Page 61
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 6
Research & Reviews: Journal of Material Sciences
ISSN: 2321-6212
Ceramics 2018
May 14-15, 2018
May 14-15, 2018 | Rome, Italy
4
th
International Conference and Expo on
Ceramics and Composite Materials
Ceramics in the system ZrO
2
-Al
2
O
3
with eutectic additives
Nikolay A. Makarov
and
Dmitry A. Antonov
D. Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology, Russia
Statement of the Problem:
The ZrO
2
-Al
2
O
3
system is key for the synthesis of various structural materials; in particular, it is
promising for manufacturing of wear-loaded items like friction pairs, cutting tools, etc. One of the most important issues in
zirconia ceramics technology is that ZrO
2
is subject to intensive recrystallization at temperatures exceeding 1100-1200°C. This
phenomenon leads to a martensitic transformation, accompanied by a significant drop in mechanical strength.
Methodology &Theoretical Orientation:
An effective way to prevent recrystallization is to affect the grain of zirconia with an
external compressive load, since in the stressed state the tetragonal solid solution does not decompose. It is possible to create
an external load by introducing a second phase into the material, the role of which is taken up by alumina. The aim of the work
is to create ceramic materials in the ZrO
2
-Al
2
O
3
system, with predominant zirconium dioxide, having a sintering temperature
of 1400-1550 °C, and high mechanical properties. An attempt was made to reduce sintering temperature by the addition of
eutectic aids to the batch. The influence of various types of alumina (commercial, obtained by chemical precipitation) on the
structural properties, mechanical strength and microstructure parameters was analyzed. Zirconia was obtained by chemical
precipitation, partial stabilization was carried out using yttrium chloride. To control the structure and properties of ceramics,
modifiers were used in CaO-Al
2
O
3
-SiO
2
and MnO-TiO
2
systems.
Findings:
It was found that ceramics with eutectic additives CaO-Al
2
O
3
-SiO
2
and MnO-TiO
2
in the ratio 1: 1 possesses the
greatest mechanical strength - 750 ± 35 MPa. Conclusion & Significance: This ceramic material is characterized by the highest
mycrohardness of 1200 N/mm
2
. The material is promising for use as elements of stop valves, mill bodies, cutting tools; wear-
resistant structural parts, etc.
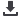
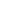
Figure 1:
Microstructure of samples from partially stabilized zirconia and alumina with eutectic additives in CaO-Al
2
O
3
-SiO
2
and MnO-TiO
2
systems
Recent Publications:
1. Makarov N.A. Composite material in the alumina-zirconia system (2007) Glass and Ceramics. 4:12-15 (in Russian).
2. Makarov N.A. (2006) Features of sintering corundum ceramics, modified with eutectic additives. Glass and Ceramics.
4:16-18 (in Russian).
3. Lukin E.S., Anufrieva E.V., Makarov N.A., Popova N.A. (2008) New generation of oxide ceramics and the field of its
application. Glass and Ceramics. 10:27-31 (in Russian).
4. Lukin E.S., Kozlov A.I., Makarov N.A., Popova N.A. (2009) Nanopowders for the production of oxide ceramics of the
new generation. Refractories and Industrial Ceramics. 11:29-34 (in Russian).
5. Makarov N.A., Sverdlikov V.L. (2005) Composite material of the corundum - zirconia system - sintering additive.
Glass and Ceramics. 11:16-18 (in Russian).
Nikolay A. Makarov et al., Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C1-014