ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
| J.Arul Hency Sheela Assistant professor of Chemistry, Bharath University, Chennai – 600073, India |
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
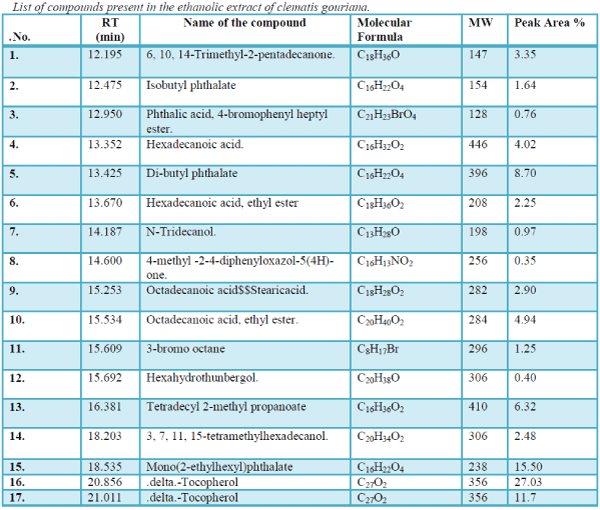
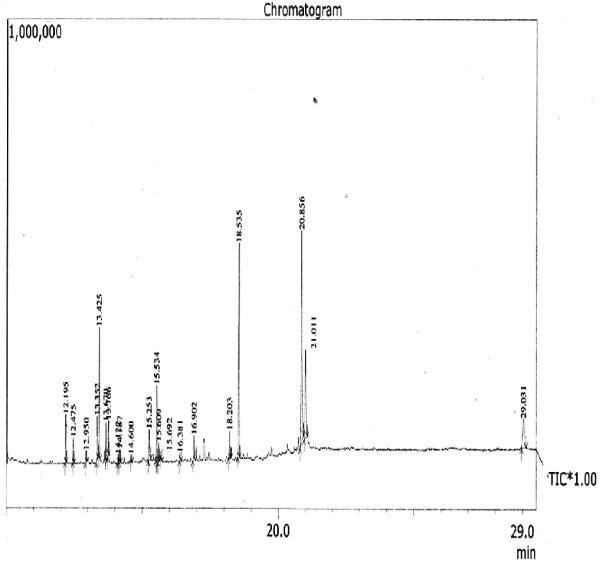
The aim of the present study was to investigate the essential chemicals of the plant clematis gouriana..The GC-MS analysis is done using the instrument GC Clarus 500 Perkin Elmer with Turbo mass 5.2 software. The sample volume is 2μL. The sample Ethanolic extract of clematis gouriana. Is run for 36 minutes. The chromatogram (Figure.10) shows 14 prominent peaks in the Retention time range 12.195-29.031.
Keywords |
| ClematisGouriana,GC-MS Analysis,Chromatogram,Retention time |
INTRODUCTION |
GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY |
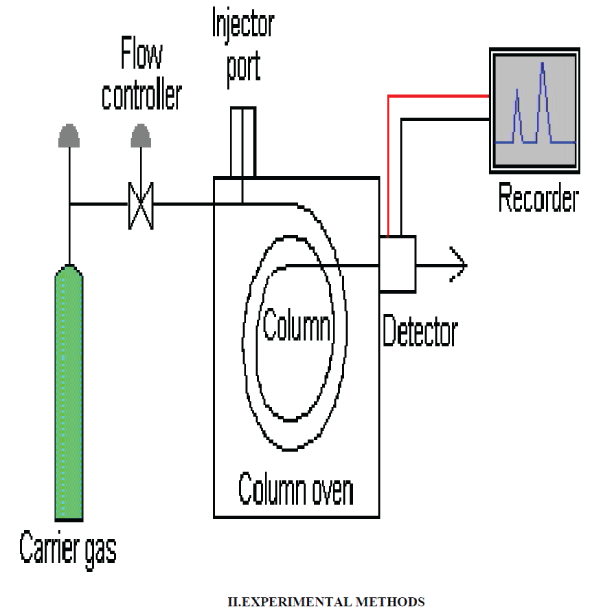
| Gas Chromatography (GC), also sometimes known as Gas-Liquid chromatography, (GLC), is a separation technique in which the mobile phase is a gas. Gas chromatography is always carried out in a column, which is typically "packed" or "capillary" (see below). |
| Gas chromatography (GC) is based on a partition equilibrium of analyte between a solid stationary phase (often a liquid silicone-based material) and a mobile gas (most often Helium). The stationary phase is adhered to the inside of a small-diameter glass tube (a capillary column) or a solid matrix inside a larger metal tube (a packed column). It is widely used in analytical chemistry; though the high temperatures used in GC make it unsuitable for high molecular weight biopolymers or proteins (heat will denature them), frequently encountered in biochemistry, it is well suited for use in the petrochemical, environmental monitoring and remediation, and industrial chemical fields. It is also used extensively in chemistry research |
 |
| Analysis of Sample: The Ethanolic extract of the plant is subjected GC-MS studies. The details are given here. |
GC PROGRAMME |
| Column Elite-1(100% dim ethyl poly siloxane), 30*0.25mm*1μmdf |
| Equipment GC Clarus 500 Perkin Elmer |
| Carrier Gas 1ml per min, Split 10:1 |
| Detector Mass detector Turbo mass gold-Perkin Elmer |
| Software Turbo mass 5.2 |
| Sample injected 2μl |
Oven temperature programme |
| 1100C-2 min hold |
| Up to 200°C at the rate of 10°C/min-No hold |
| Up to 280°C at the rate of 5°C/min-9 min hold |
| Injector temperature 250°C |
| Total GC running time 36 min |
MS PROGRAMME |
| Library used NIST Version- Year 2005 |
| Inlet line temperature 200°C |
| Source temperature 200°C |
| Electron energy 70ev |
| Mass scan (m/z) 45-450 |
| Solvent Delay 0-2 min |
| Total MS running time 36 min |
GC-MS DATA |
| The chromatogram of the GC-MS analysis is given in the Figure 1 |
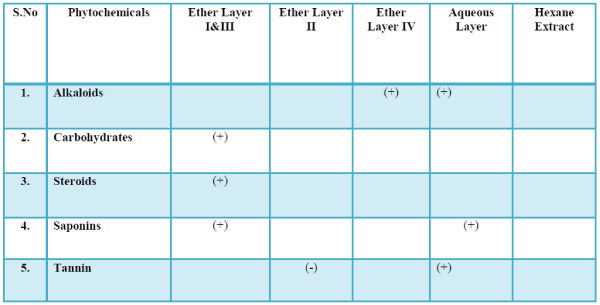
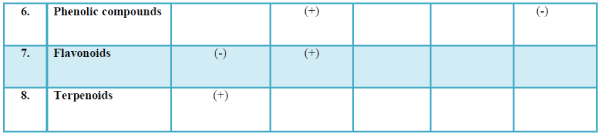
| The list of compounds predicted by the Software Turbo mass 5.2 is given in the Table 1 Photochemical screening of the plant Clematis gouriana |
 |
 |
 |
CONCLUSION |
| The GC-MS analysis is done using the instrument GC Clarus 500 Perkin Elmer with Turbo mass 5.2 software. The sample volume is 2μL. The sample Ethanolic extract of clematis gouriana. Is run for 36 minutes. The chromatogram (Figure.10) shows 14 prominent peaks in the Retention time range 12.195-29.031. The peak at 12.195 retention time is having the peak area 3.35. This largest peak is due to the presence of .Delta.-Tocopherol (Molecular weight 194). The Second less prominent peak at 18.535 retention time has the peak area 15.50 it is due to the presence of Mono (2-ethyl hexyls) phthalate (M.W.238). The third less significant peak at 21.011 retention time with the peak area11.7 is characteristic of .Delta.-Tocopherol (M.W.278). The Fourth less prominent peak at13.425 retention time (8.70 peak area) denotes the Dibutyl- phthalate (M.W. 396). The other less prominent peaks at other retention times are given in Table.11.S analysis predicts the presence of various Phytoconstituents of acids, esters, alcohols, glycosides, ethers, etc. The possible structures of these compounds are given in Figure |
References |
|
 |