ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
Uddhav Ram Lahane1PrashantUddhav Lahane2
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
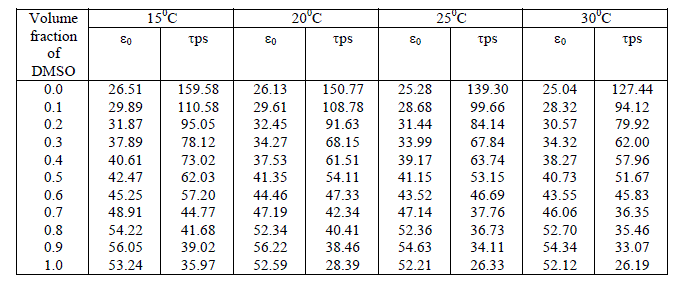
The dependence of dielectric relaxation on frequency, temperature, pressure and other external factors has been used to investigate the correlation between the morphology and electrical properties of macromolecules. Study of molecular interaction of Dimethyl Sulfoxide with Ethanol has been carried out at sampling frequency 12.4 GHz and at temperatures 150C, 200C, 250C&300C. Time domain reflectometry (TDR) in reflection mode has been used as a technique. The static dielectric constant (ε0), dielectric relaxation time (τ) and thermodynamic parameters of binary mixtures were obtained from complex reflection spectra.
Keywords |
| Dimethyl Sulfoxide, Ethanol, Dielectric relaxation, Time domain reflectometry, Fourier transformation, Dielectric constant, Relaxation time. |
INTRODUCTION |
| Time domain reflectometry (TDR) is an effective approach to understand molecular interactions in liquid. It is very interesting to correlate dielectric parameters to molecular dynamics in aqueous solutions. Study of aqueous solutions to understand change in amount of hydrogen bonding, change in size of molecular entities as well as their speed of rotation, in presence of different types of solutes was carried out by many research groups in field of dielectric spectroscopy. |
| The basics of molecular interaction in solution are hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding occurs between a proton donor and proton acceptor group. The hydroxyl ( -OH ) group is a proton donor as well as proton acceptor. Dimethyl sulfoxide (CH3)2SO an aprotic polar solvent is not a hydrogen bond donor because it does not have a hydrogen attached to an oxygen or to a nitrogen, so there are no positively charged hydrogens to form ion-dipole interactions. Aprotic polar solvents have a partial negative charge on the surface of their molecules that can solvate cations, but the partial positive charge is on the inside of the molecules, which makes it less accessible. |
EXPERIMENTAL |
| Time domain reflectometry (TDR) in reflection mode has been used as a technique. In TDR a fast rising step pulse of 25 ps is incident on the binary mixture kept in the cell. The binary mixtures were prepared at different volume percentage of Dimethyl sulfoxide (CH3)2SO in Ethanol in steps of 10 vol. % within a ± 0.01 % error limit. The reflected pulse from the cell is sampled with incident pulse in sampling oscilloscope. The reflected pulse from sample contains the information regarding dielectric behaviour of binary mixture. The reflected pulse without sample R1(t) and with sample Rx(t) were digitized in 1024 points and stored on disc. |
| The time dependent data were processed to obtain complex reflection coefficient spectra ïÃÂò*(ïÃÂ÷) using Fourier transformation (Samulon [1]; Shannon [2]) as |
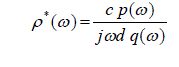 |
 |
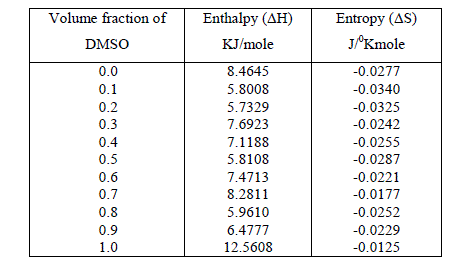
| The thermodynamic parameters molar enthalpy of activation ïÃÂÃâH and the molar entropy of activation ïÃÂÃâS were obtained using equation |
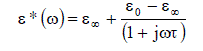 |
| and are listed in table 2. |
 |
RESULT AND CONCLUSION |
| The static permittivity increases with addition of Dimethylsulfoxide in Ethanol. This raise in permittivity is due to increase in effective dipole moment per unit volume in mixture. Relaxation time is very sensitive parameter related to molecular size as well as mobility of molecules in liquid. Relaxation time for aqueous solutions of Dimethylsulfoxide – Ethanol decreases rapidly up to 50 % concentrations and then deceases slowly with increase in volume fraction of solute in ethanol mixture. The variation in relaxation time shows that, the decrease in amount of hydrogen bonding between solute and solvent molecules, which leads to smaller molecular structures rotating fast. |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS |
| The authors are greatly obliged to UGC for the financial support through Minor Research Project Scheme. |
References |
|