Micro strip antennas (MSA) in antenna technology appeared relatively late, but in recent years has been a very large development of the design of these antennas and the huge interest in their capabilities. MSA has more advantages and better prospects. This paper describes various excitation techniques and performance of different parameters. Performance of the antenna mainly depends on the dielectric constant or permittivity of a substrate .The substrate which has a low dielectric constant will give better performance than the substrate which has a high dielectric constant. Loss tangent or dissipation factor also plays a part in antenna performance. Substrate materials play an important role in antenna design, production and finished product performance This survey suggest dielectric material like Air, RTduroid, Benzocyclobuten and Taconic TLC can be used to fabricate micro strip patch antenna in order to give better performance.
Keywords |
| Micro strip antenna, Feeding techniques, Dielectric substrate, Permittivity |
INTRODUCTION |
| Although the field of antenna engineering has a history over years it still remains as described in [2] “a vibrant field
which is bursting with activity, and is likely to remain so in the foreseeable future.” The statement has relevance even
now. The scope of antenna design moves into new pastures of technology. An antenna is the primary component in a
wireless communication system. Antenna is a transducer designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic waves. When
a signal is fed into an antenna, the antenna will emit radiation distributed in space in a certain way.There are different
types of antenna and depending upon the applications, the properties of an antenna including physical structure varies.
Every system demands for compact and efficient components to be embedded with it. Micro strip patch antenna is such
a component which is so popular by its compact size particularly in the frequency range of 1 to 6 GHz. |
MICROSTRIP PATCH ANTENNA |
| The concept of the Micro strip antenna (MSA) was first proposed in 1953 by Deschamps. However, practical antennas
were developed by Munson and Howell in the 1970s. Often micro strip antennas are also referred to as micro strip
patch antennas, or simply patch antennas. The unique property of the micro strip patch antenna is its two- dimensional
structure [3].Micro strip antennas have several advantages over conventional microwave antenna and therefore are
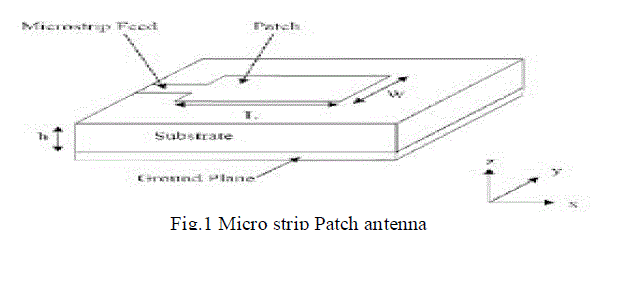
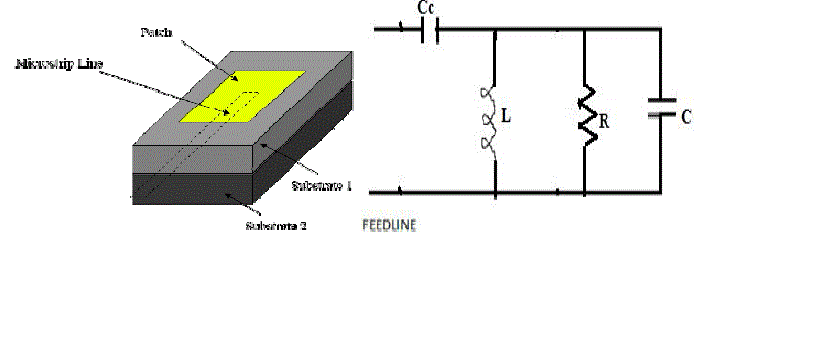
widely used in many practical applications. Micro strip antennas in its simplest configuration are shown in Fig1. |
| It consists of a radiating patch on one side of dielectric substrate (Єr≤10), which has a ground plane on other side. A
micro strip patch antenna (MSA) consists of a conducting patch of any planar or nonplanar geometry on one side of a
dielectric substrate with a ground plane on other side. It is a popular printed resonant antenna for narrow-band
microwave wireless links that require semi-hemispherical coverage. Due to its planar configuration and ease of
integration with micro strip technology, the micro strip patch antenna has been heavily studied and is often used as
elements for an array. The rectangular and circular patches are the basic and most commonly used micro strip antennas.
These patches are used for the simplest and the most demanding applications. Rectangular geometries are separable in
nature and their analysis is also simple. The circular patch antenna has the advantage of their radiation. |
| Micro strip antennas are characterized by a larger number of physical parameters than conventional microwave
antennas. They can be designed to have many geometrical shapes and dimensions [4]. All micro strip antennas can be
divided into four basic categories: |
| 1. Printed slot antennas |
| 2. Micro strip dipoles |
| 3. Micro strip patch antennas |
| 4. Micro strip Travelling-wave antennas |
Characteristics of Patch: |
| The following Table 1. Show the characteristics of the different micro strip antennas. |
ANALYSIS OF EXCITATION TECHNIQUES. |
| Excitation techniques are also commonly known as Feeding methods. Feeding of the micro strip patch antennas can be
done by a variety of methods. These methods can be classified into two categories- contacting and non-contacting. In
the contacting method, the RF power is fed directly to the radiating patch using a connecting element such as a micro
strip line. In the non-contacting scheme, electromagnetic field coupling is done to transfer power between the micro
strip line and the radiating patch. The four most popular feed techniques used are the micro strip line, coaxial probe;
both contacting schemes; aperture coupling and proximity coupling; both non-contacting schemes[1]. |
Micro strip Line Feed |
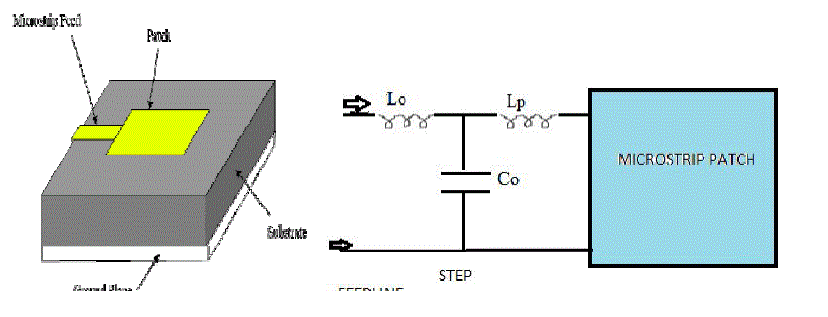
| In this type of feed technique, a conducting strip is connected directly to the edge of the Micro strip patch as shown in
Fig.3.1. The conducting strip is smaller in width compared to the patch. This kind of arrangement has the advantage of
the feed can be etched on the same substrate to provide a planar structure. |
| The purpose of the inset cut in the patch is to match the impedance of the feed line to the patch without the need for any
additional matching element. This can be achieved by properly controlling the inset position. Hence this is an easy
feeding scheme, since it provides ease of fabrication and simplicity in modeling as well as impedance matching.
However as the thickness of the dielectric substrate being used, increases, surface waves and spurious feed radiation
also increases, which hampers the bandwidth of the antenna. The feed radiation also leads to undesired cross polarized
radiation. |
Coaxial Feed |
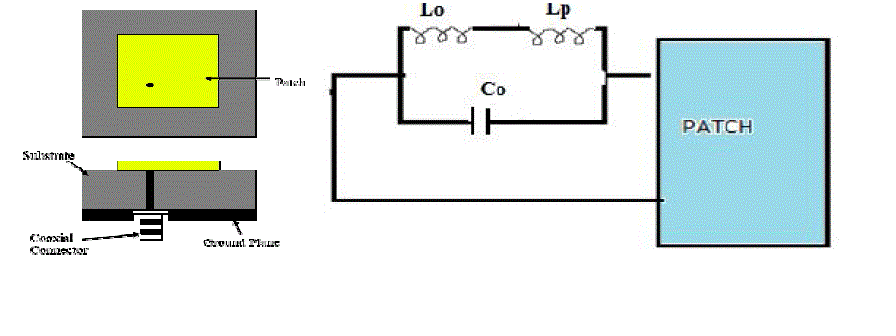
| The Coaxial feed or probe feed is a very common technique used for feeding micro strip patch antennas. As seen from
Fig.3.2, the inner conductor of the coaxial connector extends through the dielectric and is soldered to the radiating
patch, while the outer conductor is connected to the ground plane. |
| The main advantage of this type of feeding scheme is that the feed can be placed at any desired location inside the
patch in order to match with its input impedance. This feed method is easy to fabricate and has low spurious radiation.
However, a major disadvantage is that it provides narrow bandwidth and is difficult to model since a hole has to be
drilled in the substrate and the connector protrudes outside the ground plane, thus not making it completely planar for
thick substrates (h> 0.02λ). Also, for thicker substrates, the increased probe length makes the input impedance more
inductive, leading to matching problems. It is seen above that for a thick dielectric substrate, which provides broad
bandwidth, the micro strip line feed and the coaxial feed suffer from numerous disadvantages. The non-contacting feed
techniques which have been discussed below, solve these issues. |
Aperture Coupled Feed |
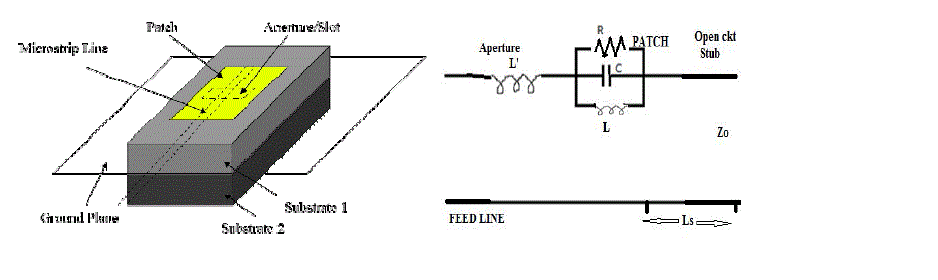
| In this type of feed technique, the radiating patch and the micro strip feed line are separated by the ground plane as
shown in Fig.3.3. Coupling between the patch and the feed line is made through a slot or an aperture in the ground |
| The coupling aperture is usually centered under the patch, leading to lower cross polarization due to symmetry of the
configuration. The amount of coupling from the feed line to the patch is determined by the shape, size and location of
the aperture. Since the ground plane separates the patch and the feed line, spurious radiation is minimized. Generally, a
high dielectric material is used for bottom substrate and a thick, low dielectric constant material is used for the top
substrate to optimize radiation from the patch. The major disadvantage of this feed technique is that it is difficult to
fabricate due to multiple layers, which also increases the antenna thickness. This feeding scheme also provides narrow
bandwidth. |
Proximity Coupled Feed |
| This type of feed technique is also called as the electromagnetic coupling scheme. As shown in Figure3.4, two
dielectric substrates are used such that the feed line is between the two substrates and the radiating patch is on top of
the upper substrate. The main advantage of this feed technique is that it eliminates spurious feed radiation and provides
very high bandwidth (as high as 13%), due to overall increase in the thickness of the micro strip patch antenna. This
scheme also provides choices between two different dielectric media, one for the patch and one for the feed line to
optimize the individual performances. |
| Matching can be achieved by controlling the length of the feed line and the width to- line ratio of the patch. The major
disadvantage of this feed scheme is that it is difficult to fabricate because of the two dielectric layers which need proper
alignment. Also, there is an increase in the overall thickness of the antenna. |
COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT EXCITATION TECHNIQUES |
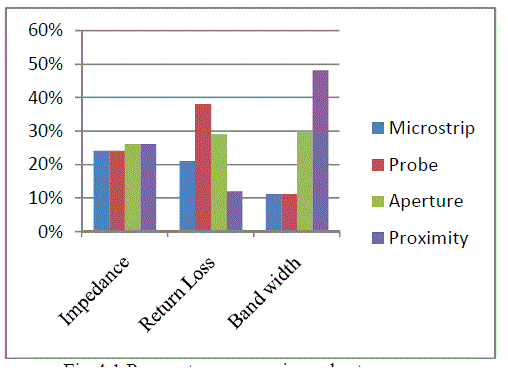
| A micro strip patch antenna excited by different excitation techniques gives different bandwidth, different gain and
different efficiency etc. We can obtain the approximate result of Return Loss, Bandwidth and Impedance of all feeding
techniques .Those feeding techniques are Micro strip Line, Probe, Proximity and Aperture which describe the
comparison of Return Loss, Bandwidth and Impedance .These feeding techniques are given below in Table 2. |
| The maximum bandwidth can be achieved by Proximity feed coupling and also it eliminates spurious feed radiation.
Both Proximity feed coupling and Aperture feed coupling gives the best impedance matching and radiation
efficiency.Typically matching is performed by controlling the width of the feed line and the length of the slot. |
DIELECTRIC SUBSTRATES |
| Substrate materials play an important role in antenna design, production and finished product performance. A simple
method that can be employed to modify the different properties of the antenna is by changing the substrate; as height
and dielectric constant of the substrate influence the antenna properties. The substrate in microstrip antenna is primarily
required for giving mechanical strength to antenna [4]. An intelligent decision has to be taken while selecting a substrate so as to satisfy both electrical and mechanical requirement for the antenna. Some properties of different
dielectric substrates are |
| The substrate properties that are taken into consideration while selecting a dielectric include: dielectric constant and
loss tangent and their variation with temperature and frequency, homogeneity, dimensional stability with processing
and temperature, humidity and aging. |
CONCLUSION |
| Micro strip patch antennas are used for many applications, especially in wireless communication and in satellite
communication. The MSA has proved to be an excellent radiator .Performance of bandwidth can be enhanced for MSA
by choosing low permittivity dielectric material because bandwidth is inversely proportional to permittivity. This
survey suggest dielectric material like air, RTduroid, Benzocyclobuten and Taconic TLC can be used to fabricate micro
strip patch antenna in order to give better performance. |
Tables at a glance |
|
|
| |
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 4 |
Figure 5 |
Figure 6 |
|
| |
References |
- Balanis C.A., ?Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design?, John Wiley &Sons, Inc, 1997.
- David M. Pozar, ?Micro strip Antennas?, Proceedings of the IEEE, Vol. 80, No 1, pp. 79-91, January 1992.
- Gary Breed, ?The Fundamentals of Patch Antenna Design and Performance?, High Frequency Electronics, pp. 48-51, March 2009.
- Ramesh Garg, PrakashBartia, InderBahl, ApisakIttipiboon, ??Micro strip Antenna Design Handbook??, 2001, pp 1-68, 253-316 .
- R. Yang, Y. Xie, P. Wang and L. Li, ?Micro strip Antennas with Left-Handed Materials Substrates,? Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications,
- F. Yang and Y. S. Rahmat, ?Electromagnetic Band Gap Structures in Antenna Engineering,? Press Cambridge, New York, 2008.
- Jian-X. Zheng, ?Electromagnetic Simulation of Micro strip Patch Antennas?, 1994 ,IEEE.
|