ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
Madhusudanan. V1*, Vijaya. S2, Gunasekaran. M3,*
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
The intuition with two-species models may be applied to community food web questions. The critical behavior to community function may arise only through the interaction of three or more species. In this paper we investigate the dynamical behavior of the system consisting of two preys with distinct functional responses and a predator. We also study the effect of harvesting on prey species. Harvesting is strong impact on the dynamics evaluation of population. To a certain extent it can control the long term stationary density of population efficiently. Finally the local and global stability analyses were carried out.
Keywords |
| Food web, Functional response, Harvesting, Local and Global stability |
INTRODUCTION |
| Population Dynamics has been a prime branch of theoretical ecology. Lotka- Volterra model describes interaction between two species in an ecosystem, a predator and a prey. The model was developed independently by Lotka [9] and Volterra [14]. After that more realistic prey-predator models were introduced by Holling [7] suggesting three kinds of functional responses for different species to model the phenomena of predation. Lotka- Volterra prey-predator model is one of the fundamental population models describing the species competency interaction in a closed habitual. The food web models are more complex and intractable as compared to food chains as more complex multilevel interactions are possible in food webs. Relatively less attention has been given to the study of food webs and their rich complex dynamical behavior [1],[4],[5],[11]. The authors [6] examined the steady state condition stability analysis and other comparivitive studies of two logistic models such as exponential and quadratic in the population dynamics of host-parasite interaction they have been observed that in the presence of parasite affects the logistic growth dynamics in the host. In Ecology there are huge number of food chain models with three or more species with different functional responses such as Holling-Tanner type[12,13], Beddington- Deangelis type[10,15] and ratio dependent type[2,3]. But most of the models have same type of growth rate and same functional response. From biological point of view, it is unrealistic in nature. In fact in the real world, predators feed on different types of consumption ways. Hence in this paper we consider two types of functional responses, one the Holling type-II and other Bedding ton- De Angelis functional response. |
II. MATHEMATICAL MODEL |
| Consider a food web, comprising of two preys and one predator species. One of the prey species is harvested. The two prey species growing logistically and direct competition is considered between them. But they are apparent competition through the shared predation. Indeed, this apparent competition appears, as both prey types are included in predator’s diet. The mathematical model for the food web is given by the following system of equations, |
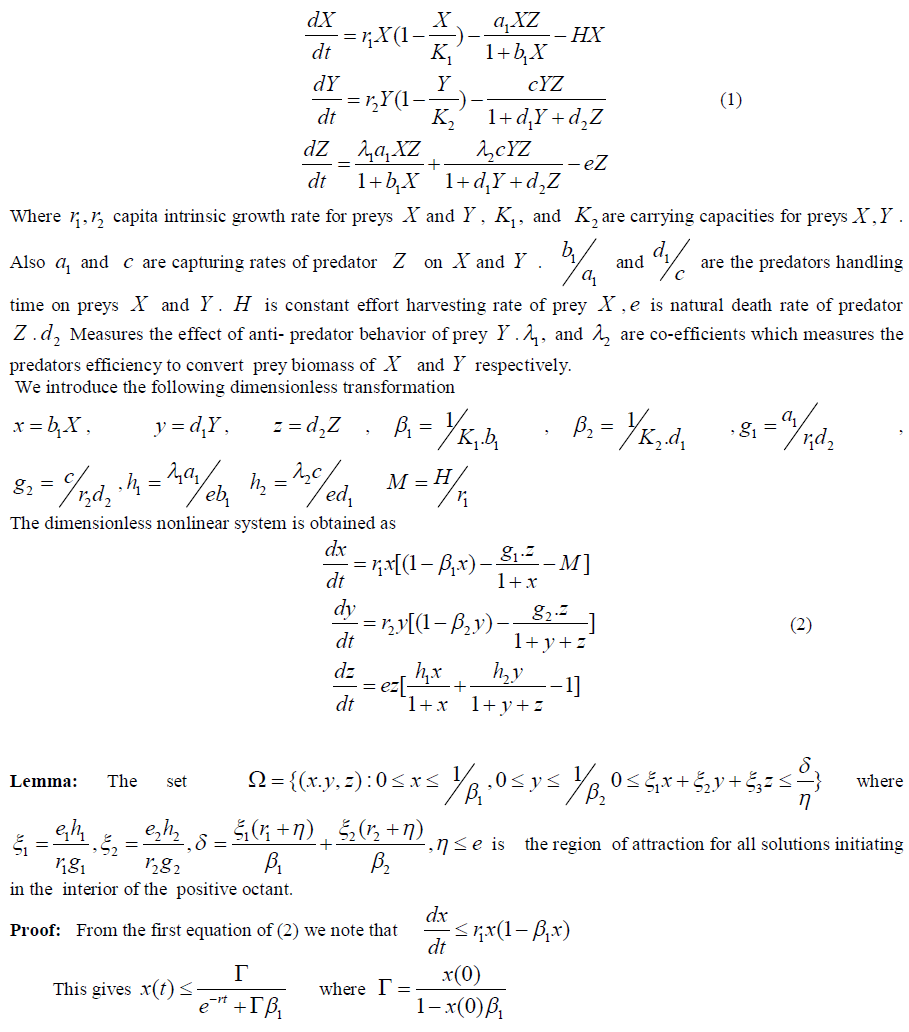 |
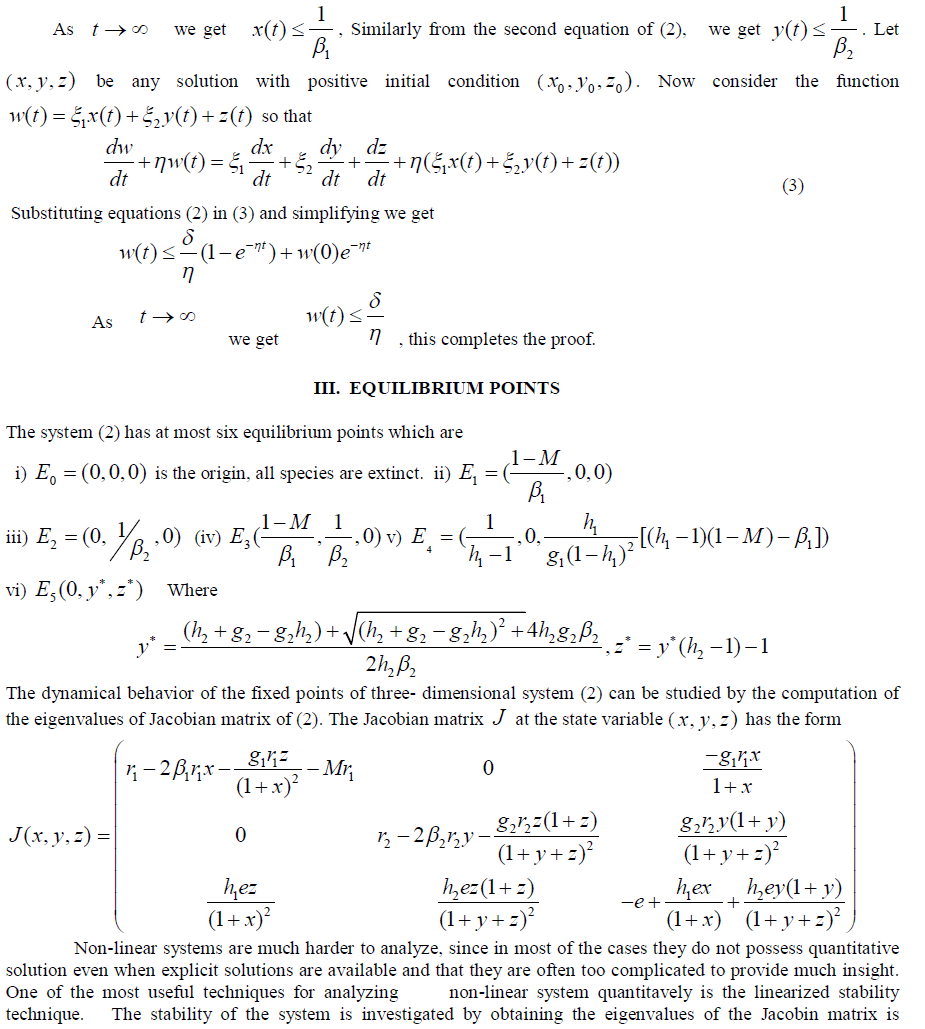 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
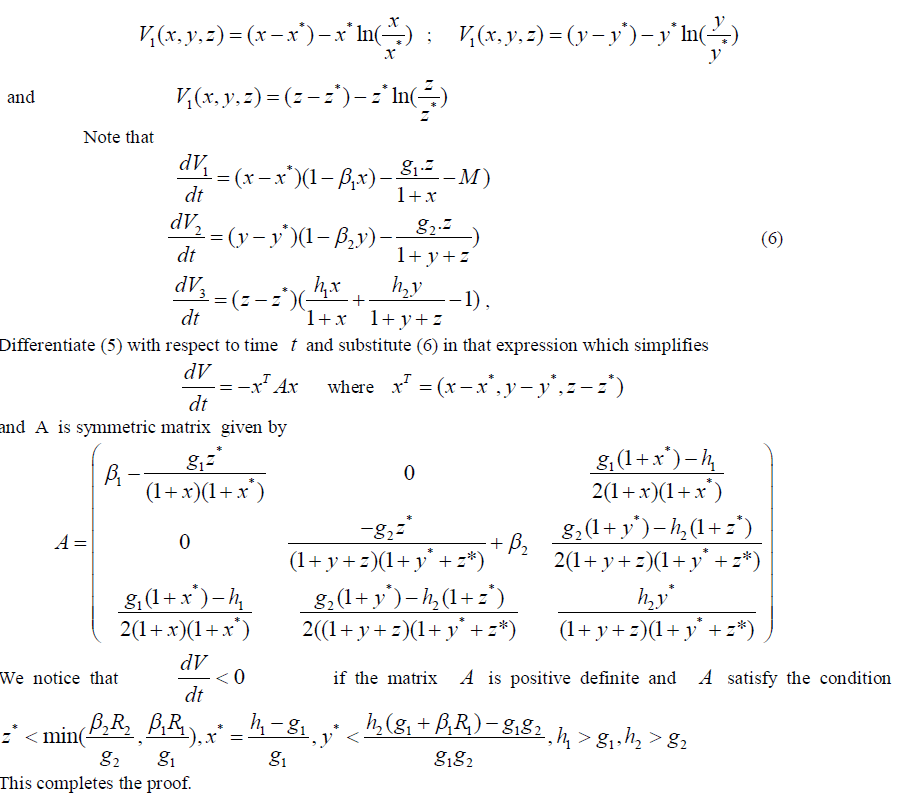 |
IV. CONCLUSION |
| The use of harvesting efforts as to control to obtain strategies for the control of prey-predator system with non- monotonic functional responses and it shows a method how to control a prey- predator system and drive the state either to equilibrium points or to a limit cycle [8]. In paper we analyzed the dynamical behavior of three species food web with two distinct functional responses of Beddington- Deangelis and Holling type-II functional responses. We also obtain the condition for existence of different equilibrium and discussed their stabilities in local and global manners by using stability theory of differential equations. Finally we investigated the dynamical behavior of the system consisting of two preys with different functional responses and a predator. We also studied the effect of harvesting on prey species. We concluded that harvesting is strong impact on the dynamics evaluation of population. To a certain extent it can control the long term stationary density of population efficiently. The local and global analyses were carried out at the end. |