e-ISSN: 2319-9849
e-ISSN: 2319-9849
GRY Institute of Pharmacy, Vidya Vihar, Borawan, Khargone, Madhya Pradesh, India.
Received: 02 January 2014 Accepted: 22 January 2014 Published: 27 January 2014
Visit for more related articles at Research & Reviews: Journal of Chemistry
Thiosemicarbazide of phenyl hydrazine on cyclization with different aromatic carboxylic acid in POCl3 gives 2-(substituted phenyl)-5- (2-phenylhydrazinyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole. 1,3,4-thiadiazole constitute a unique class of nitrogen and sulphur containing five member heterocycle. During the last years considerable evidence has also accumulated to demonstrate the efficacy of 1,3,4-thiadiazole including antifungal , anti cancer, anticonvulsant , insecticidal, anti bacterial, anti inflammatory and other biological effects. All the compounds were characterized on the basis of IR and 1HNMR spectral data & were screened for antimicrobial activity.
Thiadiazole derivatives, synthesis, antimicrobial acivity
The progress achieved in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds with biological potential is due to improvement of the methodological study of tested substances too. It is known that many 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives have biological activity, with their antibacterial, antimycobacterial, antimycotic, antifungal, antidepressive and cardiotonic action being notable. Recent research has also established for these heterocycles an antimicrobial activity. Taking these data into account, in the present study, some new 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives having a phenylhydrazine moiety have been synthesized and their structure confirmed by elemental and spectral (FT-IR, 1H-NMR, MS) analyses [1-10].
Scheme
All melting points were determined on a Melt-Temp R apparatus equipped with a digital thermometer and are uncorrected. The IR spectra were measured as potassium bromide pellets on a Digilab Scimitar Series FT-IR Spectrophotometer; the wave numbers are given in cm-1. The 1H-NMR spectra were recorded in DMSO-d6 or CD3COCD3 solutions on Bruker ARX-300 spectrometer at ambient temperature. Chemical shifts were recorded as δ values in parts per millions (ppm) and were indirectly referenced to tetramethylsilane via residual solvent signal (2.49 for 1H). MS spectra were obtained using an instrument produced by Agilent Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA. The instrument, Accurate Mass Q-TOF LC/MS 6520 was operated via the manufacture’s software, Mass Hunter. Samples were dissolved in acetonitrile/water mixture (95/5 v/v) to obtain a concentration of 10 μg/mL and 0.05 mL were directly injected into the electrospray source using the auto sampler at a rate of 0.05 ml/min. The instrument was operated in High resolution mode with an acquisition rate of 4 GHz. The source voltage was set at 4,000 V, the spray gas flow at 5 L/min, heating gas temperature at 325 °C and the fragmentor potential at 215 V. All chemical reagents were obtained from the Aldrich Chemical Company.
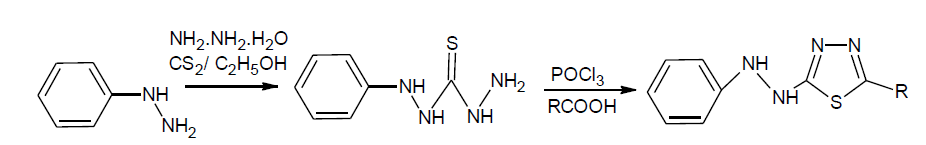
N’’-phenylthiocarbonohydrazide: phenylhydrazine (0.1 mol) was dissolve in ethanol (95%, 50ml) and ammonia solution 20 ml then CS2 (20 ml) was added slowly within 15 min with shaking and solution allow to stand for 1 hr. to it sodium chloroacetate (0.10 mol) and 50% hydrazine hydrate (20 ml)was added. The reaction mixture was warmed gently, filtered and evaporated to half of its volume and kept overnight. The solid thus obtained was filtered and purified by recrystallization from ethanol.
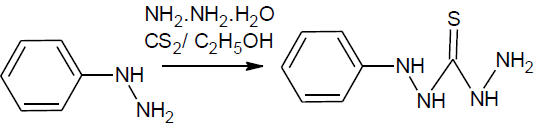
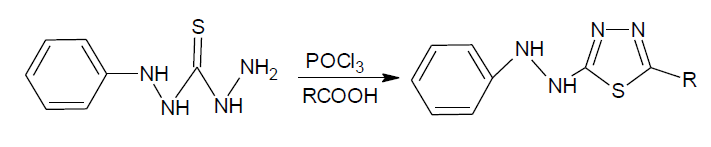
2-(substituted phenyl)-5-(2-phenylhydrazinyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole: a mixture of N’’-phenylthiocarbonohydrazide (0.10 mol), an aromatic acid and phosphorous oxychloride (25 ml) was refluxed for 18-22 hr. after cooling to RT the reaction mixture was poured into the crushed ice and kept overnight. The solid thus separated was filtered, washed with water, dried and purified by recrystallization from methanol.
Spectral Studies
1a IR (KBr):3360 (NH), 3030 cm-1 (CH), 1HNMR (DMSO-d6) : δ 7.35-7.90 (m, 10H, ArH) 8.32 (s, 2H, NH), MS m/z 268.077718 Da (M+), 269.085543 Da([M+1]+), 270.09 Da ([M+2]).1b IR (KBr):3340 (NH), 3036 (CH),750 cm-1 (C-Cl), 1HNMR (DMSO-d6) : δ 7.25-7.70 (m, 9H, ArH) 8.26 (s, 2H, NH), MS m/z: 302.038745 Da(M+),303.046571 Da(M+1), 304.04 Da(M+2). 1c IR (KBr): 3380 (NH), 3050 (CH), 755 cm-1 (C-Cl), 1HNMR (DMSO-d6) : δ 7.30-7.65 (m, 9H, ArH) 8.24 (s, 2H, NH), MS m/z: 335.999773 Da (M+),337.007598 Da (M+1), 338.04544 Da(M+2),1d IR (KBr): 3386 (NH), 3035 (CH), 1526 cm-1 (C-NO2), ), 1HNMR (DMSO-d6) : δ 7.54-7.70 (m, 9H, ArH) 8.36 (s, 2H, NH), MS m/z: 313.062796 Da (M+),314.070621 Da (M+1), 315.0346 Da(M+2), 1e IR (KBr): 3358 (NH), 3020 (CH), 1555 cm-1 (C-NH2), 1HNMR (DMSO-d6) : δ 7.48-7.56 (m, 9H, ArH) 8.36 (s, 2H, NH), MS m/z: 283.088617 Da (M+),283.089714 Da (M+1), 284.9824 Da(M+2),
All the compounds have been screened for antibacterial and antifungal properties using cup plate agar diffusion method by measuring zone of inhibition in mm. oflaxacin (50μg/ml) is used as a standard drug for antibacterial activity and ketoconazole (50μg/ml) as standard drug for antifungal activity. The compounds were screened for antibacterial activity against E.Coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aerugenosa in nutrient agar medium and for antifungal activity against A. niger and C. albicans sabourauds dextrose agar medium. These sterilized agar media is poured in to the Petri dish and allow to solidify. On the surface of the media microbial suspension were spread with the help of sterilized triangular loop. A stainless steel cylinder of 8 mm diameter (presterlized) was used to bore cavities. All the synthesized compounds (50μg/ml) were placed serially in the cavities with the help of micropipette and allow to diffuse for 1 hr. DMF was used as a solvent for all the compounds and as a control. These plates were incubated at 37 °C for 34 hr. and 28°c for 48 hr for antibacterial and antifungal activities. The zone of inhibition observed around the cups after respective incubation was measured and percentage inhibition of the compounds was calculated. The results are presented in table II and III.
The thiadiazole derivative 1c having 2,4-dichlorophenyl group showed potent activity against S. aureus (87.50%) where as compound 1c & 1d showed maximum inhibition against E.coli when compared with standard drug ofloxacin.the compound 1c having 2,4-dichlorophenyl group showed significant antibacterial activity (88.23, 87.50, 81.25 % inhibition.) against E.Coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aerugenosa respectively.
The thiadiazole derivative 1c having 2,4-dichlorophenyl group showed potent activity against S. aureus (87.50%) where as compound 1c & 1d showed maximum inhibition against E.coli when compared with standard drug ofloxacin.the compound 1c having 2,4-dichlorophenyl group showed significant antibacterial activity (88.23, 87.50, 81.25 % inhibition.) against E.Coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aerugenosa respectively.
The patern of the result of antifungal activity of test compounds was quite different from their antibacterial activity. The 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivative 1e having 4-aminophenyl group showed maximum inhibition (91.66%) against A.Niger whereas 1c having 2,4-dichlorophenyl group showed maximum inhibition (72.72%) against C.albicans.thus it is concluded that 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivative were most effective against all microorganism at the concentration of 50μg/ml.
Anti-microbial and antifungal study of newly synthesized compounds was performed using cup-plate method. The patern of the result of antifungal activity of test compounds was quite different from their antibacterial activity. The 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivative 1e having 4-aminophenyl group showed maximum inhibition (91.66%) against A.Niger whereas 1c having 2,4-dichlorophenyl group showed maximum inhibition (72.72%) against C.albicans. Thus it is concluded that 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivative were most effective against all microorganism at the concentration of 50μg/ml.
The authors would like to thank GRY institute of Pharmacy Borawan, and JNCET Borawan, Kahargone M.P.for providing the necessary research facilities.