ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
Ashraf Abd Almageed Ahmad1, Dr.Eltahar Mohammed Hussein2
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
The continuous power outages and interruptions in the instantaneous electrical parts distribution network always adversely affect the health, safety and economic activity and the low level of production in the industrial sector .the paper discusses the reliability of the electric distribution network through the study of indicators of reliability analysis technology which is characterized as a fast, efficient and know that by SAIFI, SAIDI, CAIDI, MAIFI, CTAIDI, in order to repeat the failures at different times for Lines 33KV and 11KV, from readings to the control station for the automated distribution network for the Omdurman area.
Keywords |
| SAIFI, SAIDI, CAIDI, CAIFI, MAIFI, CTAIDI, distribution, reliability. |
INTRODUCTION |
| Provide consumers with electric power in the range of distribution of electrical networks in a way that the quality of service and high reliability, and that the importance of the reliability of electrical distribution networks as a factor of development and economic growth, as studies have shown which confirmed that 80% of interruptions in the supply of electric power resulting from the problems and breakdowns in the electrical distribution networks [1,2] . |
| Electrical distribution systems are usually radially so exposed to the rates of interruption because of system components of transformers and breakers and switching devices, the growing demand for customers to provide high-quality service makes requirements for improvements in the electrical distribution network. |
| The main objective of assessing the reliability of the electrical distribution network, a qualitative analysis of indicators of to improve the reliability of supply voltage and planning system after analysis, there are two types of analysis: - |
| 1 Monte Carlo approach to simulate the user to calculate the reliability indices. |
| 2 Bayesian network approach, a more effective way of theoretical models to see replacement based on theoretical possibilities. |
| The main problems in the supply of energy are the consequences of errors in one or part of the components of a network failure overhead lines or cables[1,2,10,11,13,14]. |
II. METHODOLOGY |
| Using the analysis of the automatic control system for electrical distribution networks by using reliability indices in the case study area of Omdurman distribution network by describing the data readings and analytical tables. |
| Collect data failure rate of the distribution system to calculate the reliability in addition to collect all the data from all the interruptions caused by shedding load and the breakdown of the system scheduled maintenance or unscheduled. Data were used to calculate the reliability of the network indices city of Omdurman. |
III. RELIABILITY INDICES |
| The main reason for power outages due to the fact that there are errors in the distribution network, such as wind, rain, trees, animals, and called for all the mistakes claim indirectly for the disappearance of electrical disappear either ill unforced errors such as car accidents, equipment breakdowns . |
| Indicators are used to assess the reliability of the electric distribution network and analyse the data set of network, The indicators used in the analysis of the electrical distribution network[3,4,5] . |
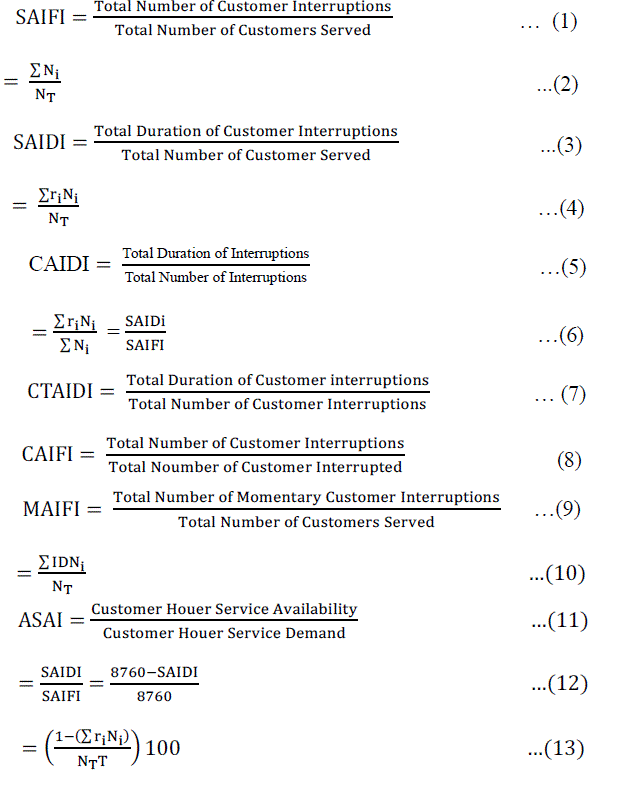 |
6- Momentary Average Interruption Frequency Index (MAIFI ):- |
| Is an indicator of the average interruption frequency for a moment and measures the average number of interruptions during the interim period of time. |
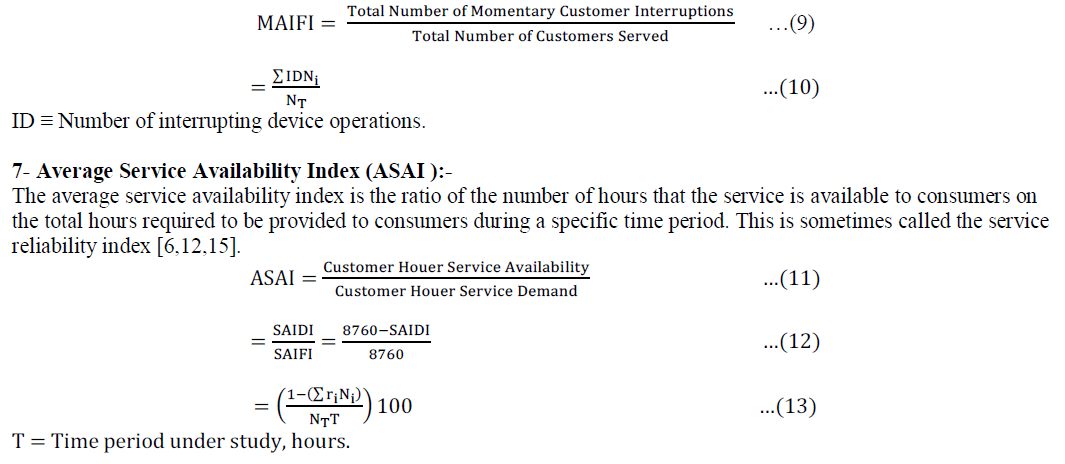 |
IV. CASE STUDY OF ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION OMDURMAN AREA RELIABILITY |
| Electricity distribution network consists of Omdurman stations distributional represents the link between the transmission and distribution lines, and these stations of different capacities are converted 110kv to 33kv and 11kv. Consider the study to the distribution system through the network reliability medium voltage lines 110kv to 33kv and 11kv, 33kv lines that supply the transformers reduction to 11kv and at distribution sub-stations. The 11kv lines that supply the transformers reduction to 240v and 415v line to line. |
| Network and the distribution of Omdurman area exposed some areas where interruption . |
| where it is to drop the following cases :- |
| 1- transient errors |
| 2- maintenance work |
| 3- commends the work |
| 4- equipment failures and breakdowns General (Faults directly) [7,8]. |
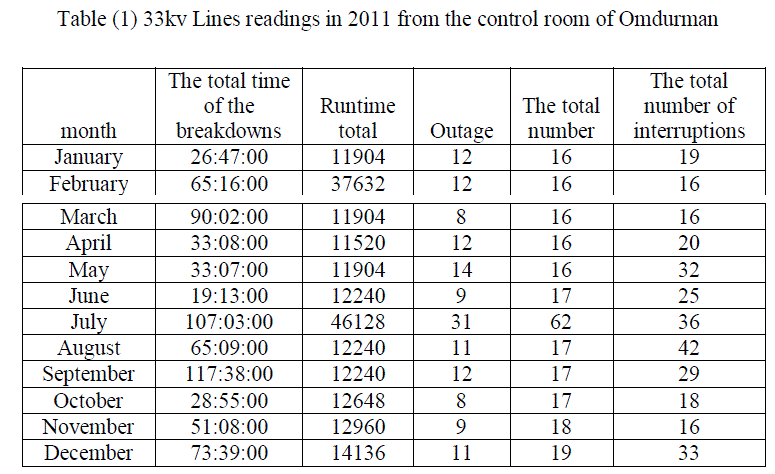
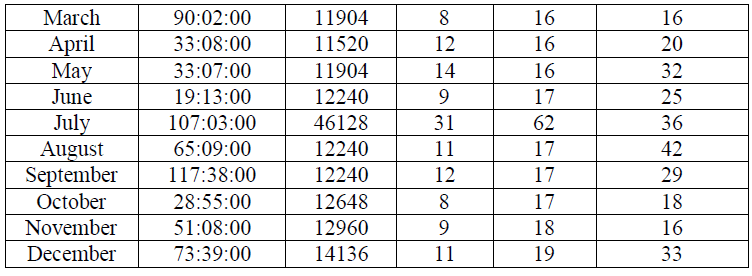
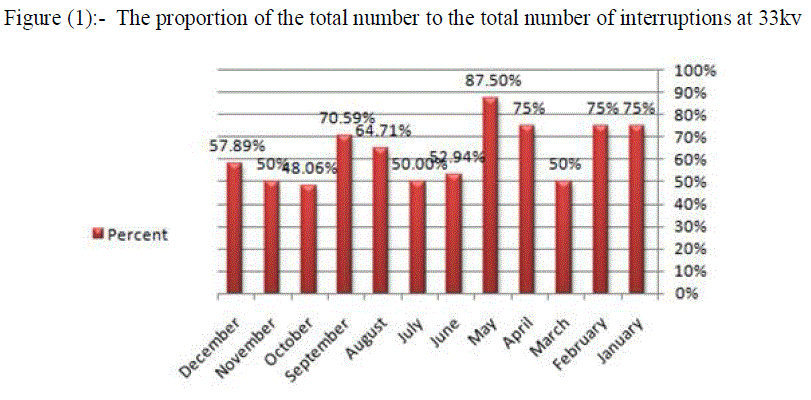
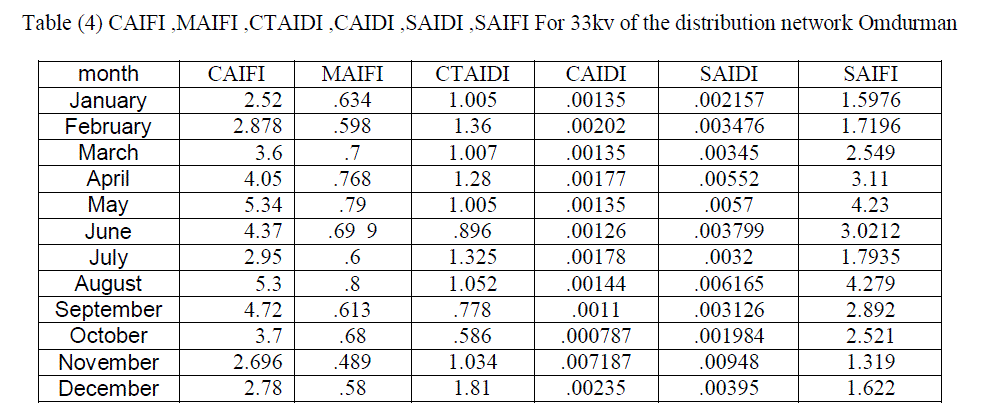
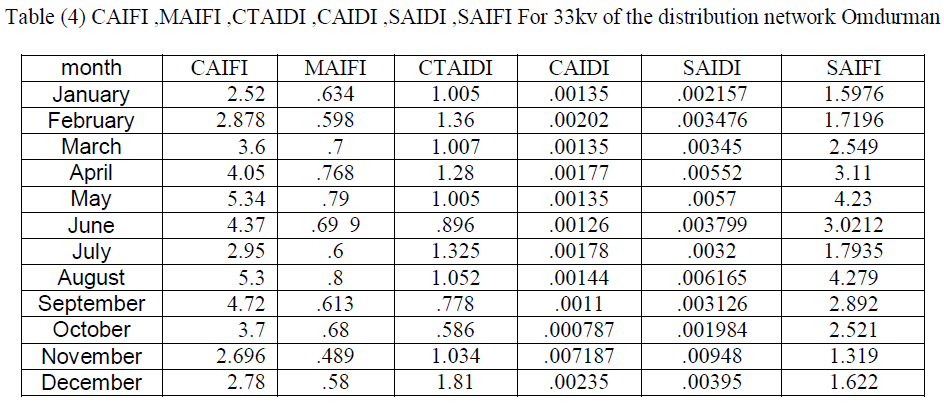
| The following table(1) shows illustrates the inter drop to 33kv lines during the year (2011). |
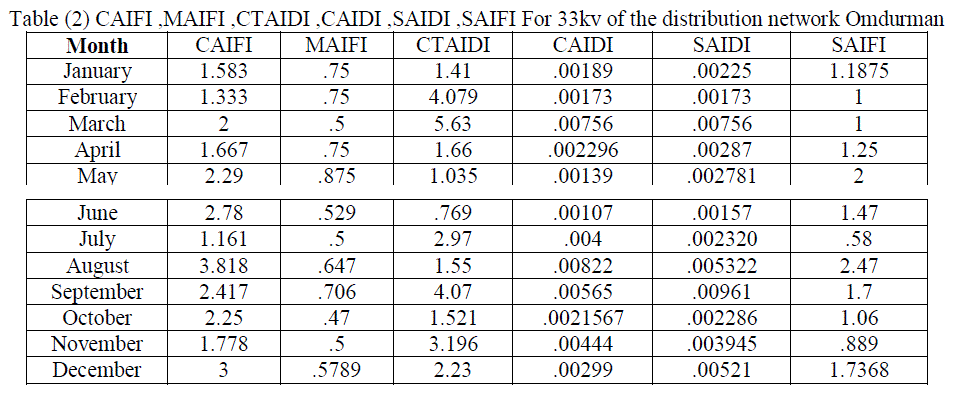
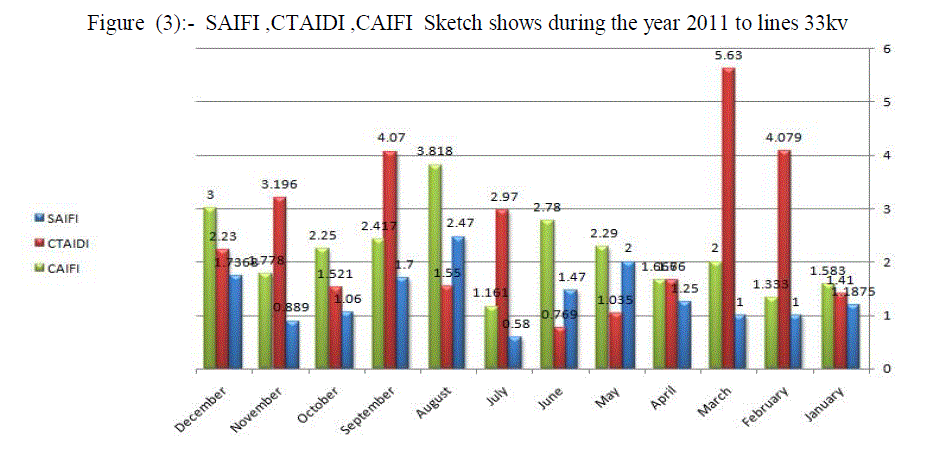
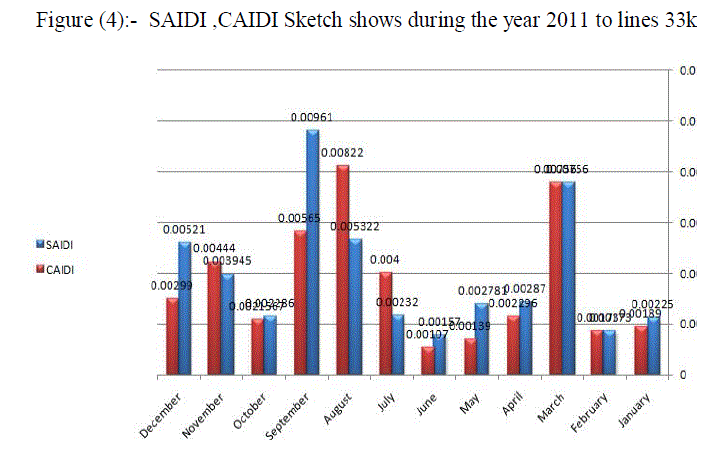
| The table(2) shows the values of readings CAIDI during the year to 33KV lines. Paper find that the system of distribution network in Omdurman area with high reliability during the month of January and February and then declining in March and then start with increase reliability and so decrease the values CAIDI and affected by the change in the values of SAIFI and SAIDI and that in the months of April and May until you reach the highest reliability during the year in June to start downward in July to reach its lowest value in the months of August and September, and that with the highest value for Said. The value remains CAIDI the seesaw in the average rate in the months October, November and December shown that at Figure (3) and Figure (4) . |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
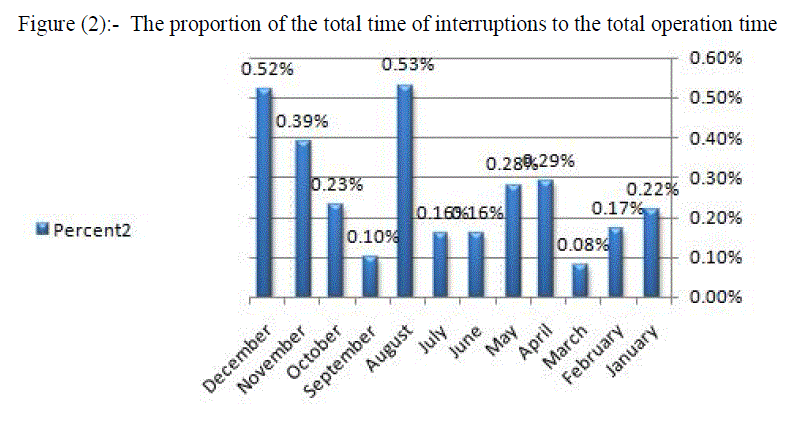 |
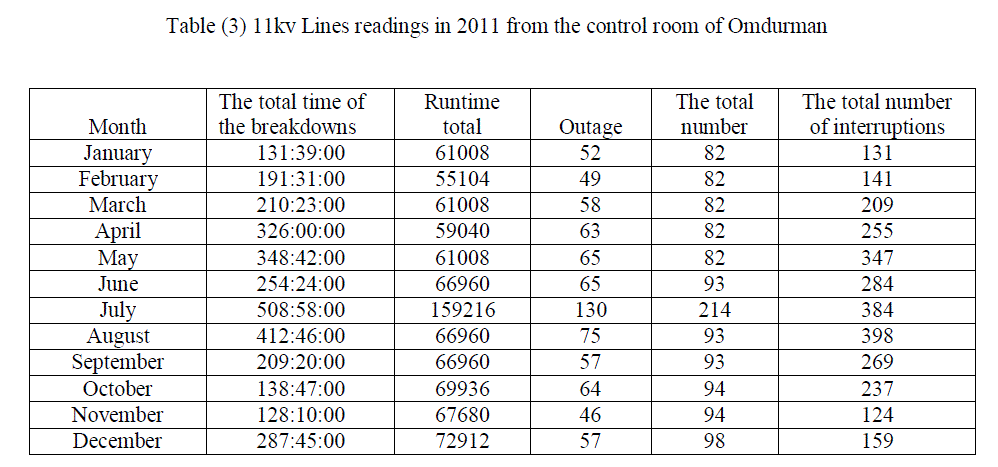
| As for the lines of 11 kV, the values of CAIDI are not rising, but in two months, November and December, the lowest reliability of months during the year, and that the values of SAIFA and SAIDI stable and the stability of these values lead to stability values CAIDI thus decrease the period of interruption at consumers. Table (3) ,Table (4), Figure (7) and figure (8). |
 |
 |
 |
 |
V.CONCLUSION |
| The study observed that CAIDI representing an indicator to measure the automated transformation of the electricity supply interruptions for customers and automated transformation process reduces the number of consumers affected by the interruptions. |
| Also, for the automated control a prominent role in the operation more efficient and by isolating and shutting down and restarting the affected areas interruptions , The transformation process in the feed Power Supply divided into sections according to consumer areas can reduce the interruptions thereby increasing reliability as measured by MAIFI , SAIFI. The reliability study will help in the work of the future plans in network expansion and rehabilitation, as well as maintenance of the lines with a number of times the most interruption. |
VI .RECOMMENDATIONS |
| To increase the reliability of the distribution network Omdurman This means reducing the period of interruption for consumers and that corrective maintenance and preventive maintenance of the lines most of the time of interruption during the study and the establishment of a secondary feed lines to minimize outage time. |
VII .ACKNOWLEDGEMENT |
| Authors thank the staff of the company for the Sudanese Electricity Distribution - Co. Ltd., which helped get loads of energy and logs errors for a year of study. |
References |
|