
Page 45
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 6
Research & Reviews: Journal of Material Sciences
ISSN: 2321-6212
Materials Physics 2018
August 16-17, 2018
August 16-17, 2018 | London, UK
4
th
International Conference on
Condensed Matter and Materials Physics
New insight in the physics of RMn
2
O
5
multiferroics
Victor Balédent
University of Paris Sud, France
R
Mn
2
O
5
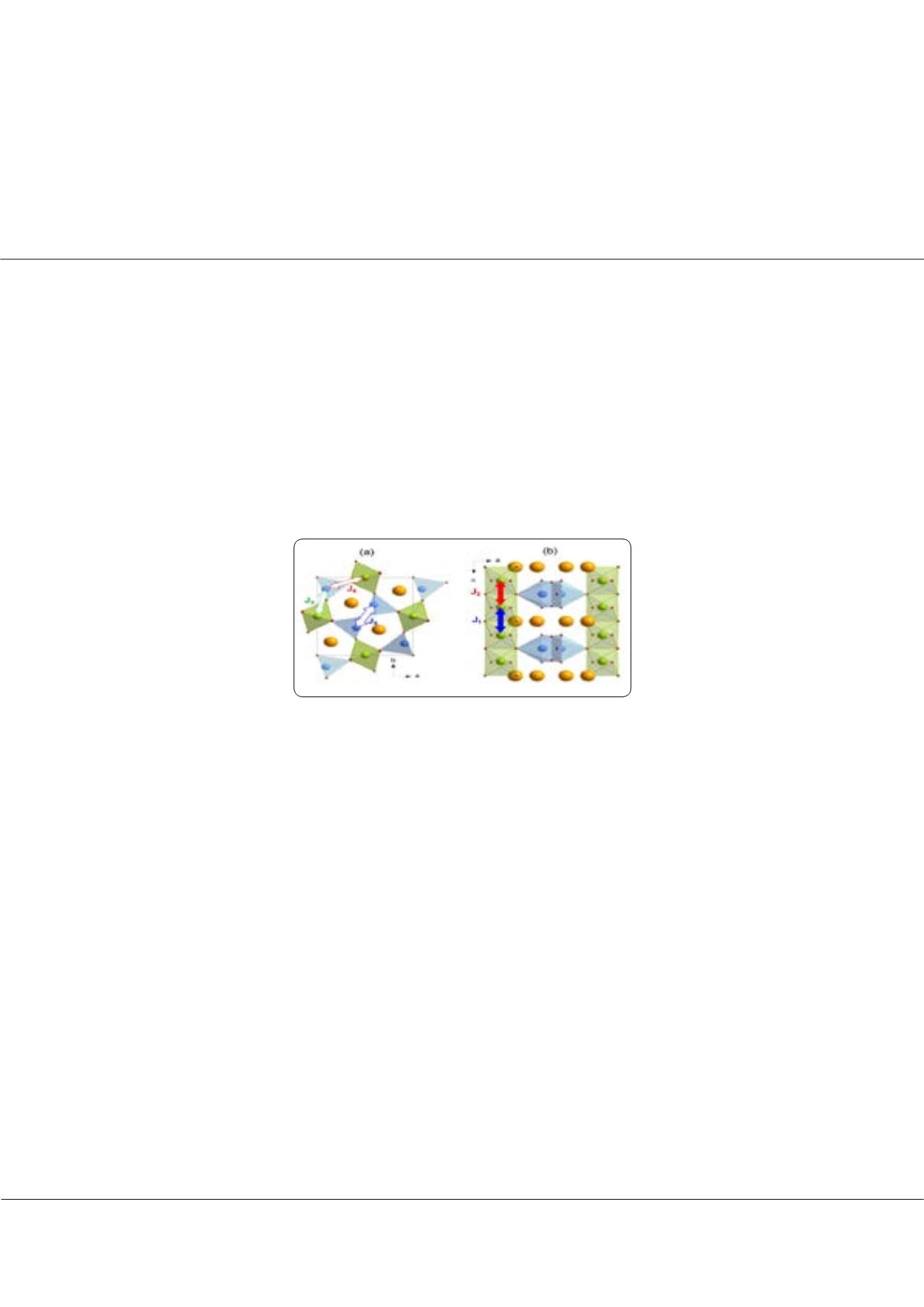
materials have long been presented as spin induced multiferroic family, where the electric polarization develops
concomitantly with a magnetic transition at low temperature. The complex magnetic order originates from the frustration
of anti-ferromagnetic loops of 5 sites in the (a,b) plane as illustrated in the Figure. What makes them particularly interesting
lies in their singular properties: an electric polarization among the strongest reported so far
(3600µC.cm -2
in GdMn
2
O
5
), a
strong magneto-electric coupling (enabling a polarization flip under a magnetic field of 2T in TbMn
2
O
5
), and a magnetism that
indicates a different fundamental mechanism than the standard Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya Interaction. In this presentation, I will
present our recent results on both atomic and magnetic structures of several members of this family, shedding a new light on
the physic and problematic of RMn
2
O
5
.
Recent Publications
1. S Chattopadhyay et al. (2017) 3d- 4f coupling and multiferroicity in frustrated Cairo pentagonal oxide DyMn
2
O
5
.
Scientific Report.
2. W Peng et al. (2017) Toward pressure- induced multiferroicity in PrMn
2
O
5
. Physical Review B. 96:054418.
3. GYahia et al. (2017) Recognition of exchange striction as the origin of magnetoelectric coupling inmultiferroics. Physical
Review B. 95:184112.
4. S Chattopadhyay et al. (2016) Evidence of multiferroicity in NdMn
2
O
5
. Physical Review B. 93:104406.
5. V Balédent S et al. (2015) Evidence for room temperature electric polarization in RMn
2
O
5
Physical Review Letters.
114:117601.
Biography
Victor Balédent obtained his PhD (Physics) in 2010 for his work on the magnetic properties of superconducting cuprates studied by neutron scattering, awarded by a
prize from the French Neutron Society. During a two years Postdoc at synchrotron SOLEIL, he extend his research to various superconducting materials (pnictides, heavy
fermions, cuprates) and widens his scientific thematics to metal-insulating transitions and multiferroicity. He is currently an Associate Professor at the University of Paris
Sud, Orsay, France. He was recruited as an Assistant Professor in 2013 at the Laboratory of Solid Physics, Orsay, France. His research focus on the manifestation of
electronic correlations in physical properties in several classes of material from Mott-insulators and superconductivity through multiferroics. Techniques used are neutron
and X-ray elastic and inelastic scattering with different sample environment : high pressure, magnetic field and low temperature.
victor.baledent@u-psud.frVictor Balédent, Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C2-017
















