E- ISSN: 2320 - 3528
P- ISSN: 2347 - 2286
E- ISSN: 2320 - 3528
P- ISSN: 2347 - 2286
Lala Behari Sukla1,2*, Jacintha Esther1,2, Sandeep Panda1, and Nilotpala Pradhan1,2
1Bioresources Engineering Department, CSIR-Institute of Minerals & Materials Technology, Bhubaneswar-751013, Orissa, India
2Academy of Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (AcSIR), India
Received date: 05/07/2014; Accepted date: 28/07/2014
Visit for more related articles at Research & Reviews: Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology
Over the past few years, the applications of certain microorganisms have gained importance in the field of applied environmental microbiology. Amongst them, biomineral processing is such field that deals with metal mining from ores, concentrates, industrial wastes, overburdens etc. under the impact of microorganisms and/or their metabolites. The most successful advancement of mineral biotechnology so far is on copper, uranium, nickel-cobalt and gold bearing ores. Treatment of mineral industry effluents by microorganisms, with incidental recovery of some metal values constitutes an equally important area of biomineral processing. The most common method followed for leaching or extraction of metal values is through shake flask (a lab scale method) followed by bioreactors or percolation columns (a bench scale method) and finally to heap leaching (a pilot scale method). Bio-leaching of mono- and multiple-sulphides is now coming to be known as an established commercial process. The present review discusses the microorganisms involved in biomineral processing, mechanism of metal extraction, molecular methodologies adopted for microbial identification with our experience on application of microorganism.
Biomineral Processing, Metal extraction, Microorganisms, Bioleaching, Environmental impact
With the advancement on several aspects of science and technology, the current scenario of utilization of mineral resources has become an area of interest to several researchers, environmentalists, mineral processing industries across the globe. With advancement in rapid mining activities, the mineral processing industries are processing the high grade ores to meet the metal demand supply on one hand with simultaneous generation of low grade on the other. Such low grade ores are often a concern for any mineral processing industry due to certain environmental issues associated with it. Over the recent few decades the process of application of certain microorganisms has been gaining importance through a process termed as bioleaching. Microbial metal-leaching processes offer a possibility to recover metal values from mineral resources not accessible by conventional mining. Microbes act as biocatalysts to convert metal compounds into their water-soluble forms in leaching processes. Additionally, it is possible to recover metal values from industrial wastes that serve as secondary raw materials by the application of microbiological solubilization processes.
Mineral processing by microorganisms has begun almost 3.5 billion years before human intervention. The microorganisms provide process energy to use waste metal compounds, produce quantities of valuable minerals and can live on hostile environment [1,2]. This effect has given rise to different interdisciplinary areas as: (a) Biogenesis and biomineralization, (b) Biomaterials processing and biomimetics, (c) Ceramics and biomedical engineering, (d) Biomineral beneficiation, (e) Bioleaching, (f) Biocorrosion, biofouling and biodeterioration (g) Bioenvironmental control.
In the recent era, biomineral processing has proven to have promising technological potential for mineral processing industries. Since the exploitation of the microbial groups especially Acidithiobacillus genera, bioleaching of copper [3-6] and uranium ores [7] has made significant progress in the biomineral processing for extraction of different metal values from a variety of low-grade ores, minerals and concentrates. The practical utility of biomineral processing have significant industrial application in areas such as bioleaching for metal extraction, bio-beneficiation of low grade ores, bioremediation of contaminated soil and utilization of solid waste, treatment of effluents and waste waters for metal decontamination etc.[8].
In the past few decades, bioleaching of low-grade laterite ore using micro-organisms has proved to be of vital importance due to following advantages over the conventional leaching methods:
• Bioleaching process is economical and simple
• The effluent generated is eco-friendly and has pose no threat to the environment
• It is a low energy consuming process as it does not require high temperature and pressure
• Bioleaching process is capable of treating low grade ores
• Bioleaching process is site-specific and employs indigenous microorganisms
• Growth of microorganisms in large scale is feasible with the latest advances in the field
• Bioleaching process requires simple technological outlay
• Large scale trials of heap and bioreactor leaching can be easily performed
• Cost of plant erection will be minimum compared to conventional process
Bioleaching processes are now increasingly used as an alternative and supplementary method because of the depletion of high-grade ore reserves, increased energy costs and environmental preservation [8]. The bio-hydrometallurgical extraction of several metals from a wide variety of ores is being commercially practiced in Canada, US, Russia, South America, Australia, and few European countries [9, 10]. Large quantities of copper, uranium and gold ore are processed by microbial technology on an industrial scale, and recovery of several other metals is also possible using such methods [11]. Some of the main areas of mineral biotechnology have been discussed in the present review.
Microorganisms Widely Used In Mineral Processing
Bioleaching using Autotrophs
Autotrophs are considered to be the first biotic metabolism indicating the origin of life. Autotrophs are strict chemolithotrophic microorganisms that utilize inorganic carbon as carbon source and derive energy for growth from oxidation of reduced sulphur compounds, Fe (II), Mn (II), metal sulphides like pyrites, hydrogen, etc. Autotrophs are found to produce nitric or sulphuric acid depending on their source of energy and are capable of indirectly chemical reaction with minerals leading to partial or complete dissolution or alteration in the mineralogy of the matrix.
Pseudomonas arsenitoxidans is the first obligate autotroph found to utilize arsenic as its sole energy source [12]. Later, facultative autotrophs belonging to Agrobacterium-Rhizobium branch of the α-Proteobacteria was found [13]. Recently, D’Imperio et al., [14] reported a microbe phylogenetically related to Acidicaldus but its ability to oxidize arsenite was inhibited by H2S. Table 1 lists the nutritional details of few such microbes.
Thiobacillus (now Acidithiobacillus) ferrooxidans have been reported to alter antimony containing sulfides by oxidizing the ferrous or sulfide moiety. Stibiobacter senarmontii, an autotroph has been first reported to oxidize trivalent antimony in Sb2O3 or Sb2O4 to pentavalent antimony (Sb2O5)[20].
Autotrophs that derive energy by oxidation of iron are predominantly acidophiles with optimum growth at pH 1.5-2. pH plays a vital role in the oxidation state of Fe with pH< 5 more favourable for oxidation of Fe. They thrive at different temperatures and are hence classified as mesophiles (20-40ºC), moderate thermophiles (40-60ºC), and thermophiles (60- 80ºC). The mesophiles actively involved in biooxidation and bioleaching are Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, Acidithiobacillus caldus, Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, Leptospirillum ferrodiazotrophum, Leptospirillum thermoferrooxidans and Leptospirillum ferriphilum. The moderately thermophiles are Acidimicrobium ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus caldus and Sulphobacillus thermosulphooxidans, while the thermophiles are Sulfolobus metallicus, Sulphobacillus sp. and Metallosphaera sedula.
Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is a commercially recognized biomining organism used to recover copper, gold, and uranium from their sulfidic ores or concentrates. Preferentially, a consortium of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus caldus and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans are used for effective bioleaching. Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is capable of leaching nickel laterites and oxidic ores anaerobically in the presence of elemental sulphur or pyrite as energy source [21, 22].
Bioleaching using Heterotrophs
Heterotrophic microorganisms utilize organic carbon as energy and carbon source for their growth. The metabolic by-products produced from the consumption of organic carbon interact with the mineral surface leading to partial or complete dissolution or alteration of the mineral surface. The metabolic by-products are usually organic acids such as acetic, citric, oxalic, and keto-gluconic acid [23,24]. Heterotrophic microorganisms also produce exopolysaccharides, amino acids and proteins that can solubilize the metals through different mechanisms [25]. However, organic acids such as citrate, gluconate and oxalate play a greater role in mineral dissolution due to its dual effect of lowering the lixiviant pH and metals solublization by complexing/chelating into soluble organo-metallic complexes [26]. Fungal bioleaching occurs by either of the following mechanisms (i) Acidolysis (ii) Complexolysis (iii) Redoxolysis (iv) Bioaccumulation [27]. The effectiveness of fungal bioleaching depends on the production capacity of these extracellular products and their metal resistance. But commercially, fungal bioleaching has proved ineffective due to the cumbersome downstream processing, production of large biomass in addition to low recovery of metals. The capacity of few heterotrophs to leach metals from various ores is listed in Table 2.
Leaching mechanisms of nonsulfidic minerals (carbonates, oxides and silicates) using heterotrophs have received less attention from microbiologists. Among the heterotrophic bacteria, members of the genus Bacillus have been found effective in biobeneficiation of bauxite[28]. Fungi from the genera Penicillium and Aspergillus have also been used in mineral leaching [29,30].
Bioleaching using Dissimilatory Metal Reducing Bacteria (DMRB)
Dissimilatory metal reducing bacteria are group of microorganisms that are capable of reducing metals under anoxic conditions, thereby separating them from their complex. This extrication would result in either structure conformational changes or slackening of an ore matrix making it susceptible for enhanced metal recovery on leaching. Dissimilatory Iron Reducing Bacteria (DIRB) in specific has found wide range of application in bio-beneficiation for removal of iron impurities from different ores and in bioremediation for detoxification of heavy metals, hazardous pollutants, etc. Numerous research works have been reported for bio-beneficiation of kaolin [40], bauxite [41] by IRB. But reductive bioleaching via bio-reduction of oxidic lateritic ore by IRB have received little attention [42] and requires extensive study. IRB has been reported to reduce the Fe (III) of the lateritic ore to Fe (II), thereby causing a phase change with the embedded nickel exposed for further enhanced leaching process [43].
Bioleaching Mechanism
Oxidative Bioleaching
The activity of oxidative bioleaching is facilitated by three ways: (i) via Microbe-Mineral contact mechanism or direct leaching mechanism; (ii) via Microbe-Mineral non-contact mechanism or indirect leaching mechanism (iii) via Co-operative mechanism. In microbe-mineral contact mechanism, EPS (extrapolymeric matrix) containing the microorganisms adhere to the mineral surface via electrostatic interactions to mineral sulphides whereas hydrophobic interactions are involved during adherence to elemental sulfur [44]. In non-contact or indirect leaching mechanism, the microorganisms are sessile in the bioleaching lixiviant and the ferric iron produced on bio-oxidation of ferrous iron indirectly oxidizes the mineral surface releasing ferrous iron back into the cycle. In co-operative mechanism, both the contact and sessile microorganisms symbiotically leach metals from their ore.
Oxidative bioleaching is more suitable in recovery of metals from sulphidic ores. Oxidative bioleaching predominantly occurs through thiosulphate pathway efficient in dissolution of acid insoluble metal sulphides or through polysulphide pathway which is efficient in dissolution of acid soluble metal sulphides.
Reductive Bioleaching
Reductive bioleaching is more suitable in recovery of metals from oxidic ores through a conformational change in the ore matrix. Reductive dissolution is favored under anaerobic conditions. In the recent past, the chemolithotrophic bacteria, A.ferroxidans, though play an active role in bio-oxidation was found to enhance metal recovery by reductive dissolution of oxidic ores under anaerobic conditions with sulphur as its electron acceptor [45].
Dissimilatory Metal Reducing Bacteria (DMRB) is the group of microorganisms more actively involved reductive bioleaching/bio-beneficiation via electron transfer i.e.by utilizing the oxidized metal as electron acceptor with organic carbon as its electron donor.
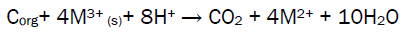 (1)
(1)
The activity of reductive bioleaching is demonstrated by the reductive dissolution which is facilitated by electron transfer between the microorganism and mineral which has been conceptualized to occur in the following ways (i) by direct contact of bacterial cell surface redox-active compounds to the mineral surface; (ii) through contact mediated by pili of also known as ‘protein nanowires’ between bacteria and mineral surface; (iii) by redox cycling of electron shuttle between the bacterial cell and mineral surface; (iv) through ligands (chelators/siderophores) which solubilize metals by complex formation [46].
Molecular methodologies for identification of leaching microbes
Study of microbial ecology in bioleaching environments has gained immense scientific interest in the recent years as clear understanding of microbe dynamics can help develop and improve the design and operation of bioleaching processes [47-49]. The interest of bioleaching experts have shifted towards understanding the microbial ecology of the process as its lucid understanding would help improvising this technology [47, 50]. There is a rapid advance in the suitable tools to characterize the microbes prevalent in the industrial bioleaching process.
Around 99% microbes in a niche remain far from being identified as they are not culturable and hence, culture-independent methods are being immensely applied to study the microbial ecology and dynamics in various environmental settings. Though culture-independent methods are all-encompassing [51], the complementary use of both culture-dependent and independent methods will yield a more detailed result targeting different microbes [52]. Though culture-dependent methods are cheap with low coverage and more laborious task, they are extremely useful for better understanding of the physiological potential of the microbes whereas cost-intensive culture-independent methods are high-throughput tools providing a richness of microbial coverage.
Culture-independent methods are mostly based on the ribosomal sequences which contain highly conserved regions which is necessary to distinguish between microorganisms.Culture-independent methods include cloning of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), RAP-PCR (Random Arbitrary primed polymerase chain reaction), amplified universal sequences, DGGE (Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis), whole cell hybridization using FISH (Fluoresent In Situ Hybridization), RAPD (Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA), tRFLP (Terminal Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism).The details of these molecular methods along their advantages and disadvantages have been reviewed by Sanz & Kochling, [54]. Application of various molecular methods in different bioleaching environments have been summarized in Table 3.
The advanced molecular technique, CARD-FISH (Catalyzed Reporter Deposition Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization) has helped to study the specific microbe-mineral adhesion of different mineral surfaces. Using this technique, Echeverría & Demergasso, 2009 [54] , in their study, found that microbes vaguely adhered to pyrite and chalcopyrite but not to chalcosite.
Though most modern microbiologist consider culture-dependent methods obsolete, several studies of different microbial communities highlight the fact that culture-independent methods cannot totally replace the former but both the methods are mutually complementary for a complete understanding of the microbial niches [55,56] . Several reviews have discussed the advances in cultivating the uncultivable microbes, their ecology and developed metagenomic techniques [57,58].
Identification, characterization and dynamics of microbial communities in bioleaching process can be achieved by the use of suitable culture-dependent and independent methods, but efforts towards understanding the functionality of these communities requires the input of OMICS and microarray technology. Various formats of microarrays like Functional gene arrays, Community genome arrays, Phylogenetic oligonucleotide arrays are used for analysis of microbial communities [64, 65].
Methods of Bioleaching
Biomineral processing of ores by bioleaching is gaining interest to recover the valuable metal values. But optimization of the various factors and parameters [22] for efficient recovery is a pre-requisite of every process. Initially, bioleaching is performed in shaking flasks for studying the amenability of the ore where several physicochemical and biological parameters are varied [67, 68] by varying the different parameters. Using these optimum parameters, the bioleaching experiment is scaled up in bioreactors or percolation columns. Rotary drum reactors have gained significance over the conventional stirred tank bioreactor which overcomes the drawbacks of rigorous collision and friction between the ore particles reducing microbial activity, thereby resulting in inefficiency of sulphide mineral bio-oxidation in stirred tank bioreactors [69]. Several other types of bench scale bioreactor systems like air-lift bioreactor [70], packed bed reactor, immobilized cell bioreactor [71] , etc. are the advanced bioreactor systems whose functionality is relatively simple with low power input providing effective heat and mass transfer and negligible shear stress. With the results obtained from bench-scale studies, bioleaching is further scaled up to industrial scale through well designed engineered systems of heap or dump bioleaching. Heap or dump bioleaching have been commercialized for extraction of copper [72, 73], gold [74], uranium [75] from their oxides and sulphides.
Downstream Processing of Bioleachate
Bioleached liquor containing varying concentrations of different metals obtained after bioleaching for respective metals are further subjected to the hydrometallurgical routes of unit operations such as Solvent Extraction (SX) and Electrowinning (EW) [5, 76]. In solvent extraction, each metal will be stripped to pure solution at a suitable pH to obtain pure metallic solutions. These pure metal solutions will be subjected to chemical precipitation or electrowinning to obtain pure metal. In electrowinning, the metal will be deposited on the cathode from an aqueous bath containing corresponding metal ions.
Biomineral Processing: Our Experience
Reductive Dissolution using Acidithiobacillus ferroxidans for Recovery of Nickel and Cobalt
Chromite overburden (COB) is a low-grade nickel lateritic ore in which nickel is ingrained with ferric iron minerals, such as goethite [FeOOH]. Microbial processing of laterites have been investigated for extraction of metal values, however an economically viable process has not been developed so far. The bacterium Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (isolated from the Turamdih mine water) for microbial extraction of nickel from lateritic chromite overburdens (COB), Sukinda was used. Since, COB is an oxidic ore; aerobic bioleaching using chemolithotrophs has not been quite successful. Hence, we have studied the possible anaerobic reductive dissolution of ferric iron (goethite) minerals using A. ferrooxidans to facilitate the extraction of nickel from lateritic COB. In anoxic environment, A. ferrooxidans reduced the ferric iron in goethite [FeOOH] mineral of COB by using elemental sulphur as electron donor.

Nickel embedded in the complex goethite [FeOOH] matrix of COB has been successfully recovered by cumulative action of sulphuric acid, generated by oxidation of elemental sulphur and reduction of ferric iron in goethite matrix by A. ferrooxidans. About 41% of nickel present in COB was extracted in a 3L scale bioreactor maintained in anoxic environment (pH -1.8±0.05, temperature- 28 ±2°C). [22]
Bio-reduction of chromite overburden using Dissimilatory Iron Reducing Bacteria (DIRB)
In order to further enhance the nickel and cobalt recovery from chromite overburden (COB), further investigation was carried out using dissimilatory iron reducing bacteria (DIRB) under facultative anaerobic condition. DIRB has the inherent capacity to reduce the Fe (III) phase (goethite) to Fe (II) phase (hematite, magnetite), thereby, producing a conformational change in the goethite matrix resulting in liberation of the embedded nickel on acid leaching. XRD and FESEM studies confirmed the phase conversion by the appearance of magnetite peaks and formation magnetite globules on the extrapolymeric matrix on ore respectively. 70% Ni and 81% Co was recovered on acid-leaching of DIRB-treated ore whereas only 54% Ni and 57% Co was recovered on acid leaching of untreated COB [43]. Hence, pre-treatment of COB with DIRB can enhance the recovery of nickel.
Microbial recovery of copper from low grade copper ores
The copper industry is also increasingly faced with the problems of extracting metals from low grade ores due to the non-suitability of conventional mineral processing methodologies on one hand and its dumping on the other which in turn causes several environmental problems. With our experience we have studied the biorecovery of copper from the low grade chalcopyrite of Malanjkhand Copper Project (MCP), India. Shake flask studies have showed the optimized bio-physico-chemical parameters [67] which have further been scaled up for the industrial feasibility of our process. In this context, a BACFOX bioreactor technology has been developed to efficiently use meso-acidophilic bacteria for extraction of copper from low grade ore [67, 77]. Bench scale studies were conducted to optimize the lixiviant flow rates and acid consumption for extraction of copper from low grade ore using BACFOX bioreactor technology [4, 5, 67, 77]. Based on the optimized conditions at bench scale, pilot scale practices were undergone to test the feasibility of the BACFOX process at an industrial setting [3, 76, 77]. The outcome of the entire study was development of process flow sheets for the extraction of copper from low grade chalcopyrite using BACFOX bioreactor through bio-hydrometallurgical route.
Microbial Removal of Phosphorus from LD Slags
Occurrence of high amount of phosphorous in the LD slag, manganese ore, iron ore and coke makes them unsuitable for their utilization in mineral based industries like iron and steel making etc. Many microbial species (Bacteria, Fungi, yeast and Actinomycetes) are capable of solubilizing sparingly soluble phosphorous compounds. A Five Ton capacity biobenefication plant was set up at Vishakhapatnam Steel Plant to remove phosphorus from LD slag, after successful completion of 1 ton capacity Pilot scale at CSIR-IMMT, Bhubaneswar.
With the drawbacks associated with conventional methodologies adopted for metal extraction, the use of certain microorganisms through the application of biomineral processing has gained importance over the past few years. In order to treat the low/complex ores, biomineral processing is an important area of research. Further, the flotation of minerals, alteration of flotation characteristics of minerals, flocculation of ferric and phosphatic slime, removal of cyanide and other toxic chemicals discharged from mineral industrial operations are certain potential areas where significant applications and advances of microbial effects are likely to have commercial viability. Genetical study of the microorganisms used in biomineral processing with the fundamental biochemistry needs to be studied in details for further exploitation of such microorganisms at an industrial scale. As a whole, bioprocessing of minerals provides economically viable and environmentally friendly process for mineral industry. It is expected that the coming years will see a more advanced area of biomineral processing for extraction of metal values from low and complex ores.
The authors are thankful to CSIR for their grant-in-aid through the Emeritus Scientist Scheme. One of the authors Mr. Sandeep Panda is thankful to CSIR, New Delhi for the award of Senior Research Fellowship.