ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
M.M.Sahu1 and J.L.Bhagoria2
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
In the present paper an attempt has been made to review on thermal performance of solar air heater by using different roughness on absorber plate. The convective heat transfer coefficient of solar air heater is low due to the presence of viscous sub layer between the air and absorber plate. This can be improved by providing artificial roughness on the heat transferring surface. The thermal performance of solar air heater by providing artificial roughness on absorb plate by various investigators have been reviewed and presented
Keywords |
| Artificial Roughness, Heat Transfer Coefficient, Absorber Plate, Solar air heater |
INTRODUCTION |
| Solar air heaters are generally used for collecting solar energy which absorbs the incoming solar radiations, converting it into thermal energy at absorbing plates and transferring heat to fluid( air) flowing through the collector. Solar air heaters due to simplicity and low cost are most widely used collection devises. They are used for several applications such as space heating, crop drying etc.[1] The thermal efficiency of solar air heater is comparatively poor due to the low heat transfer coefficient between the absorber plates and flowing air. To make solar air heater more economical their thermal efficiency need to be improved by increasing their heat transfer coefficient [2]. The heat transfer coefficient of solar air heater can be enhanced by breaking the laminar sub layer formed on the vicinity of absorber plates. The use of artificial roughness on the surface of absorber plate is an effective technique to enhance the heat transfer between absorber plate and air flowing over it. The application of artificial roughness in the form of fine wires and ribs of different shapes has been recommended to enhance the heat transfer coefficient by several investigators [3]. The use of artificial roughness would also result in an increase in friction losses and hence greater power is required for pumping air through the duct. In order to keep the friction losses at a low level, the turbulence must be created only in the region very close to the surface. A number of investigations have been carried out on the heat transfer characteristics and friction of the absorber plate with different types of roughness element on it. |
VARIOUS ROUGHNESS USED BY INVESTIGATORS |
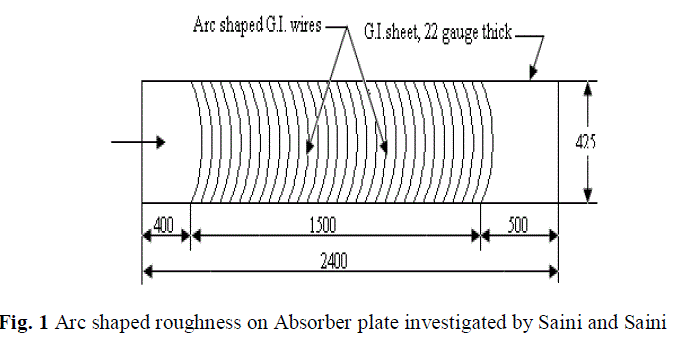
| Saini and Saini [4] investigate solar air heater having artificial roughness in the form of arc-shape parallel wire. The effect of system parameters such as relative roughness height (e/d) and arc angle (a/90) have been studied on Nusselt number (Nu) and friction factor (f) with Reynolds number (Re) varied from 2000 to 17000. The maximum enhancement in Nusselt number has been obtained as 3.80 times corresponding the relative arc angle (a/90) of 0.3333 at relative roughness height of 0.0422. However, the increment in friction factor corresponding to these parameters has been observed 1.75 times only. |
 |
 |
 |
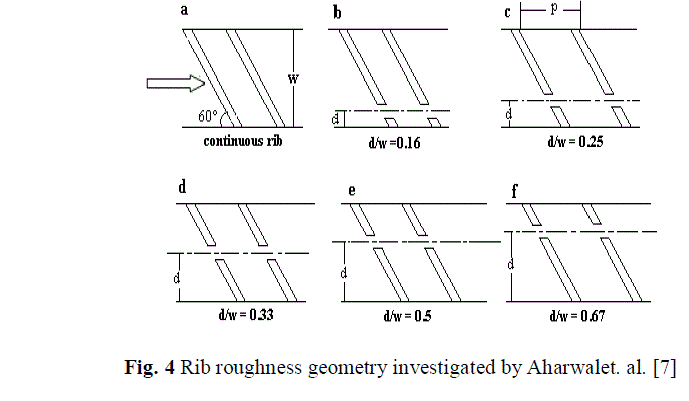
| Arvindkumaret. al.[11]carried out an experimental investigation to study the heat transfer and friction characteristics in solar air heater by using discrete W-shaped roughness on one broad wall of solar air heater with an aspect ratio of 8:1. the parameters used were Reynolds number(Re) range from 3000-15000, relative roughness height (e/Dh) in the range of 0.0168-0.0338, relative roughness pitch (p/e) 10 and the angle of attack (α) in the range of 30 o – 75 o. the maximum enhancement of nussult number and friction factor has been found to be 2.16 and 2.75 times that of smooth duct for an angle of attack of 60°. |
 |
CONCLUSION |
| It can be concluded from the present review that various type of artificial roughness of different shapes and sizes has been investigated and found that considerable enhancement in the heat transfer can be achieved with some increment of friction. |
References |
|