ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
| S.Sudha, Dr. A.Mukunthan Department of Physics, Bharath Institute of Higher Education And Research, Chennai – 600073, India |
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
Heat is a form of energy and is required for the functions of different organs of the body. Every food stuff contain heat in the form of carbohydrates and glucose. The heat is released during the digestion of food stuffs (calorific value of food) taken by human beings and animals. Even when we are sleeping heart and lungs are functioning using the help of heat delivered by the food stuff. Heat is the cause and the temperature is the effect. Temperature can be measured with thermometer. Heat cannot be measured directly and is sensed by touching. For the survival human beings and animals, the maintenance of the temperature is a must. Excess of body temperature causes fever(caused by virus)and deficiency of body temperature causes fits(body shivering). There is a mechanism called hypothalamus in brain which regulates the temperature properly. In this paper we have discussed briefly how the body temperature is regulated by different mechanism, variation of body temperature due to different factors and the reactions taking place in our body due to sudden change in temperature.
Keywords |
| Homeothermic, poikilothermic, oral and surface temperature, hypothalamus, heat gain and heat loss centers, sweating, hyperthermia, hypothermia, saliva, panting, metabolic activities, hemorrhage, hypopituitarism, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, diabetes, insipidus, hormones. |
INTRODUCTION |
| Based on body temperature let us first classify the living organism. The living organisms can be classified into two groups depending upon the maintenance (regulation) of body temperature namely homeothermic and poikilothermic animals. In homeothermic animals, the body temperature is maintained at a constant level irrespective of the environmental temperature. Birds and mammals include man belong to this category. They are also called warm blooded animals. In poikilothermic animals the body temperature is not a constant. It varies according to environmental temperature. Amphibians and reptiles are the poikilothermic animals. These animals are also called cold blooded animals. |
| Most of us are thinking that the measured temperature is constant throughout the body and is also common for age groups, sex and time duration but measured temperature is not a constant throughout the body and differs at different parts of the body. It also depends on the factors like age group, sex, time duration. etc. Body temperature can be measured by placing the clinical thermometer in different parts of the body such as mouth (oral temperature), axilla (axillary temperature). On the skin (surface temperature) and rectum (rectal temperature).The normal body temperature in human is 37 0c(98.6 0F), when measured by placing the clinical thermometer in the mouth (oral temperature). It varies between 35.80c (96.40F) and 37.30c (99.10F). Axillary temperature is slightly lower (about 0.370c or 10F) than the oral temperature . And ,the rectal temperature is slightly higher (about 0.370c or 0F) than oral temperature. The superficial temperature (skin of surface temperature) varies between 29.5 C (85 0F) and 33.9 0C (93 0F).The average temperature in deeper tissues of the body is called core temperature .The core temperature is always more than oral or rectal temperature. It is about 37.8 0C (100 0F). |
II.VARIATIONS OF BODY TEMPERTURE DUE TO DIFFERENT FACTORS |
| Here we are going to discuss the facts and figures about the variations of the body temperature due to different factors like age, sex, time duration, different functioning of the body. |
 |
| Heat balance (Temperature regulation): |
| Normally a temperature body is maintain at a constant level by some mechanisms in the body. This is done by adjusting the heat production is equal to the heat loss. The balance between heat production in the body and heat loss in the body is known as heat balance. |
| Heat Gain: |
| The gain of heat produced in the body by some factors are summarized in the following tabular form. |
 |
III.HEAT LOSS |
| Let us now summarize the heat loss from the body through some transmission process. They are listed below. |
 |
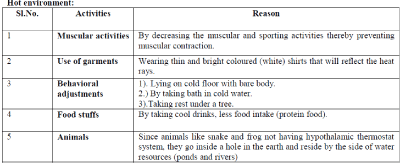
IV.BEHAVIOURAL AJDUSTMENTS IN COLD AND HOT ENVIRONMENTS |
| Cold Environment: |
 |
| Hot environment: |
 |
| REGULATION OF BODY TEMPERATURE BY HYPOTHALAMUS (BIOTHERMOSTAT): |
| The body temperature is regulated by hypothalamus. There are two centers in hypothalamus which are connected with temperature regulation |
V.HEAT LOSS CENTER AND HEAT GAIN CENTER |
| HEAT LOSS CENTER: |
| This center is situated in preoptic nucleus of anterior hypothalamus. The neurons of this nucleus are sensitive to heat when body temperature is increased the warm blood stimulates the heat sensitive neurons. Now this center reduces body temperature by two methods. |
| 1. INCREASING THE SWEAT SECRETION: |
| The anterior hypothalamic center (heat loss center ) sends inhibitory impulses to the sympathetic center in posterior hypothalamus. Normally, this sympathetic centers causes constriction of blood vessels in skin. when these centers are inhibited, there is peripheral vasodilatation. Now blood flow through skin increases, causing excess sweating. Evaporation of water from sweating increases the heat loss thereby decreasing the body temperature. |
| 2. DECREASING HEAT PRODUCTION: |
| The mechanisms involved in heat productions like shivering and chemical (metabolic) reaction are inhibited. |
| HEAT GAIN CENTER: |
| This is otherwise known as heat production center. This is situated in posterior hypothalamic nucleus. This part of hypothalamus has neurons, which are sensitive to cold when body temperature is reduced this center plays important role in maintaining the temperature by preventing heat loss from body and by increasing heat production. When body temperature becomes low, the heat gain center in posterior nucleus of hypothalamus is simulated. This activates the sympathetic centers which in turn cause vasoconstriction in skin and reduction in blood flow. Due to reduce blood flow to skin, sweat secretion is decreased and thereby heat loss is prevented. Increase in the production of heat is done by two processes: 1. Shivering, 2. Increased metabolic reactions. |
| 1. Shivering: |
| The primary motor center for shivering is situated in posterior hypothalamus. This is activated by heat production center when the body temperature is low at once shivering occurs producing enormous heat due to severe muscular activities. Hence body temperature rises. |
| 2. Increased metabolic reactions: |
| The sympathetic centers which are activated by heat production stimulate the secretion of adrenaline and nonadrenaline. These hormones increase the heat production by the acceleration of cellular metabolic activities. Simultaneously hypothalamus stimulate thyroid to release hormones from pituitary. This in turn, release thyroxin from thyroid. This thyroxin accelerates metabolic activities so that heat production is increased. |
VI.CONCLUSION |
| So far we have briefly discussed about the maintenance of body temperature by different mechanism like heat loss control and heat gain control which are located in hypothalamus in brain. We have also discussed briefly about the variation of body temperature by due factors. The maintenance of temperature regulation is an important factor through our over life for the regular work, sleep, rest etc, and is clearly being done by hypothalamus. |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT |
| The authors are very thankful to our Hon.Chairman, Chancellor, Vice-Chancellor and Registrar, Dean (R&D) and Dean (Engg.) for their continuous support and encouragement given to bring out this research paper. |