ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
|
Bharthvajan R Assistant Professor, Bharath School of Business, Bharath University, Chennai – 600073, India |
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
Entrepreneurship serves as a catalyst of economic development of the country. It is one of the largest sections for capital accumulation. In fact economic growth is the result of the efforts taken by the entrepreneurs. Similarly entrepreneurs can dictate the economic growth by their actions and decisions. Now many have begun to realize that for achieving the goal of economic development, it is necessary to promote entrepreneurship both qualitatively and quantitatively in the country. Only active and enthusiastic entrepreneurs fully explore the potentialities of the country’s available resources – labour, technology and capital.
INTRODUCTION |
| In under developed economies the need of entrepreneurship is been recognized as the major factor of growth in an economy. As the number of entrepreneurs increasing in an economy the growth rate is high, reduction of employment and it also helps in the economic growth of the country. Entrepreneurship serves as a catalyst of economic development of the country. It is one of the largest sections for capital accumulation. In fact economic growth is the result of the efforts taken by the entrepreneurs. Similarly entrepreneurs can dictate the economic growth by their actions and decisions. Now many have begun to realize that for achieving the goal of economic development, it is necessary to promote entrepreneurship both qualitatively and quantitatively in the country. Only active and enthusiastic entrepreneurs fully explore the potentialities of the country’s available resources – labour, technology and capital. |
| Key Elements Of Entrepreneurship |
| Innovation |
| Risk Taking |
| ` Vision |
| Organizational skills |
| Women Entrepreneurs |
| Government of India has defined women entrepreneur is “ an enterprise owned and controlled by a women having a minimum financial interest of 51% of the capital and giving at least 51% of the employment generated in the enterprise to women”. |
| In most countries, regions and sectors, the majority of business owner/managers are male (from 65% to 75%). However, there is increasing evidence that more and more women are becoming interested in small business ownership and/or actually starting up in business. In addition, rates of self employment among women are increasing in several EU countries. Although there are no official statistics relating businesses to the gender of their owner/manager, there is a good deal of evidence to suggest a significant increase in female entrepreneurship. |
| According to the Women’s Financial Network, women start businesses at two times the rate of men. While women are starting more businesses than men, they find it harder at the outset to grow their businesses and access venture capital. Women entrepreneurs constitute 10 % of the number of entrepreneurs in our country. "All over the world there is a realization that the best way to tackle poverty and enable the community to improve its quality of life is through social mobilization of poor, especially women into self help groups. Ever since independence a number of innovative schemes have been launched for the upliftment of women in our country. Indian government has taken lot of initiatives to strengthen the institutional rural credit system and development programmes. Viewing it in the welfare programmes of Ninth Five Year Plan (1997-2002) and shifting the concept of Development to Empowerment. The Indian government adopted the approach of Self Help Groups (SHGs) to uplift the rural poor women. The empowerment of women through Self Help Groups (SHGs) would lead to benefits not only to the individual woman and women groups but also the families and community as a whole through collective action for development. Most women business owners in Indian organization were either housewives or fresh graduates with no previous experience of running a business, These women business owners were in traditionally women - oriented business like garments, beauty care, and fashion designing, which either do not require any formalized training or are developed from a hobby or an interest into a business, The classic example will be of herbal queen Lady Shehnaz Hussain who started her herbal-based treatment from a relatively small scale. Infact, she started literally from her kitchen domain to a chain of beauty parlors spread out across the nation and world. |
AIMS, OBJECTIVES AND METHODOLOGY |
| The main aim of the research was to identify the key issues and problems facing women entrepreneurs (i.e. women running their own businesses), co-entrepreneurs (i.e. female entrepreneurs assisting their spouses) and entrepreneurs from ethnic minorities,. It is a descriptive research work carried out by the researcher. Secondary data is the source for this study. |
| ROLE OF WOMEN ENTREPRENEURS |
 |
| Women has to play multiple roles |
| Sometimes she has to play the role of either wife or mother |
| Or she has to adorn the role of parents or daughter |
| Simultaneously in the social setting she has to play the different roles in community |
| Playing these roles, women sometimes submerged her own self role and her own real |
STATUS OF WOMEN ENTREPRENEURS |
| Since the 21st century, the status of women in India has been changing as a result to growing industrialization and urbanization, spasmodic mobility and social legislation. Over the years, more and more women are going in for higher education, technical and professional education and their proportion in the workforce has also been increased. With the spread of education and awareness, women have shifted from the kitchen, handicrafts and traditional cottage industries to non-traditional higher levels of activities. Even the government has laid special emphasis on the need for conducting special entrepreneurial training programs for women to enable them to start their own ventures. Financial institutions and banks have also set up special cells to assist women entrepreneurs, this has boomerang the women entrepreneurs on the economic scene in the recent years although many women's entrepreneurship enterprises are still remained a much neglected field. However, for women there are several handicaps to enter into and manage business ownership due to the deeply embedded traditional mindset and stringent values of the Indian society. Lets us look at what these obstacles that are faced by women entrepreneurs. |
BARRIERS FACED BY WOMEN ENTREPRENEURS |
| The problems and constraints experienced by women entrepreneurs have resulted in restricting and inhibited the expansion of women entrepreneurship. The major barriers encountered y women entrepreneurs are displayed in the chart. |
| 1. FINANCE |
| The majority of women business owners have had to rely to a significant extent on self generated finance during the start up period of their business. Bank loans and grants have only been used in a minority of cases and have usually been accompanied by some form of self generated finance. The availability of bank credit appears to increase once businesses become established and/or a good relationship with the bank has been developed. Banks are reported to have been more forthcoming in the provision of loans once a business has begun to demonstrate a track record. Because of limited funds, they are not able to stock new materials and spend on advertising. |
| Perceptions of specialist agencies of the main Problems facing women entrepreneurs |
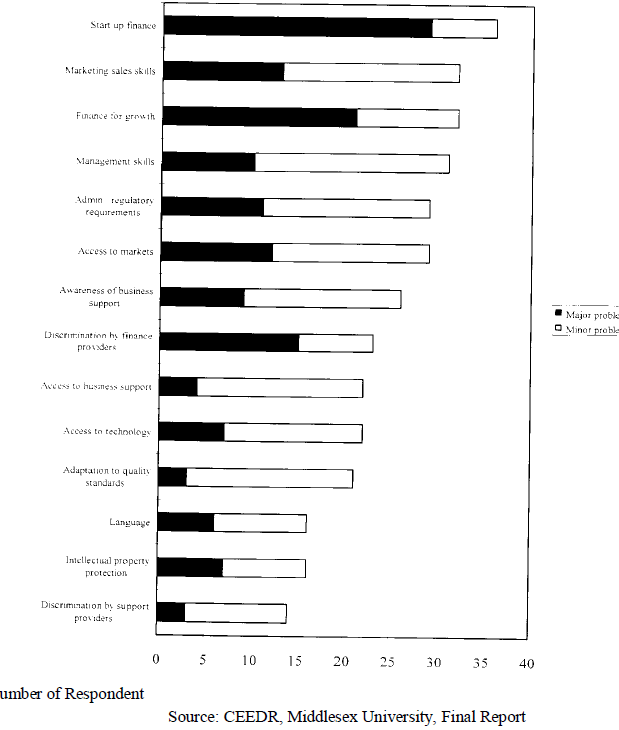 |
| 2. ADMINISTRATIVE AND REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS |
| Problems with administrative and/or regulatory requirements were judged to be major issues of female entrepreneurs. Micro enterprises of all types can experience problems in meeting administrative and regulatory requirements, because of the disproportionate effect of compliance costs on small companies compared with large firms. As a consequence, it is not surprising that almost half the support organizations specializing in support for female entrepreneurs identified a problem for their clients in this respect. At the same time, with a few exceptions, administrative and regulatory barriers more significant for female owned businesses than for male owned firms of a similar size. |
| 3. LACK OF MANAGEMENT SKILLS OR TRAINING |
| Women entrepreneurs lacked management skills to a greater extent than small businesses in general, perhaps because of their lower propensity to have had previous business experience Although difficulties in accessing business advice or support appears to be a minor rather than major problem for women entrepreneurs, a significant minority of specialist organizations felt than women are particularly disadvantaged in this respect. Difficulties with language caused problems for their clients or members, with five feeling that women faced specific difficulties in this respect. |
| 4. MARKETING |
| A lack of sales and marketing skills was the most commonly reported problem faced by female entrepreneurs, after finance. The fact that this is a characteristic shared with many other micro enterprises and small firms does not make it any less important to female entrepreneurs. It may be seen as part of a general need to raise the level of management skills and competencies in female owned and other small businesses. |
| 5 TECHNOLOGY |
| Access to technology and problems with intellectual property protection were regarded as problems for women entrepreneurs. The lack of computer knowledge of employees is a major problem as computer skills are a key part of the business. Another firm used computer extensively for word processing, desk top publishing, e-mail and research purposes but saw no value in increasing their use further. |
| 6. LACK OF CONFIDENCE |
| As women are accepting a subordinate status, as a result they lack confidence of their own capabilities, Even at home, family members do not have much faith in women possessing the abilities of decision-making. |
| 7. LACK OF WORKING CAPITAL |
| To be women and to do something on their own becomes quite difficult for them because of lack of access to funds as women do not possess any tangible security and credit in the market. Before marriage she has to depend on father and after marriage she has to follow the footsteps of the husband. As such, women do not enjoy the right over the property of any form and they have limited access over external sources of funds, even getting loans from either a bank or financial institution becomes exceedingly difficult. |
| 8. LIMITED MOBILITY |
| Due to primary household responsibilities towards her family, her time gets divided between the two worlds. She has restricted timings for work due to which, she is not in a position to travel frequently and be away for longer periods. Thus, her mobility is restricted. This also has an implication on business. |
| 9. MALE DOMINATED SOCIETY |
| A woman is dominated by men in her family as well as business. Often she has to obtain permission from men for almost everything. They are not treated as equals. Her freedom is restricted. She always has to consult and get approval of men. |
| 10. LOW RISK BEARING ABILITY |
| This is so because right from the childhood, her parents take decisions for her and after marriage her husband takes over. She is protected throughout and thus the risk bearing ability gets reduced. |
| 11. SOCIO-CULTURAL BARRIERS |
| Woman has to perform multiple roles be it familial or social irrespective of her career as working woman or an entrepreneur. In our society, more importance is being given to male child as compared to female child. This mindset results in lack of schooling and necessary training for women. As a result this impediments the progress of women and handicap them in the world of work. |
SUGGESTIONS |
| Women entrepreneurs also explored their perceptions of the types of support that might be most helpful for them in addressing the issues and problems that they are facing. |
| Financial Aspects: Special schemes should be implemented whereby women can get bank loans at decent conditions |
| Childcare: More childcare facilities should be provided to fit women entrepreneurs’ needs. This would entail extended opening hours or flexible opening hours according to the woman entrepreneur’s needs. Alternatively measures should be taken for fathers to be in the position to take parental leave, and men should be encouraged to take the leave. |
| Household: It should be made easier for women entrepreneurs to get help for their households, and initiatives like the “cheques services” implemented by the Belgian government should be copied. This system would alleviate the work load of the female entrepreneurs and at the same time decrease the number of unemployed persons. |
| Working time: Self-employed women should be encouraged to employ on a part-time or full-time basis at least one person so that they have more time for their family and can take interest in other occupations, actively participate in decision-making bodies. |
| Training, advice or consultancy targeted solely or mainly at women entrepreneurs |
| Start up programmes for women, particularly those returning to the labour market. |
| Special targeting of women in general campaigns to boost levels of entrepreneurship. |
| Equal opportunities policies aiming for equal access for women to services. |
| Need to have network with other firms to generate business and access informal advice. |
| Encouraging and assisting relevant business support initiatives |
| Wild Women Entrepreneurs (Wild WE), the leading networking organization for women entrepreneurs, announced today that the organization has entered into a partnership with Ready Talk to help area women enhance their professional development without restrictions.. It is also found that compared to men, women were less concerned with making money and often choose business proprietorship as a result of career dissatisfaction. Secondly, women find entrepreneurship as a tool of meeting their career needs and childcare role. |
CONCLUSIONS |
| In most countries, regions and sectors, the majority of business owner/managers are male (from 65% to 75%). However, there is increasing evidence that more and more women are becoming interested in small business ownership and/or actually starting up in business. Women are working in this multifaceted world. The organization scenario changes like a kaleidoscope with every responsibility, accountability and multiple pulls and pushes, which women have faced and came out with success. In addition, rates of self employment among women are increasing in several countries. Although there are no official statistics relating businesses to the gender of their owner/manager, there is a good deal of evidence to suggest a significant increase in female entrepreneurship. One consequence of this is that women are a relatively new group of entrepreneurs compared with men, which means that they are more likely to run younger businesses. This in turn has some implications for the problems they face and their ability to deal with them. |