ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
| P.Prabhu1, C.Poongodi2, P.Sarwesh3, Dr. A. Shanmugam4 PG scholar, Dept. of ECE, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Tamil Nadu, India1 Associate Professor, Dept. of IT, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Tamil Nadu, India2 PG scholar, Dept. of ECE, K.Ramakrishana College Of Engineering, Tamil Nadu, India3 Principal, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Tamil Nadu, India4 |
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
In this paper low profile printed monopole antenna for RFID applications is presented ,this antenna is designed for RFID coverage, In this work design and simulation confined RFID communication can be achieved with this antenna geometry ,a low profile RFID antenna is designed and resonant frequency is computed using Method of Momentum(MOM) in ADS software, by varying the dimensions of the proposed antenna can achieve resonant frequency ,the low profile printed monopole antenna achieves a desirable radiation characteristics with gain 3.8dBi for operating frequency 2.4GHz.
Keywords |
||||||||||
| RFID antenna; monopole antenna; low profile; gain | ||||||||||
INTRODUCTION |
||||||||||
| Over the last few years lot of low profile printed monopole antenna have been developed for RFID antennas ,especially for RFID applications at 2.4GHz ,the printed monopole antenna are omnidirectional radiation pattern ,using for medium to large range range of RFID systems such as single frequency and narrow bandwidth applications[1][2],but with the radiation capacity and radiation pattern characteristics, low cost and easy to fabricate process, To increasing working bandwidth of the RFID antenna many improve structure used such printed metal wreath feed structure[3].multi antenna array wreath types of arms [4].These methods size of antenna complicate structure of the antenna ,we introduce the new structure the printed slotted monopole antenna .it will increase the radiation characteristics of antenna ,but the size of the antenna increase the compare to existing antenna s structure [7].It can increase the working bandwidth of an RFID antenna . RFID tag antenna operating with in the limited space, the simplified structure it have excellent radiation pattern. | ||||||||||
| To increase the bandwidth of the antenna with this simplified structure, In slotted printed monopole antenna patches are scattered electromagnetic waves. | ||||||||||
| The operating frequency for the RFID antennas allocated by the around 868-878 MHz and 2.4-2.45 GHz [8] .Thus, the low profile slotted printed monopole antenna, covers the 2.4 GHz. | ||||||||||
II. STRUCTURE DESIGN OF AN ANTENNA |
||||||||||
| In structural design of a printed monopole antenna slotted on the rectangular patch, according to the FCC RFID operating frequency ,we designed a low profile printed monopole antenna for RFID applications .propose antenna using Rogers_Ro4003 dielectric substrate with thickness 2.0 mm and dielectric constant εr=3.38 , | ||||||||||
| The proposed geometry size is L*W is 95*25 mm and patch and slot length is L1=17mm,L2=15mm,L3=1mm,L4=20mm,L5=14mm,L6=12mm,L7=14mm patch width of the antenna is W1=10mm,W2=3mm,W3=5mm,W4=8mm,S1=3mm, length of the ground plane is S2=1mm,S3=3mm,g1=3mm,Sg=3mm, in this above mentioned geometry of the antenna theoretically designed using following equations The lower frequency equation is given below | ||||||||||
 |
||||||||||
| The effective dielectric contant is calculated by using this equation is | ||||||||||
 |
||||||||||
| Fundamental resonant length of the monopole arm is | ||||||||||
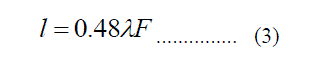 |
||||||||||
Where, 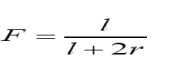 |
||||||||||
| From the alternative equation for the resonant frequency is | ||||||||||
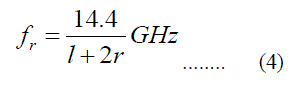 |
||||||||||
| To find the width of the antenna is using this equation is | ||||||||||
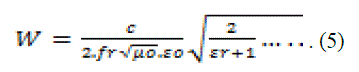 |
||||||||||
| Where, | ||||||||||
| fr = Resonant Frequency | ||||||||||
| ε r = Relative dielectric constant | ||||||||||
| ε o = 8.9x10−12 C2 /Nm2 | ||||||||||
| μo = 4π.x10−7 Tm/A | ||||||||||
| Antenna length here donaote as „L? is designed by following equation | ||||||||||
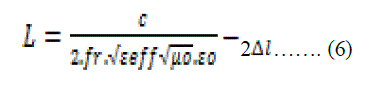 |
||||||||||
| Where, | ||||||||||
| fr = Resonant Frequency | ||||||||||
| ε r = Relative dielectric constant | ||||||||||
| ε o = 8.9x10−12 C2 /Nm2 | ||||||||||
| μo = 4π.x10−7 Tm/A | ||||||||||
III. SIMULATED RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS |
||||||||||
| Simulated return loss of the slotted printed monopole antenna is shown in fig.2, from the figure the operating frequency at 2.4GHz which return loss S11 is -17 dB. In this resonant frequency 2.4 GHz perfectly suitable for the RFID applications .In proposed antenna using microstrip feed line to exciting the monopole antenna it will scattering the electromagnetic waves in a slot of the antenna, slot of the printed antenna and microstrip fed line with 50 Ω achieves the impedance matching, the proposed antenna acquired efficient radiation characteristics such as E-plane polarization, H-plane polarization, gain and directivity. In this proposed antenna operating at 2.4 GHz band for RFID applications, simulated using Method of momentum (MOM) in ADS simulator. | ||||||||||
| The proposed antenna radiated in the omnidirectional radiation pattern shown in fig.5, In this antenna achieves perfect radiation characteristics gain and directivity of the antenna at 2.4GHz is 3.41dBi and 3.1 dBi respectively. Simulated results of a proposed of Low Profile Monopole Antenna can operate at 2.4 GHz for RFID applications. | ||||||||||
IV. CONCLUSION |
||||||||||
| A new type of low profile monopole antenna for RFID applications has been proposed and simulated all monopole antennas printed on the thin substrate, which is Rogers Ro4003 dielectric printed board used for this proposed antenna, In this proposed monopole slotted antenna achieved desired radiation pattern with gain of 3.41 dBi at 2.4GHz and return loss -17 dB at 2.4GHz, Thus it perfectly suitable for the short range of RFID applications. | ||||||||||
Figures at a glance |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
References |
||||||||||
|