Page 89
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 6
Research & Reviews: Journal of Material Sciences
ISSN: 2321-6212
Ceramics 2018
May 14-15, 2018
May 14-15, 2018 | Rome, Italy
4
th
International Conference and Expo on
Ceramics and Composite Materials
Centrifugally spun alumina zirconia fibers
N. Thamarai Selvi
and
Parag Bhargava
IIT Bombay, India
S
tatement of the Problem: Ceramic fibers (micron or nano meter dia.) are being used in place of conventional refractory
bricks due to their exceptional thermal insulation properties like low thermal mass, low thermal conductivity etc. There
are high and low temperature methods to synthesize fibers. But the low temperature methods conserve lot of energy. Hence,
sol-gel with centrifugal spinning was chosen to synthesize fibers. The purpose of this study is to synthesize alumina zirconia
(stabilized and unstabilized) fibers and to understand the grain growth controlling mechanisms. Methodology & Theoretical
Orientation: In the present work, alumina zirconia (5-20 wt. % zirconia) fibers were synthesized by sol-gel with centrifugal
spinning. Monolithic alumina fibers had an average grain size of ~4 µmwhich is huge and it will degrade mechanical properties.
Hence zirconia was added to control the grain growth. Findings: The diameter of the fibers was between 5-15µm. Fiber index
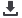
after sieving at 90 µm sieve was around 96 %. SEM images confirmed that the fibers were devoid of any abnormal grains (Fig.
1 (a-d)). Average alumina grain size was ~ 4 µm. Alumina fibers with zirconia showed homogeneous distribution of zirconia
throughout the fibers (Fig. 1 (b-d)). It was also confirmed that zirconia controlled the growth by triple junction pinning effect
which is in good agreement with the mechanisms reported. With the increase of zirconia content from 5 wt. % to 20 wt. %
more number of grain boundary junctions are pinned which controls the grain boundary mobility effectively. Conclusion
& Significance: Alumina zirconia fibers of 5-15 µm dia. were synthesized using sol-gel with centrifugal spinning. Average
alumina grain size was ~ 4 µm. This got reduced to 2.8 µm and 1.1 µm respectively for 5 and 20 wt. % and it varied in between
for 10 and 15 wt. % zirconia Zirconia controlled the growth by secondary phase pinning which is in good agreement with the
mechanisms reported.
thamarain123@gmail.comRes. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C1-015