programmes to farmers. TV is being used periodically mainly for institutional and teaching purpose and mass programmes in extension by SVVU. Among Non Governmental Organizations and Cooperative Organizations, JK Trust Gram Vikas Yojana were utilizing daily while ANTHRA once in a week used TV as a mass media tool for information to farmers regarding various aspects of A.H. NECC also reported to be utilizing this tool 2-3 times in a week to keep track of the market trends in eggs. |
| Television was one of the channel widely used by several organizations either directly or indirectly i.e. by providing inputs, contents and expertise to Doordarshan and other private TV channels like E TV ( Annadata- Velugubata) etc. |
Extent of use of Mobile phones by A.H. organizations |
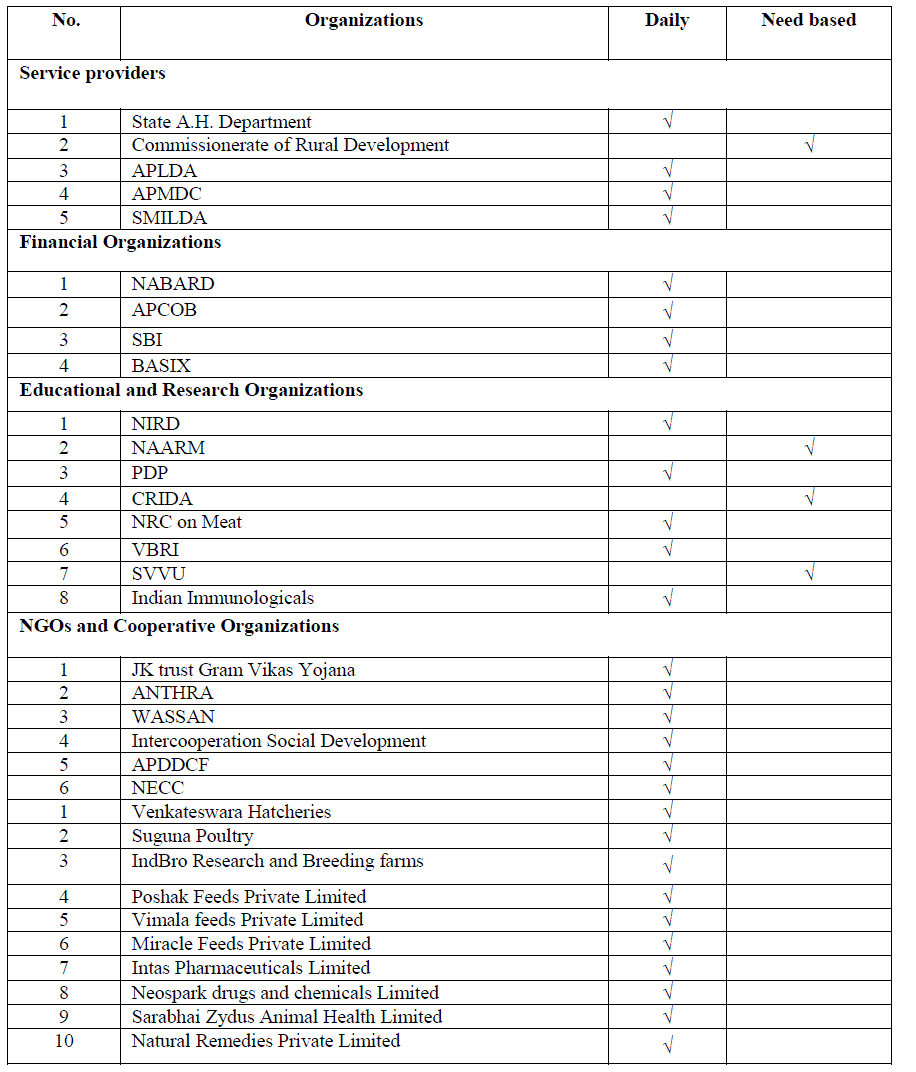
| From Table 3 it is found that among Service Providers, State A.H. Department, APLDA, APMDC, SMILDA were found to be using mobile phones daily and Commissionerate of Rural Development need based mainly for the purpose of information dissemination and information sharing with the officials, colleagues and sub-ordinates in view of its portability, its easy availability and instant accessibility. Animal Husbandry department officials were connected effectively through mobile phones by a CUG (Common User Group) for quick and effective sharing of information among themselves and similarly other organizations are also connected among themselves. All the Financial Organizations also reported to be utilizing mobile phones every day for the purpose of information sharing with their personnel. Among the Educational and Research Organizations, NIRD, PDP, NRC on Meat, VBRI and Indian Immunologicals were using mobile phones daily while CRIDA, SVVU, NAARM need based for communication among the personnel where as PDP communicate regularly even with farmers. All the Non Governmental Organizations and Cooperative Organizations were utilizing mobile phones daily while all the Private Organizations were also using mobile phones daily for the purpose of communication with their personnel for business and marketing of their products. As the mobile phone is widely used among the different organizations; integration of various CUGs working for the livestock development is essential for the overall development. Integration of CUGs paves the way for development of linkages among the organizations, which is very weak at present. |
| The findings are in conformity with the findings of Cebeci and Aykut (2003), Maru (2005) and Orin et al. (2005) that mobile phone is one of the common ICT tool used. |
 |
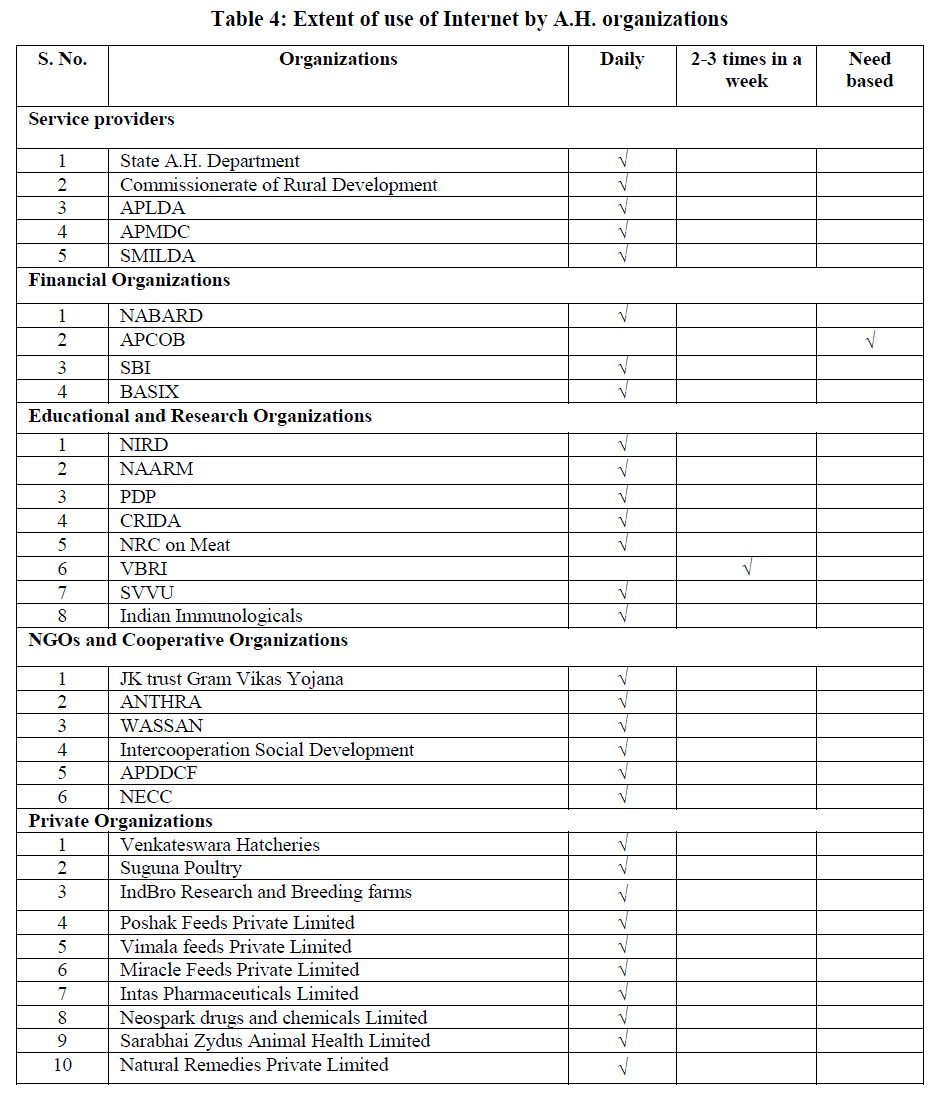
Extent of use of Internet by A.H. organizations |
| Table 4 portrays that all the Service Providers utilize Internet daily for various purposes including technical information on A.H. Email is one of the main internet based tool widely used for exchange of information such as administrative reports, monthly progress reports. Among the Financial Organizations, NABARD, SBI, BASIX were using Internet daily where as APCOB need based to send any reports. All the Educational and Research Organizations except VBRI use Internet daily whereas VBRI reported to be utilizing 2-3 times in a week to collect updated information on A.H. and to know the recent developments and innovations. All the Non Governmental Organizations were using Internet to keep abreast with the latest and current trends in A.H. Cooperative Organizations were also using Internet to know have updated information on A.H. and also to send reports and also to know market trends. All the Private Organizations are using Internet to have update information on A.H. and also keep with the latest developments and market trends. |
| The findings are in accordance with Cebeci and Aykut (2003), Salampasis (2004), Buiten (2005) and Orin et al. (2005) that Internet is one of the most widely used ICT tool. |
 |
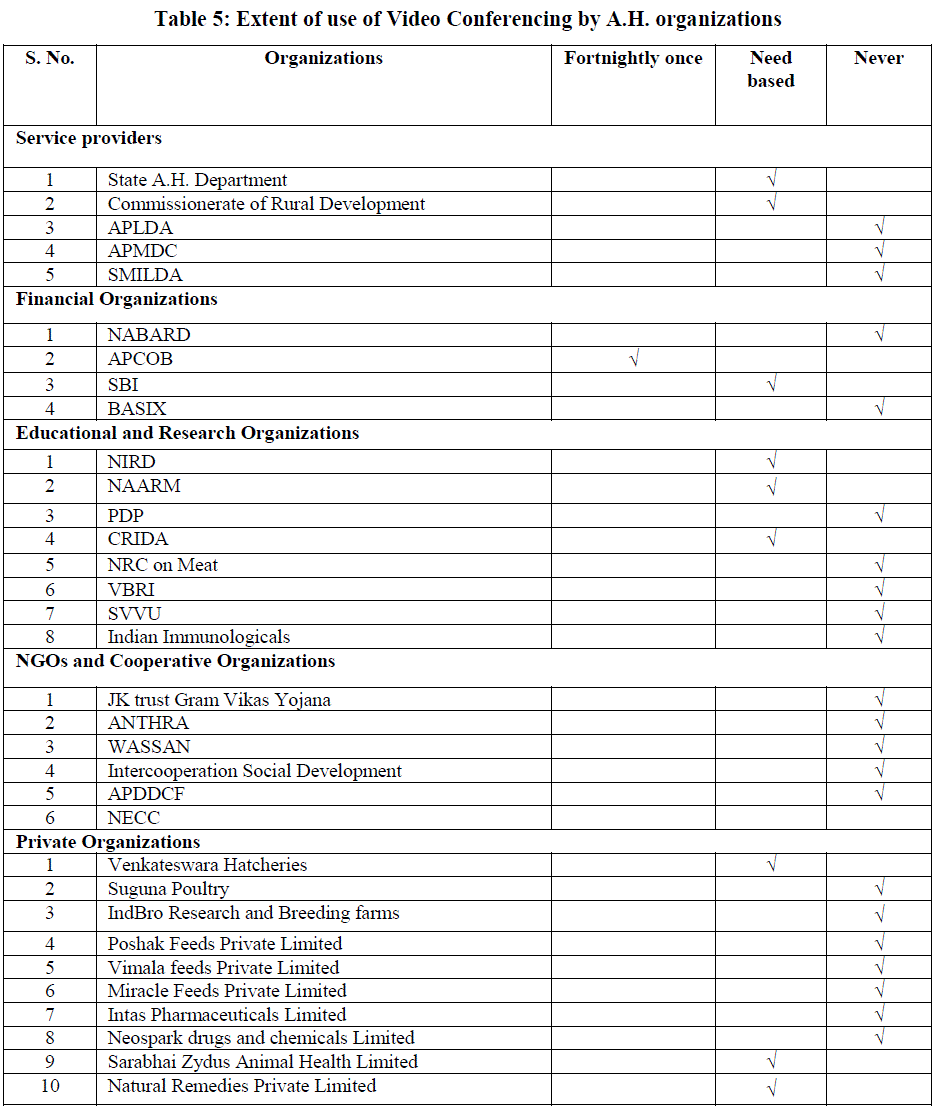 |
| From Table 5 it was brought out that among the Service Providers, State A.H. Department are utilizing video conferencing for any important programmes and when required and they hire it from Andhra Pradesh Technology Services. The purpose of conducting video conferencing is to communicate with senior field officials of the district and also with officials of the other departments. Commissionerate Rural Development reported to be utilizing video conferencing when occasion arises and they reported to be using from the District Collectorate office. Among the Financial Organizations APCOB indicated on the use of video conferencing on hire basis fortnightly once to report the status quo to the officials and SBI is also using this tool occasionally and others never used at all. Among the Educational and Research Organizations, NIRD, NAARM and CRIDA make use of video conferencing units available with them and use for interaction with experts as and when needed where as others were never using it at all. Among the NGOs and Private organizations, none of the organizations was found to be using video conferencing atleast once. Among Private Organizations, Venkateswara hatcheries, Sarabhai Zydus Animal Health Limited and Natural Remedies Private Limited mentioned to have video conferencing units and use for their business purposes as and when needed. The remaining organizations could not afford to have video conferencing units in view of prohibitive cost. |
Extent of use of Tele Conferencing by A.H. organizations |
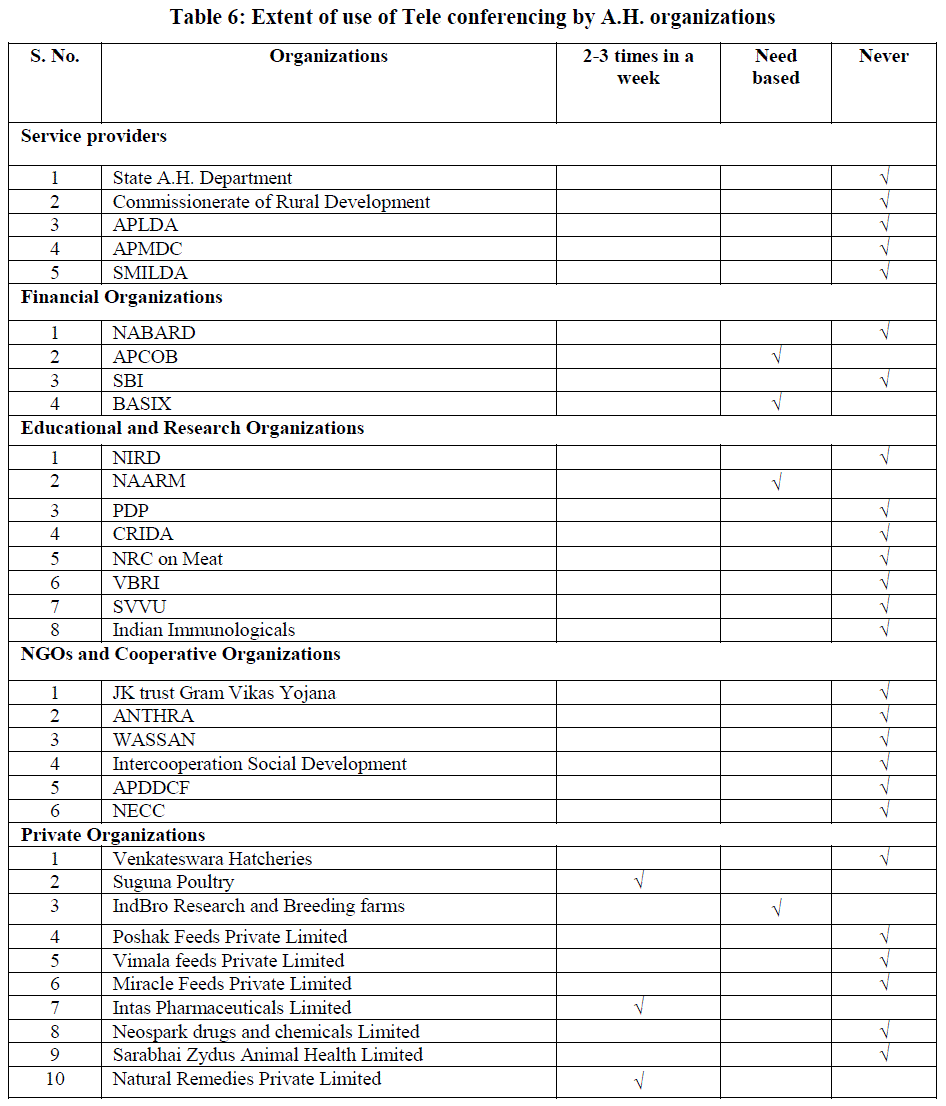 |
| Table 6 indicated that among the Service Providers no organization was utilizing Tele conferencing as they do not possess the Tele conferencing units. Among the Financial Organizations, APCOB and SBI utilize Tele conferencing for the purpose of communication with officials as and when required. Among Educational and Research Organizations, NAARM also used Tele conferencing unit and mostly used for group communication while others have never used it. Among the NGOs and Cooperative organizations, none of the organizations used teleconferencing atleast once. The Private Organizations like Suguna Poultry, Intas Pharmaceuticals, Natural Remedies Private Limited utilize Tele conferencing 2-3 times in a week and IndBro Research and Breeding Farms for business communication as need arises. |
Extent of use of Multimedia CDs by A.H. organizations |
| Table 7 brought out that among the Service Providers, APLDA make use of Multimedia CDs for the purpose of imparting training to farmers when required while SMILDA daily uses the same for giving training to A.H. personnel. Among Financial Organizations, NABARD utilize Multimedia CDs once in a fortnight for their project preparation while BASIX utilize Multimedia CDs need based for imparting training to farmers. The Educational and Research Organizations like NIRD, NAARM were using Multimedia CDs for institutional purposes in various training programmes. NRC on Meat, VBRI, Indian Immunologicals, CRIDA make use of Multimedia CDs mostly during presentations in training to their personnel and CRIDA also use Multimedia CDs need based for giving training to the farmers. Multimedia CDs are being used by the faculty of SVVU mostly for imparting knowledge and skills in teaching to the students in their respective disciplines and also used during training programmes to farmers. Among the Non Governmental Organizations and Cooperative Organizations, ANTHRA are using Multimedia CDs daily for their activities, Intercooperation Social Development 2-3 times in a week while WASSAN indicated to use the same need based for the purpose of educating and enlightening farmers on various issues and JK Trust Gram Vikas Yojana, APDDCF never used the same . NECC utilizes Multimedia CDs 2-3 times in a week for projection on marketing trends in eggs. Among Private Organizations, Suguna Poultry utilize Multimedia CDs as and when occasion arises, IndBro Research and Breeding Farms once in a month, Intas Pharmaceuticals Limited and Natural Remedies Limited on daily basis for training to the personnel in the organizations and also during the meetings conducted by them during the promotion of their products. |
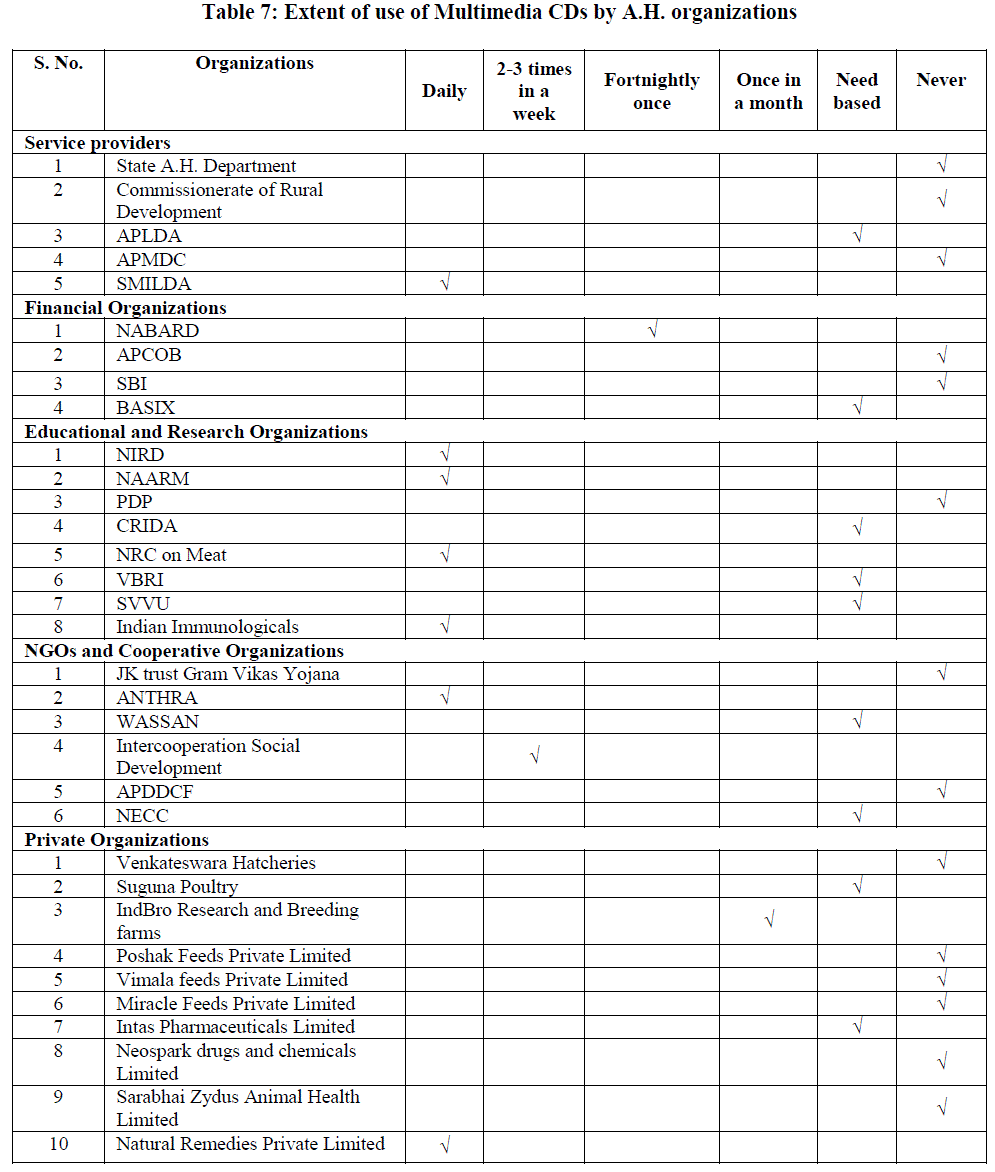 |
 |
| Table 8 depicted that among the Service Providers none possess information kiosk as such the extent of use. Among Financial Organizations, BASIX reported to have installed Information Kiosk daily because they have set up information kiosks in Chittoor district of AndhraPradesh and use for dissemination of information to the farmers. Among Educational and Research Organizations, only NAARM reported have information kiosk daily and are being used for information acquiring by the users. None of the Non Governmental Organizations, Cooperative Organizations and Private Organizations have expressed on the use of information kiosk as these organizations do not possess the same. |
Extent of use of Personal Computers by A.H. organizations |
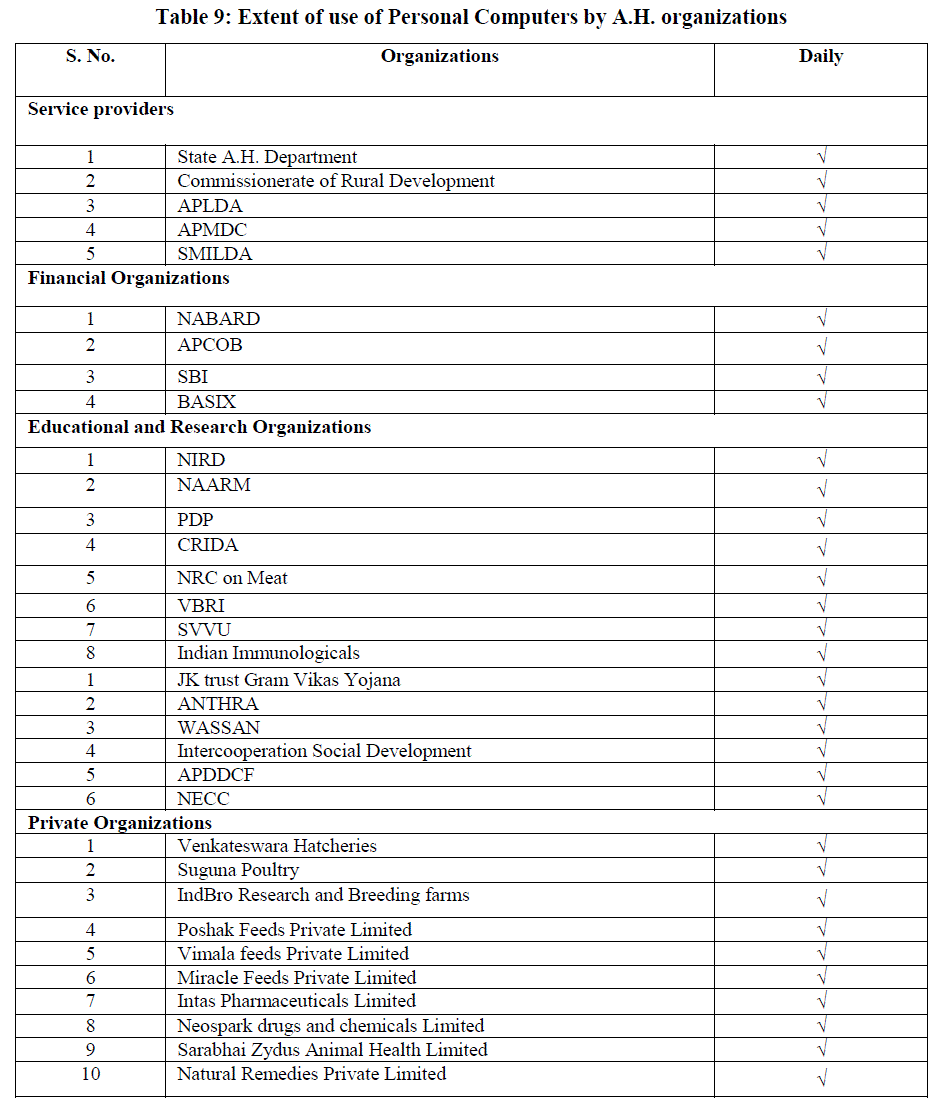 |
| From Table 9 it was indicated that all the organizations under Service, Research, NGO, Cooperative and Private sector were using Personal computers everyday as it has multifarious utility particularly it is easy to work faster. It infers that the organizations have realized the importance of personal computers as ICT tool for A.H. This is a positive trend observed in the IT revolution in A.H. sector. |
Extent of use of Fax by A.H. organizations |
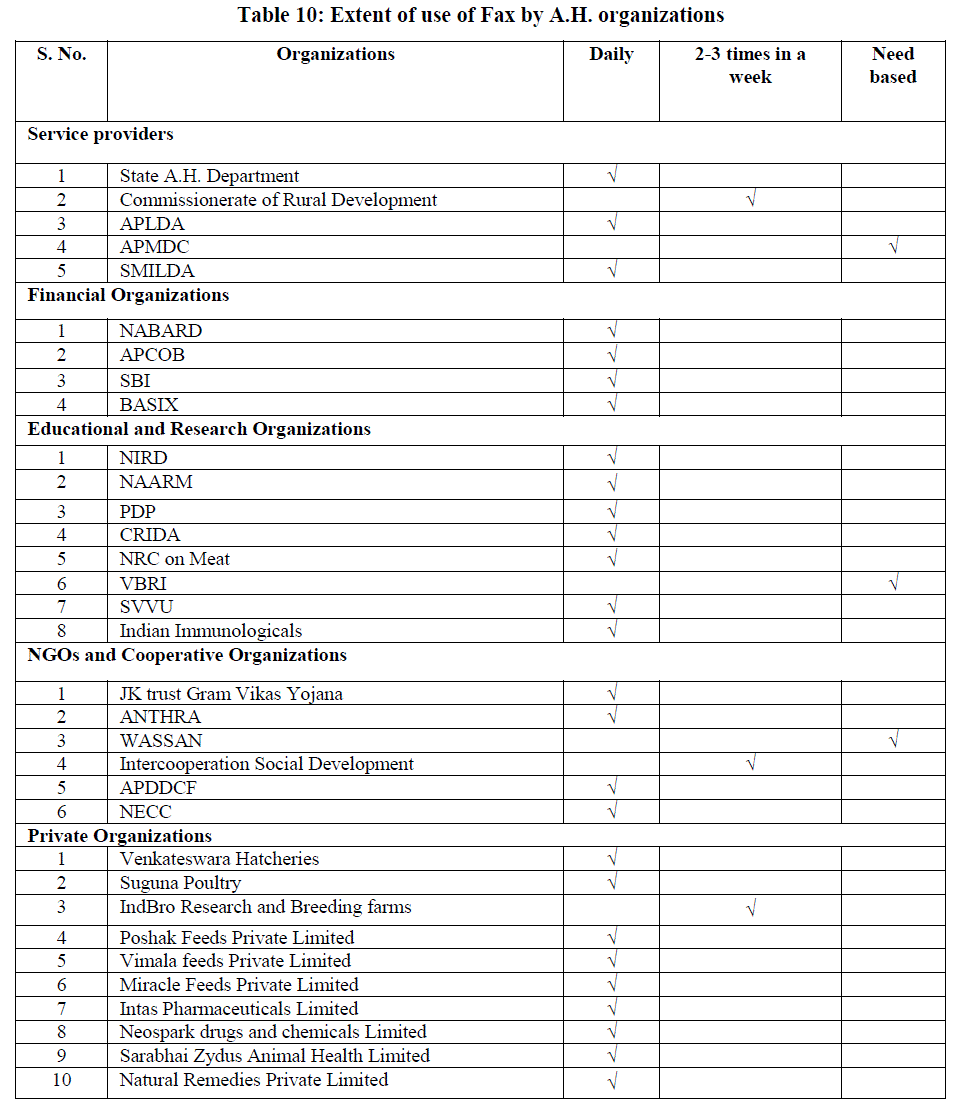 |
| It was clear from Table 10 that among the Service Providers, State A.H. Department, APLDA and SMILDA reported to be using Fax daily for transmitting information for A.H. where as Commissionerate of Rural Development were using Fax 2-3 times in a week and APMDC was utilizing the same as per the need. Among the Financial Organizations, all of them were utilizing Fax everyday. Among the Educational and Research Organizations all the organizations were utilizing Fax daily except VBRI which reported to be using Fax as per the need. Among NGOs and Cooperative Organizations, JK Trust Gram Vikas Yojana, ANTHRA, APDDCF and NECC were using Fax on day to day basis and Intercooperation Social Development was utilizing it 2-3 times in a week and WASSAN has reported to be using Fax as per the need. Among the Private Organizations, all the organizations indicated the use of Fax daily except IndBro Research and Breeding farms which was using Fax 2-3 times in a week. It projects that all the organizations reported to be using fax for the purpose of receiving and sending information which is a cheaper and faster form of communication in ICT tools |
Extent of use of other ICTs by A.H. organizations |
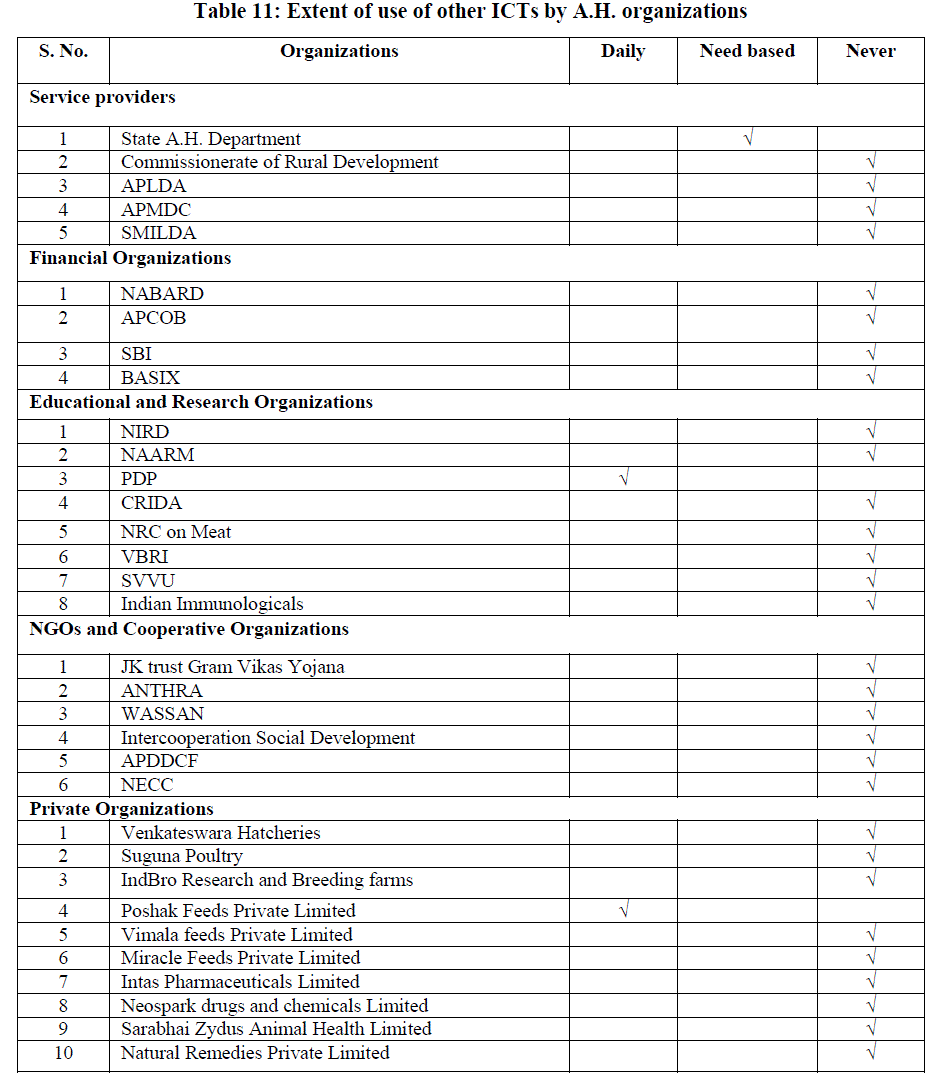 |
| The other ICTs that are being used by Service Providers particularly was that State A.H. Department which has the facility of wireless set conferencing which is used for direct communication of the director with the respective Joint directors of the districts. Project Directorate on Poultry and Poshak feeds private Limited were reported to be utilizing Local Area Network which facilitates in the use of networking within the institution. |
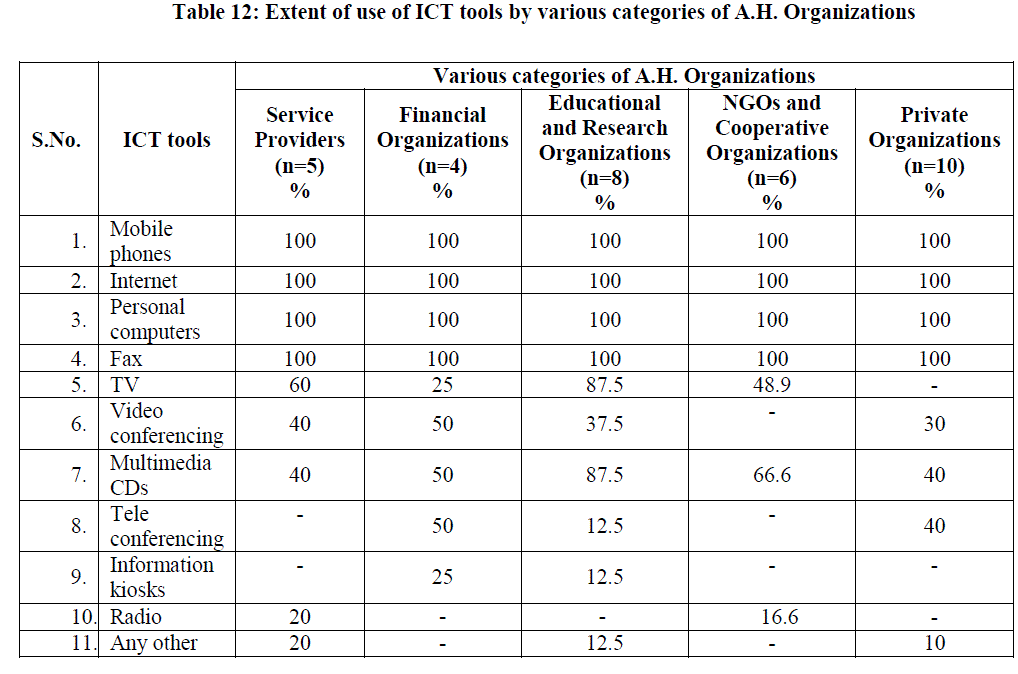
Extent of use of ICT tools by various categories of A.H. Organizations |
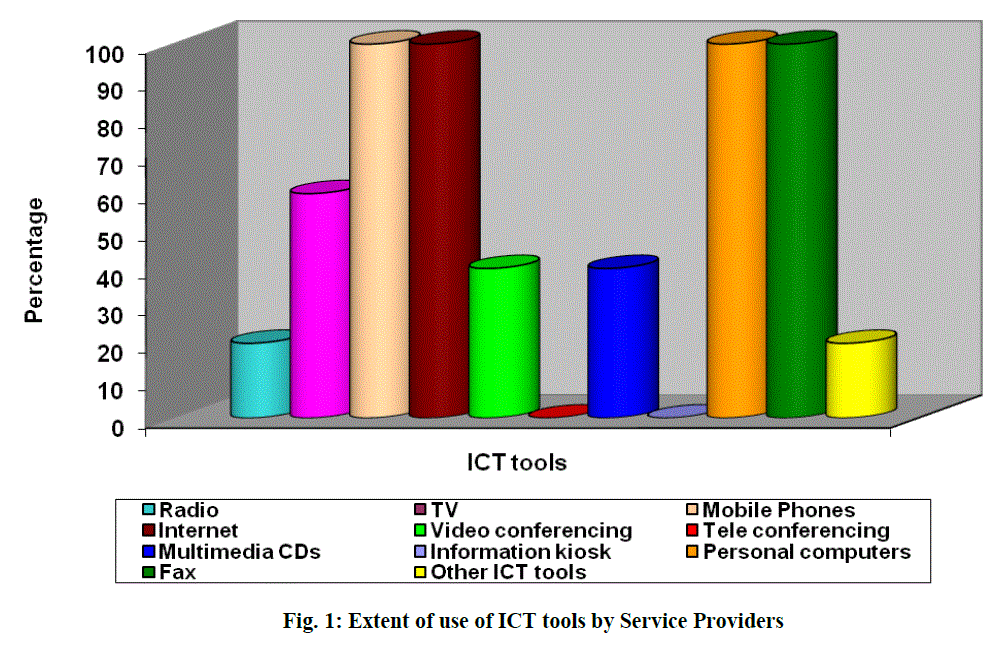
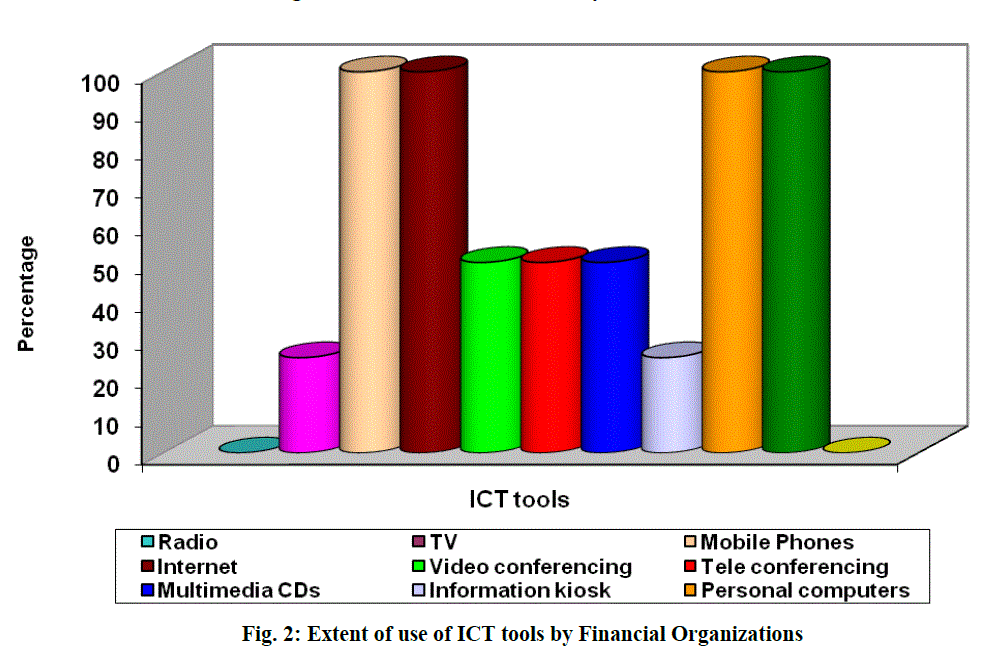
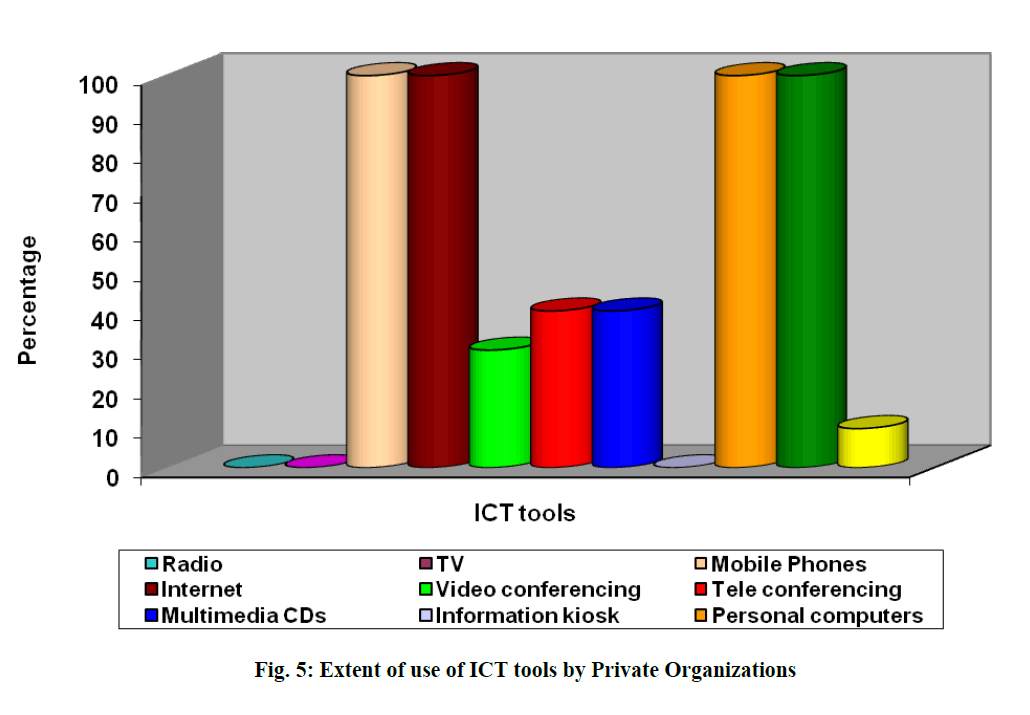
| It was evident from table 12 that all the categories of the A.H. organizations used mobile phones, Internet, Personal computers and Fax. 20% of the Service Providers and 16.6% of the Non Governmental and Cooperative Organizations utilize Radio for the interest of beneficiaries. TV was used by 60% of Service Providers, 25% of Financial Organizations, 87.5% of Research Organizations, 48.9% of Non Governmental Organizations for various activities like various purposes like training, teaching, institutional purpose etc. Video conferencing was used by 40% of the Service Providers, 50% of Financial Organizations, 37.5% of Educational and Research Organizations and 30% of Private Organizations for communication with officials either by hiring or if possessed by them as it saves time and can be used to communicate from the place they stay . Tele conferencing was used by 50% of Financial Organizations, 12.5% of Educational and Research Organizations, 40% of the Private Organizations for the purpose of communication. Multimedia CDs were used by 40% of Service Providers, 50% of Financial Organizations, 87.5% of the Educational and Research Organizations, 66.6% of Non Governmental and Cooperative Organizations and 40% of the Private Organizations for various purposes like teaching, training, and business purposes. Information kiosk was used by only 25% of Financial Organizations and 12.5% of Educational and Research Organizations because they were used by the organizations which installed them. Other ICT tools were used by 20% of Service Providers, 12.5% of Educational and Research Organizations and 10% of Private Organizations according to their need.(Fig.1 to Fig.5) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
References |
|