e-ISSN: 2319-9849
e-ISSN: 2319-9849
Dumkal College, Basantapur, Dumkal, Murshidabad, West Bengal, India
Received date: 15/01/2018 Accepted date: 22/01/2018 Published date: 29/01/2017
Visit for more related articles at Research & Reviews: Journal of Chemistry
Present study shows the correlation of activity of as many as 13 Anti-bacterial (containing benzimidazole and beta-lactam moiety) drugs in terms of global reactivity descriptors under paradigm of QSPR/QSAR study. Investigation of antimicrobial activity of the compounds was done by using Gram- positive (S. aureus, S. mutans and B. subtilis) bacteria. The global descriptors nicely correlate the variation of activity with structures of the drug molecules
QSAR/QSPR, Drug, Quantum chemical descriptors, Bacteria
The benzimidazole ring is a significant pharmacophore in contemporary drug discovery. A variety of benzimidazole are in use, like thiabendazole and flubendazole (anthelmintic), omeprazole and lansoprazole (antiulcer) and astemizole (antihistaminic). The chemistry and pharmacology of benzimidazoles have been of great interest to medicinal chemistry [1,2] because its derivatives possessed various biological activities such as antioxidant [3,4], antimicrobial [5–10], antihelmintic [11–13], anticancer [14], antihypertensive [15], antineoplastic [16], anti-inflammatory [17,18], analgesic [19], antiprotozoal [20,21] and anti-hepatitis B virus activity [22]. In addition, a large number of antibiotics contain the 2-azetidinone (commonly known as β-lactam) moiety [23] such as penicillin, cephalosporin and carbapenem. It is also associated with a variety of therapeutic activities [24–28].
In continuation of this work, the study has been done to develop potential relation between some theoretical quantum chemical descriptors and their anti-bacterial activity of some derivatives of the structure type containing the above mentioned moieties.
The present study relates the antibacterial activity of the thirteen heterocyclic compounds with benzimidazole and their beta-lactam derivatives. The parent structure of this hetero cyclic compound has been presented in the Figures 1 and 2. The derivatives of bio active hetero cyclic compounds which have been used in this study are arranged in the Table 1. Some inherent properties encoded in the structure of these molecules as some well-known quantum chemical descriptors was evaluated and modeled with the experimental activities have been collected from literature [29-31].
| Compound | R | I.A(ev) | E.A(ev) | η(ev) | S(ev) | µ (dipole moment in Debye) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | 0 | 9.34851 | 0.58491 | 4.3818 | 0.22822 | 2.8280425 |
| 1B | -CH2CH3 | 9.34092 | 0.58167 | 4.37963 | 0.22833 | 3.20915566 |
| 1C | -CH2CH2CH3 | 9.34476 | 0.58276 | 4.381 | 0.22826 | 2.94105482 |
| 1D | -C6H5 | 9.30849 | 0.53593 | 4.38628 | 0.22798 | 3.37419896 |
| 1E | 2- CH3C6H4 | 9.30215 | 0.53062 | 4.38576 | 0.22801 | 3.23990746 |
| 1F | 3- CH3C6H4 | 9.29336 | 0.52523 | 4.38406 | 0.2281 | 3.37429827 |
| 1G | 2- ClC6H4 | 9.30106 | 0.64221 | 4.32942 | 0.23098 | 3.72177136 |
| 1H | 4- ClC6H4 | 9.34751 | 0.66177 | 4.34287 | 0.23026 | 2.62695568 |
| 1I | 2-OHC6H4 | 9.36242 | 0.60803 | 4.37719 | 0.22846 | 2.89527034 |
| 1J | 3-OHC6H4 | 9.3296 | 0.56327 | 4.38316 | 0.22815 | 2.49369662 |
| 1K | 4-OHC6H4 | 9.30489 | 0.53212 | 4.38639 | 0.22798 | 3.03293654 |
| 1L | 2-OCH3C6H4 | 9.2025 | 0.52368 | 4.33941 | 0.23045 | 4.97220158 |
| 1M | 2-OCH3C6H4 | 9.31624 | 0.55081 | 4.38271 | 0.22817 | 3.16729949 |
Table 1: Calculated values of ionization potential (I.A), Electron affinity (E.A), hardness (η), Softness (S) in electron volt and dipolemoment (μ) in Debye.
The 3D modeling of these bioactive compounds have been performed with the help of Gaussian 09 software [32].
Gaussian 09 software [32] has been used to calculate the global descriptors by using the DFT methods at B3LYP/6-31 G* basis set.
According to Koopmans’ theorem the ionization potential (I) and the electron affinity (A) are computed as follows:

Where εHOMO and εLUMO are the orbital energies of the highest occupied and the lowest unoccupied orbitals.
Parr et al. [33-35] defined the chemical potential, μ, electronegativity, χ, and hardness, η, in the framework of density functional theory, DFT as:
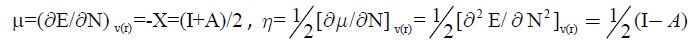
Where E, N, v(r), I and A are the energy, the number of electrons, the external potential, the ionization energy and the electron affinity of a chemical system respectively.
Softness is a reactivity index and is defined as the reciprocal of hardness, S=(1/η). The observed activity and as well as the quantum mechanical reactivity descriptors such as Ionization potential (I), electron affinity(A), global hardness(η), global softness (S), and dipole moment (μ) are also presented in Table 2.
| Compounds | Mean Zone inhibition (in mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-bacterial activity | Anti-fungal activity | |||||
| S. aures | S. mutans | B. subtilis | Candida albicans | Aspergillus niger | Aspergillus flavus | |
| 1A | 38 | 20 | 28 | 26 | 24 | 22 |
| 1B | 37 | 18 | 28 | 24 | 25 | 24 |
| 1C | 32 | 18 | 22 | 24 | 24 | 20 |
| 1D | 36 | 16 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 27 |
| 1E | 30 | 15 | 20 | 22 | 18 | 14 |
| 1F | 30 | 13 | 20 | 20 | 18 | 13 |
| 1G | 31 | 13 | 18 | 20 | 16 | 15 |
| 1H | 31 | 10 | 20 | 18 | 14 | 14 |
| 1I | 37 | 16 | 27 | 27 | 28 | 26 |
| 1J | 36 | 16 | 26 | 15 | 20 | 13 |
| 1K | 36 | 15 | 26 | 15 | 14 | 18 |
| 1L | 25 | 14 | 22 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 1M | 22 | 16 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 16 |
Table 2: Anti-bacterial activity and Antifungal activity of compounds (1A-1M).
Also use Minitab17 [36] to perform the MLR (multi-linear regression) for the calculation of the different co-efficient presented in Tables 3-5.
| Compounds | R2 (%) | Regression Equation | Odd molecule |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1A-1L | 66.92 | S aureus=-996+75.5 I.E+73.5 η+ 1.42 µ | 1M |
Table 3: Regression Analysis: S aureus versus IE, S(ev), dipole moment.
| Compounds | R2 (%) | Regression Equation | Odd molecule |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1A-1L | 62.38 | S. mutans=-208 + 67.8 I.E - 1852 S + 4.79 µ |
1M |
Table 4: Regression Analysis of S. mutans versus I.E, S(ev), dipolemoment.
| Compounds | R2 (%) | Regression Equation | Odd molecule |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1A-1L | 60.81 | B. subtilis=-594180+ 68014 η+1290179 S+ 186.6 I.E | nil |
Table 5: Regression Analysis of B. subtilis versus η(ev), S(ev), I.E.
To model the relation with the computed values of different well known quantum chemical descriptors of the compounds (1A-1M) having anti-microbial activities are interrelated with the gram- positive (S. aureus, S. mutans and B. subtilis) bacteria via multi linear regression.
The R2 values obtained from the regression result for the each sets, S aureus versus I.E, S (ev), dipolemoment; S mutans versus I.E, S (ev), dipolemoment and B. subtilis versus η (ev), S (ev), I.E having values 66.92, 62.38 and 60.81 respectively revels the efficacy of the model.
A combination of several quantum chemical parameters to form a composite index, which could be correlated to the experimental drug efficiency, often provides valuable information on the relationship between quantum chemical parameters and experimental drug efficiency. In the present report, studied a correlation of activity of as many as 13 anti-bacterial drugs in terms of global reactivity descriptors under paradigm of QSPR/QSAR study. The global descriptors nicely correlate the variation of activity with structures of the drug molecules.