e-ISSN:2320-1215 p-ISSN: 2322-0112
e-ISSN:2320-1215 p-ISSN: 2322-0112
Sakthi Vel M*
1Department of Business Administration, Annamalai University, Chiambaram, Tamilnadu, India
Received: 27-Aug-2022, Manuscript No. JPPS-22-73098; Editor assigned: 30-Aug-2022, PreQC No. JPPS-22-73098 (PQ); Reviewed: 13-Sep-2022, QC No. JPPS-22-73098; Revised: 03-Jan-2023, Manuscript No. JPPS-22-73098 (R); Published: 11-Jan-2023, DOI: 10.4172/2320-1215.12.1.001
Citation: Vel SM. Formulation and Evaluation of Extended Release Tablets of Glipizide Using Different Polymers. RRJ Pharm Pharm Sci. 2023;12:001.
Copyright: © 2023 Vel SM. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Research & Reviews in Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences
The aim of the work was to prepare and characterize extended release tablets of Glipizide using direct compression technique. Preformulation studies such as bulk density, tapped density, compressibility index, and angle of repose were evaluated for the powder blend. After compression extended release tablets were evaluated for hardness, weight variation, thickness, friability, drug content and in-vitro dissolution studies. In vitro dissolution studies was performed by using USP dissolution apparatus (paddle type) using phosphate buffer pH 7.4 for 10 hrs. Decrease in release rate was noticed by increasing the ratio of polymer ratio, due to swelling of the gum. Formulation F7 containing Carbopol showed controlled drug release after 10 hrs, selected as best formulation.
Glipizide; Dissolution studies; Carbopol; Preformulation studies; Polymer ratio
The terms of "sustained or extended release", "prolonged release, and controlled release" as applied to drug formulations, have the meanings ascribed to them in Remington's pharmaceutical sciences, sustained or extended release drug systems include any drug delivery system which achieves the slow release of drug over an extended period of time, and include both prolonged and controlled release system. If such a release system is effective in maintaining substantially constant drug level in the blood or target. It is considered a prolonged released system. The goal of any drug delivery system is to provide a therapeutic amount of drug at the target site in the body. It aims to achieve and maintain the desired drug concentration. This idealized objective points to the two aspects of drug delivery like spatial placement and temporal delivery of drug. Spatial placement relates to the targeting of the drug to a specific organ or tissue while temporal delivery system can be a major step towards solving these two problems. Over the past decade an entirely new technique for the delivery of a drug and other biologically active agents has been developed. This technique for the drug administration is termed as sustained release or controlled release.
Drug suited for extended release formulations are
• A drug that is highly soluble at intestinal pH and is absorbed by passive diffusion has an ideal characteristic for fabrication of extended release dosage forms [1].
• A drug with no site specific absorption characteristic is preferred.
• A drug with low aqueous solubility (less than 1 mg/ml) may already Posses inherent extended release dosage form.
• Drug candidates with permeability greater than 4 x 10-4 nms-1 are likely to be suitable for formulations into extended release dosage form.
• A drug with biological half-life of between two and six hours is preferred for inclusion in extended release dosage form to avoid accumulation in the body.
• Drugs with dosage not exceeding 125 mg - 325 mg are most suited as extended release products in order to limit the size of delivery system.
Breakthrough of the Extended Release (ER) formulations
The Extended Release (ER) formulation of the present invention which comprise a pharmaceutically acceptable polymer, provide extended release in vivo when given once daily, drug delivery systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated pharmaceutical scientist to sequire the better understanding of the physiochemical and biological parameters pertinent to their performance. Despite tremendous advancements in drug delivery, the oral route remains the preferred for the administration of therapeutic agents because the low cost of therapy and ease of administration lead to high levels of patient compliance. It also remains the most popular and successful route used for controlled delivery of drug because of convenience and greater flexibility in dosage form design [2].
Oral extended release dosage forms have therapeutic
Improved patient convenience and compliance due to less frequent drug administration reduction in functions in steady state level and better control of disease condition and reduced intensity of local or systemic side effects. Increased safety margin of high potency drugs due to better control of plasma level. Maximum utilization of drug enabling reduction in the total amount of dose administered reduction in health care cost through improved therapy, shorter treatment period less frequency of dosing and reduction in personal time to dispense, administer, and monitor patients. Is advantages: Decreased systemic availability in comparison to immediate release conventional dosage forms: This may be sue to incomplete release, increased first pass metabolism, increased in stability, and insufficient residence time for complete release pH dependent solubility. Retrieval of drug is difficult in the case of toxicity, poisoning or hypersensitivity reactions [3].
Glipizide is a gift sample from Aurabindo pharma Hyderabad, Xanthan gum, Carbopoland Guar gum was supplied by Taian Ruitai Cellulose Co.Ltd (Chennai), Microcrystalline Cellulose was supplied fron Nacto pharma Ltd, Hyderabad, Magnesium stearate were procured from Peter Greven, the Netherlands. All other materials were of analytical grade [4].
Calibration of Glipizide: The stock solution was serially diluted to get solution in the range of 5-25 ug/mlusing pH 7.4 buffer solution and ⅄max of the solution was found out [5].
Micromeritic studies: The powder blends of all the formulations were evaluated for bulk density, tapped bulk density, carr’s index, Hausner ratio, angle of repose, and drug content. Similarly the prepared floating tablets were evaluated for hardness, thickness, and diameter, friability (Tables 1-4 and Figure 1) [6].
| Formulation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Xanthan gum | 15 | 25 | 35 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Guar gum | - | - | - | 15 | 25 | 35 | - | - | - |
| Carbopol | - | - | - | - | - | - | 15 | 25 | 35 |
| Mg.st | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Talc | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MCC | 144.5 | 114.5 | 84.5 | 114.5 | 84.5 | 54.5 | 54.55 | 54.5 | 54.5 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
Table 1. Composition of Glipizide tablets.
| Matrix material | Formula code | Angle of repose | Bulk density (gm/ml) | Tapped density (gm/ml) | C.I (%) | Hausner ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Carbopol |
F1 | 24O86’ | 0.481 | 0.532 | 16.16% | 1.166 |
| F2 | 27O28’ | 0.485 | 0.535 | 14.31% | 1.167 | |
| F3 | 24O49’ | 0.483 | 0.533 | 15.04% | 1.175 | |
| F4 | 25O15’ | 0.484 | 0.531 | 15.22% | 1.174 | |
| F5 | 26O02’ | 0.482 | 0.534 | 14.33% | 1.161 | |
| F6 | 24O52’ | 0.485 | 0.535 | 15.07% | 1.173 | |
| F7 | 23O38’ | 0.480 | 0.531 | 14.68% | 1.165 | |
| F8 | 27O02’ | 0.483 | 0.534 | 15.43% | 1.177 | |
| F9 | 24O56’ | 0.485 | 0.531 | 14.26% | 1.179 |
Table 2. Micromeritic properties of directly compressible powder.
| Formulation | Thickness (mm) | Weight variation (mg) | Hardness (kg/cm2 ) | Friability (%) | Drug content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 2.55 ± 0.07 | 99.2 ± 1.37 | 5-6 | 0.43 | 98.52 |
| F2 | 2.53 ± 0.09 | 98.3 ± 1.36 | 4-5 | 0.41 | 96.46 |
| F3 | 2.52 ± 0.05 | 102 ± 1.42 | 5-6 | 0.73 | 97.56 |
| F4 | 2.64 ± 0.08 | 101.2 ± 1.4 | 10-11 | 0.54 | 94.84 |
| F5 | 2.42 ± 0.01 | 99.6 ± 1.38 | 9-10 | 0.36 | 97.21 |
| F6 | 2.50 ± 0.07 | 102 ± 1.36 | 10-12 | 0.23 | 98.62 |
| F7 | 2.65 ± 0.09 | 99.2 ± 1.31 | 10-12 | 0.29 | 99.01 |
| F8 | 2.60 ± 0.06 | 98.3 ± 1.36 | 10-12 | 0.15 | 97.88 |
| F9 | 2.46 ± 0.02 | 101.3 ± 1.3 | 10-12 | 0.38 | 98.14 |
Table 3. Results of thickness, weight, hardness, friability and drug content.
| Formulation | 0 Hour | 1 Hour | 3 Hours | 6 Hours | 10 Hours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0 | 21.43 ± 0.01 | 34.65 ± 0.05 | 44.53 ± 0.04 | 59.34 ± 0.02 |
| F2 | 0 | 18.32 ± 0.06 | 38.66 ± 0.02 | 47.46 ± 0.06 | 56.48 ± 0.04 |
| F3 | 0 | 17.37 ± 0.05 | 37.35 ± 0.01 | 45.51 ± 0.02 | 55.74 ± 0.03 |
| F4 | 0 | 31.88 ± 0.04 | 58.96 ± 0.01 | 62.57 ± 0.04 | 87.23 ± 0.05 |
| F5 | 0 | 32.46 ± 0.02 | 54.88 ± 0.03 | 68.54 ± 0.02 | 86.41 ± 0.03 |
| F6 | 0 | 53.65 ± 0.01 | 60.74 ± 0.04 | 74.34 ± 0,03 | 83.36 ± 0.01 |
| F7 | 0 | 42.85 ± 0.05 | 59.27 ± 0.03 | 76.21 ± 0.01 | 92.78 ± 0.03 |
| F8 | 0 | 47.76 ± 0.03 | 58.32 ± 0.01 | 62.43 ± 0.03 | 77.51 ± 0.02 |
| F9 | 0 | 41.84 ± 0.08 | 52.28 ± 0.03 | 72.18 ± 0.04 | 79.53 ± 0.04 |
Table 4. Formulation results of different time intervals.
Determination of bulk density
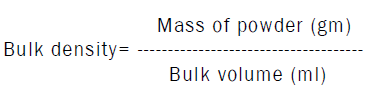
Determination of tapped density
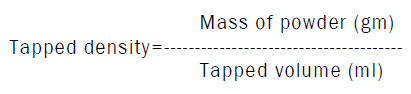
Determination of Carr’s index

Determination of Hausner ratio
Hausner ratio=Tapped density/Bulk density
Determination of angle of repose
Tan ø=h/r
Ø=tan-1 h/r
h=height of pile (cm)
r=radius of pile (Cm).s
Different types of polymer guar gum, xanthangum, carbopol combination were studied.
Formulation F7 containing carbopol as combination showed controlled drug release 10 hrs emerging as best formulation.
The accumulative percentage drug was decreased by increase in polymer concentration [7].
The stability studies were carried out according to ICH guideline and selected F7 formulation was stable at 400C/75% RH up to 3 months.
The controlled and efficient drug delivery system developed in the present study will maintain plasma glipizide levels better, which will overcome the drawback associated with the conventional therapy.
When the polymer ratio increases which is inversely proportional to the rate of release i.e, rate of release will decrease.
When the release rate is decreased by increasing the polymer ratio. This is due to swelling of the gum, the viscosity increases, the release rate is decreased.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]