ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
| Emad Shafiei M.A Student of Business Management, Islamic Azad University, Rasht Branch, Rasht, Iran |
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
International trade in recent decades has considerable growth, so that world trade of goods has exceeded 9 trillion U.S. dollars per year. It is evident that most conducted traded in this area is associated with monetary and financial system and many banks and financial institutions do financing the exchange of goods and services. Over the past years, we have been witness gradual development of integrated global economic system. After Second World War, international trade has faster growth so that in recent years world trade growth has been faster than world production. In the meantime, the share of developing countries in international trade has been more growing than total trade. Foreign trade and its relationship with economic growth is one of the highly controversial issues in particular, the choice of development strategies in developing countries and still there isn't accord among economists for how relationship between trade policies and economic growth. More economists believe that trade is the engine of development in modern societies. They claim that international trade creates possible of benefiting from the potential economic empowerment, according to available relative advantages and reveals clear signs for investment in the lucrative economic projects in the global arena. Also, international trade will be affected growth rate of the economy through access to foreign markets, technology and resources.
Keywords |
| International Trade, Economic Growth |
INTRODUCTION |
| International trade in recent decades has considerable growth, so that world trade of goods has exceeded 9 trillion U.S. dollars per year. It is evident that most conducted traded in this area is associated with monetary and financial system and many banks and financial institutions do financing the exchange of goods and services (11). Over the past years, we have been witness gradual development of integrated global economic system. Developing of science and technology in the various areas has followed different conditions of business in these years (13). On the one hand, communications development and widespread access of customer to information, has changed markets face and influenced their demands, on the other hand production based on advanced technology and improved methods provides possible of respond to the changing demands of customers. (8) |
II. THE PROCESS OF INTERNATIONAL TRADE |
| After Second World War, international trade has faster growth so that in recent years world trade growth has been faster than world production. In the meantime, the share of developing countries in international trade has been more growing than total trade (9). The international trade perch in the agenda all countries as one of the main components, widely and economic factors pressure and the tremendous growth communication technologies and telecommunications provided a new type of commercial relationships between different countries and regions of the world. Also product trade growth and foreign investment has increased the role of these factors in country's economic growth. (14) International economics argues about economic interdependence among countries. International economics deals to study the goods and services flow and payments of a country with other countries. (3) |
III. UNCONTROLLABLE FACTORS INTERNATIONAL ENVIRONMENT |
| The most important of uncontrollable factors international environment are as follows: |
| 1. Legal political Factors |
| 2. Cultural Factors |
| 3. Economic Factors |
| 4. Infrastructure, Technology, Competitors, Distribution System, etc (1) |
LITERATURE |
| Romer (1989) believes that trade liberalization makes domestic firms achieve to production factors large scale and lower costs which be caused transfer of the production function to the outside. Rodrik and Rodriguez (2000) found that lower barriers to trade policies (Less tariff and non-tariff barriers) be leads to economic growth. Edwards (1992) will analysis such countries that have adopted trade liberalization policies will accumulated global knowledge with faster growth and higher rates. Kavoussi (1984) showed that effects of export on the economic growth caused through primary exports in low-income countries and also through export factory in middle-income countries. (6) |
V. GLOBAL REGIONAL STRUCTURE OF THE INTERNATIONAL TRADE |
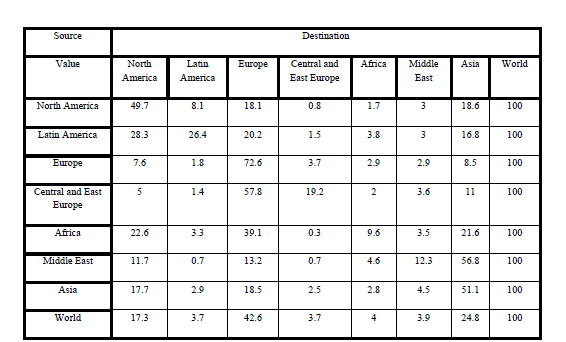 |
VI. INTERNATIONAL TRADE AND ECONOMIC GROWTH |
| Foreign trade and its relationship with economic growth is one of the highly controversial issues in particular, the choice of development strategies in developing countries and still there isn't accord among economists for how relationship between trade policies and economic growth. (2) More economists believe that trade is the engine of development in modern societies. They claim that international trade creates possible of benefiting from the potential economic empowerment, according to available relative advantages and reveals clear signs for investment in the lucrative economic projects in the global arena. Also, international trade will be affected growth rate of the economy through access to foreign markets, technology and resources. (7) |
VII. GROWTH OF TRADE IN EXPORT, IMPORT AND TRADE OF IRAN THROUGH INTERNATIONAL TRADE |
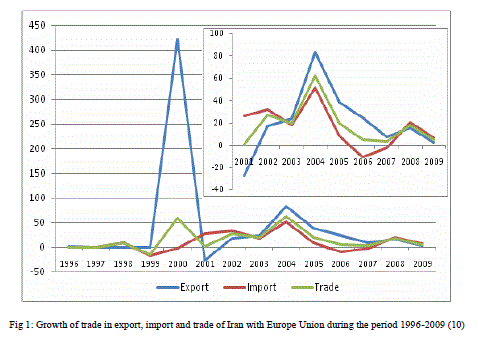 |
| For developing and less developed countries are defined four main strategies for economic structure healthy and strong: Import substitution strategy, export development strategy, balanced growth strategy, and unbalanced growth strategy (5). In these countries, trade policies placed in two distinct classes: |
| 1. Import Substitution: It is a way for economic development that placed in strategic framework of tendency to within or supportive approach. (15) |
| 2. Export Development: Export development policy is considered in policy framework of tendency to overseas. This policies show that nation how much have attention to foreign market and function its requirements. Guide of country that is type of succession politics export almost should move contrary to order import substitution. (4) |
VIII. CONCLUSIONS |
| International economics argues about economic interdependence among countries. International economics deals to study the goods and services flow and payments of a country with other countries. Foreign trade and its relationship with economic growth is one of the highly controversial issues in particular, the choice of development strategies in developing countries. |
| The most important of uncontrollable factors international environment are included legal political factors, cultural factors, economic factors, infrastructure, technology, competitors, distribution system, etc. |
| For developing and less developed countries are defined four main strategies for economic structure healthy and strong: Import substitution strategy, export development strategy, balanced growth strategy, and unbalanced growth strategy. In these countries, trade policies placed in two distinct classes import substitution, export development. Guide of country that is type of succession politics export almost should move contrary to order import substitution. |
References |
|