In case of private cloud environment access is limited to a group of users or an organization. Even though there are many aspects in cloud environment. The data security, confidentiality and privacy play a major role in cloud deployment model. In private cloud the identity and secured data storage becomes essential to address. In this paper, a frame work double authentication techniques and specialized procedures is proposed that can efficiently protect the data from the beginning to the end, i.e., from the owner to the cloud and then to the user. A method for Access, identity and secure data storage in private cloud using DS (Digital Signature) is proposed and implemented.
Keywords |
| Digital Signature, RSA, Encryption, Authentication |
INTRODUCTION |
| Cloud computing is the best solution for providing a flexible, on-demand, and dynamically scalable computing
infrastructure for many applications. Adoption of cloud computing is clearly a strategic direction for many companies.
The convergence of inexpensive computing, pervasive mobility, and virtualization technologies has created a platform
for more agile and cost-effective business applications and IT infrastructure. In case of private cloud environment
access is limited to a group of users or an organization [2]. Even though there are many aspects in cloud environment.
The data security, confidentiality and privacy play a major role in cloud deployment model. [2][3][4]. In private cloud
the Access, Identity and secured data storage becomes essential to address. [2]. |
| The proposed model has been structured by bringing together various techniques and utilizing them to perform the
task of data security in cloud. This combination of diverse methods operate as a wall stood together against the security
challenges, which have been constantly creating the loop holes in the efficient functioning and growth of the cloud.
This model is described in such a way that it provides a complete view of processing the data at different levels. The
model uses Double authentication process to get access to the cloud. It uses Digital Certificates as the main
fundamental protection scheme. Encryption is the conversion of data into encrypted form called a cipher text that
cannot be easily understood by unauthorized person and can be decrypted by the authorized person having a valid
decryption key. Apart from this, the model positively handles the security issues by employing strict authentication
parameters, like login-id and password. Thus all these parameters result into a defined mechanism that encourages the
proper functioning of cloud computing. In this computing model, owner sends the encrypted data to cloud where it is
stored in different sections depending on the sensitivity rating and then the data can be retrieved by user from the cloud
when requested. However, this is achievable only after passing the authentication parameters [9]. |
| This paper is structured as follow: Section 2 summarizes the related work for security of data. In Section 3, a
model is proposed which is designed to solve the security issue of cloud computing. Section 4 provides the security
analysis of the designed model. Section 5 compares functionality of proposed model with other security models.
Section 6 shows the evaluation procedure and Section 7 concludes this paper. |
RELATED WORK |
| The cloud is a terminology with a long history in telephony, which has in the past decade, been adopted as a metaphor
for internet based services, with a common depiction in network diagrams as a cloud outline. The underlying concept
dates back to 1960 when John McCarthy opinion that ‘‘Computation may someday be organized as a public utility’’;
indeed it shares characteristics with service bureaus which date back to the 1960s. The term cloud had already come into commercial use in the early1990s to refer to large Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networks. By the turn of
the 21st century, the term ‘‘cloud computing’’ had started to appear, although major focus at this time was on Software
as a Service (SaaS). In 1999, sales-force.com was established by Marc Benioff, Parker Harris. They applied many
technologies of consumer web sites like Google and Yahoo! to business applications. They also provided the concept of
‘‘on demand’’ and ‘‘SaaS’’ with their real business and successful customers. IBM extended these concepts in 2001, as
detailed in the Autonomic Computing Manifesto, which describes advanced automation techniques such as selfmonitoring,
self-healing, self-configuring and self-optimizing in the management of complex IT systems with
heterogeneous storage, servers, applications, networks, security mechanisms and other system elements that can be
virtualized across an enterprise. Amazon.com played a key role in the development of cloud computing by modernizing
their data centers. It found that the new cloud architecture resulted in significant internal efficiency improvements and
providing access to their systems by way of Amazon Web Services in 2005 on a utility computing basis. 2007 saw
increased activity with Google, IBM and a number of universities embarking on a large scale cloud computing research
project, around the time the term started gaining popularity in the mainstream press. In August 2008, Gartner Research
observed that ‘‘organizations are switching from company-owned hardware and software assets to per-use servicebased
models’’. The projected shift to cloud computing will result in dramatic growth in IT products in some areas and
in significant reductions in other areas. Despite all the hope of gaining maximum advantage from this cloud computing,
it seems to have born with security and management concerns, which time to time hinders its growth. For this, lot of
research work has been done to secure the data in cloud computing (primary concern) from every perspective, but
everything seems to face a new challenge as soon as it is employed. |
PROPOSED MODEL |
| Proposed framework has been structured to provide complete security to the data throughout the entire process of cloud
computing, be it in cloud or in transit. We use the Double authentication method (Login/Password, and Digital
Signature) for providing the security. Thus, multiple mechanisms and available techniques are applied to shield the
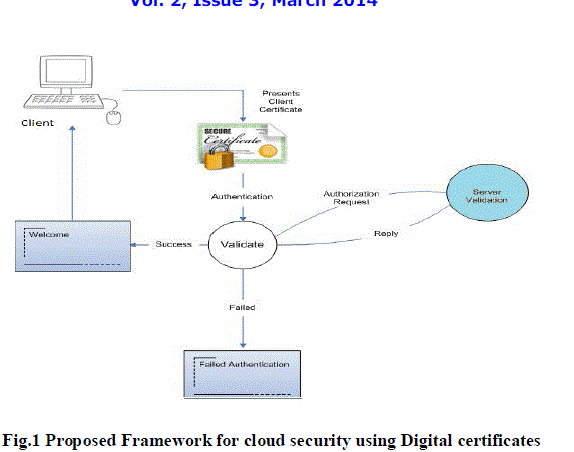
critical information from unauthorized parties. The proposed frame work is shown below in Fig. |
| • Phase 1(Authorization Request) |
| The user has to get the authority from the Admin of the cloud. The cloud Admin will provide a login id and
password to access the cloud. |
| • Phase 2(Authentication and Validation) |
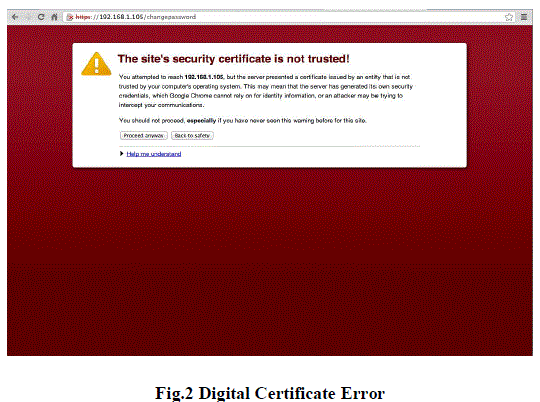
| • Once the user filled the login details, it will be asked for the security certificates. |
| • If the certificate is not install at the client machine, the following security error will occur as shown below in
fig 2 |
| • To overcome the problem client has to install the security certificates. |
| • The certificates will be imported from the Trusted Root Certificate directory of the cloud. |
| • Now the certificate has to be installed on client machine. |
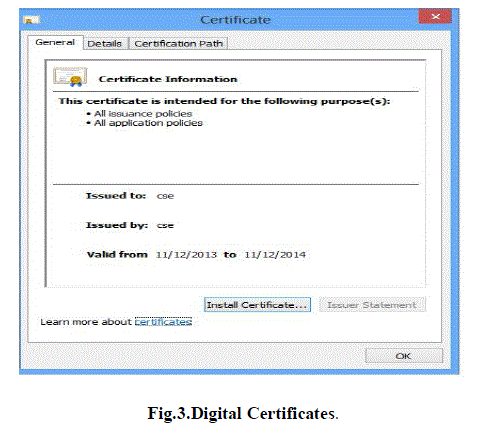
| • When the client will login after installation of the certificate, the access to the cloud will be provided without |
| security error. The security certificate created by us is shown below in Fig.3. |
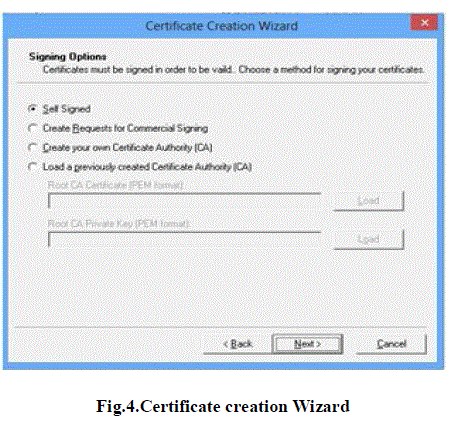
| We have used the basic SSL utilities provided to create the certificates. The certificates creation wizard is shown
below In Fig. [4, 5]. |
| The algorithm used for creating certificates is RSA. The Key size is 2048. |
| RSA Algorithm |
| • Select two large prime numbers a and b. |
| • Compute n=a*b. The computed n is made public |
| • Now compute f(n) = (a-1) * (b-1) |
| • Choose a random number ‘e’ as the public key in the range 1< e < f(n) such that GCD
(e, f(n)) = 1. |
| • Find private key d such that d = e -1 mod f (n), where d and f(n) are mutually prime. |
| Encryption |
| 1. Consider the user A that needs to send a message to B in a secured manner using RSA algorithm |
| 2. Now e is B’s public key. Since e is public, A is allowed access to e. |
| 3. For encryption the message M of A which is in the range 0<M<n is converted to cipher |
| 4. Where the Cipher text C = M e mod n. |
| Decryption |
| • Now the cipher text C is sent to B from A. |
| • User B calculates the Message with its private key ȕ, where message M = C b mod n. |
SECURITY ANALYSIS |
| Digital certificates are an essential part of the foundation that enables secure digital communications, providing
secure access to data, applications and cloud infrastructures. Digital certificates are an established, standards-based
method to enhance trust over vulnerable networks. They are the digital equivalent of a driver’s license or any other
form of identity issued by a trusted third party in the physical world. Just as physical IDs ensure trust in the real world,
digital certificates ensure trust across the Internet and within private networks, allowing parties to use digital identities
to authenticate to each other and subsequently secure transactions and communication between their servers, systems,
machines and users in enterprise and cloud environments. |
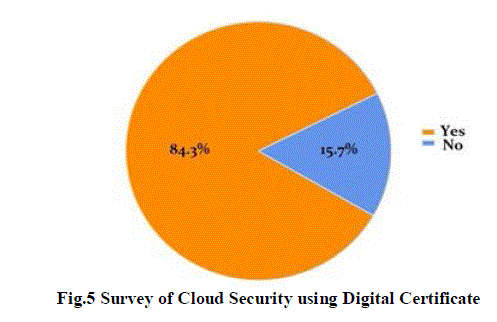
| Recently conducted a survey of enterprise IT professionals on the advantages of using a SaaS CA versus an
internal CA such as Microsoft Certificate Services. It found that an overwhelming 84 percent of the professionals
surveyed use digital certificates to secure applications accessed by internal and external digital identities, and that many
of these companies utilize both internal and third-party certificates (Fig 5). The following are key findings of the survey
and show how enterprises use CAs to ensure trusted communications. |
| The analysis of the proposed model for security of data through-out the whole traversing into this cloud computing
paradigm comes up with the following mentioned steps where data can be very vulnerable to threats like data leakage,
modification, privacy of users and confidentiality etc. The proposed model is designed to tackle all these security issues
very efficiently. |
UNAUTHORIZED USER |
| As the data needs to be transmitted over a network to the cloud, there are numerous means through which an
attacker can easily get into the internet based network and act as a cloud server to the owner of data, hence resulting
into the loss of data. To prevent the loss of data in this situation, SSL certification in this model is used. Certificate
Authorities (CAs) issue each certificate, which is a credential for the online world, to only one specific domain or
server. The cloud server first sends the identification information to the owner when it connects then sends the owner a
copy of its SSL Certificate. The owner verifies the certificate and then sends a message to the server and the server
sends back a digitally signed acknowledgement to start an SSL encrypted session, enabling encrypted data transfer
between the browser and the server. Moreover, the data are stored on the cloud in encrypted form [3]. |
BRUTE FORCE ATTACK |
| The data while in transmission to cloud over an internet network can be attacked by various unauthorized
interceptors. Since SSL offers encryption that prevents interceptors from reading data traversing the cloud. it is not
difficult to crack using today’s computers which can crunch large number combinations quickly in order to determine
every possible key in an effort known as a brute force attack. Thus, in proposed model we are using 128-bit SSL
encryption which provides more bits of key length than the previous one SSL (40 bit) and also can be shifted to 256-bit
whenever required. 128-bit SSL is complex enough to make a brute force attack mostly useless at this time. The
proposed model uses strongest encryption, being done by owner and other using SSL. The processing power needed,
among other things, would render most attackers ineffective. Hence this approach not only safeguards data where it
lives, but also helps assure customers that data is secure while in transit[1][7]. |
FUNCTIONALITY ANALYSIS |
| An efficient cloud data security model should be able to overcome all the possible issues of cloud computing, so as
to provide the benefits of cloud computing to reach its maximum heights and propel in the direction it is designed for,
by preventing the owner’s data from all the risks associated. Table 2 shows the comparison of the proposed model with
other data security models. |
EXPERIMENTAL RESULT |
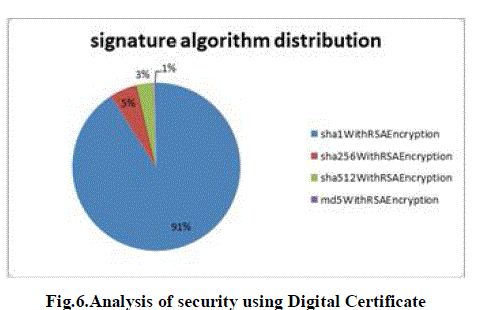
| The proposed technique is analyzed with respect to implementation. This model is tested on a private cloud using
Windows server 2012 essential. Fig.6 shows that the status of security after implementation of security parameters
namely Digital certificates using RSA and sha1, Security and Encryption technique. Overall, the security of data related
to owner is very good. It results in very good security of the proposed model. |
CONCLUSION |
| The proposed technique provides a way to protect the data, check the integrity and authentication by following the
best possible industry mechanisms. It introduces encryption, authentication of user by owner and other by cloud and
verification of digital signature of the owner. Proposed method achieves the availability, reliability and integrity of
data traversing through owner to cloud and cloud to user. The solution, presents a horizontal level of service, available
to all implicated entities, that realizes a security mesh through federations, within which essential trust is maintained. |
Tables at a glance |
 |
 |
| Table 1 |
Table 2 |
|
| |
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 4 |
Figure 5 |
Figure 6 |
|
References |
- DimitriosZissis , DimitriosLekkas, Addressing cloud computing security issues, Future Generation Computer Systems volume 28(2012) 583âÃâ¬Ãâ59
- K.Govindaa, Dr.E.Sathiyamoorthyb Identity Anonymization and Secure Data Storage using Group Signature in Private Cloud, ProcediaTechnology,vol 4 (2012).
- Mark D. Ryan, Cloud computing security: The scientific challenge and a survey of solutions, The Journal of Systems and Software vol-86 (2013).
- Sandeep K. Sood, A combined approach to ensure data security in cloud computing, Journal of Network and Computer Applications,vol-35 (2012).
- Loganayagi.Bb, S.Sujathaa, Enhanced Cloud Security by Combining Virtualization and Policy Monitoring Techniques, The InternationalConference on Communication Technology and System Design ,vol2,issue 5 mar 2011.
- Cost and Security Benefits of SaaS-based Certificate Authorities, Global sign Technical notes-2013.(Book).
- LeenaKhanna et al, Cloud Computing: Security Issues And Description Of Encryption Based Algorithms To Overcome Them,ijarcsse-Volume 3, Issue 3, March 2013
- The RSA Encryption Algorithm, R.L. Rivest, A. Shamir, L.M. Adleman, "A method of Obtaining Digital Signatures and Public-KeyCryptosystems", Communications of the ACM, v. 21,2010.
- UmerKhalida, Abdul Ghafoor, et al, Cloud based Secure and Privacy Enhanced Authentication &Authorization Protocol, 17thInternational Conference in Knowledge Based and Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems - KES2013.
- M. Mackay a, T. Baker b, A. Al-Yasiri , Security-oriented cloud computing platform for critical Infrastructures, computer law & securityreview,vol- 28 (2012 ).
- Wenxue Tan et al, Analysis of RSA based on Quantitating Key Security Strength, Advanced in Control Engineering and InformationScience(2011).
- NirKshetri et al, Privacy and security issues in cloud computing: The role of institutions and institutional evolution, TelecommunicationsPolicy 37 (2013).
- ChunmingRong, Son T. Nguyen, Martin GiljeJaatun, Beyond lightning: A survey on security challenges in cloud computing, Computersand Electrical Engineering,volume 39 (2013) 47âÃâ¬Ãâ54.
- Cloud Security Alliance. <http://www.cloudsecurityalliance.org/>.
- Zhao Gansen, RongChunming, Li Jin, Zhang Feng, Tang Yong. Trusted data sharing over untrusted cloud storage providers. In:Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE international conference on cloud computing technology and science (CloudCom 2010); 2010.
- Bishop, 2004 "Introduction to Computer Security", 0-321-24744-2, Prentice Hall PTR, Section 9.3 Cryptographic Key Infrastructures
- Cloud Security Alliance, 2011, âÃâ¬ÃÅSecurity as a Service.âÃâ¬ÃÂ
- S. Yu, 2010, "Achieving Secure, Scalable, and Fine-grained Data Access Control in Cloud Computing".
- Popa RA, lorch JR, Molnar D, Wang HJ, ZhuangL , Enabling security in cloud storage SLAs with cloud proof. Technical report.Microsoft Research May 2010.
- Kamara S, Lauter K. Cryptographic cloud storage. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2010; 6054:136âÃâ¬Ãâ49.21.
- Prasad P, Ojha B, Shahi RR, Lal R. 3-dimensional security in cloud computing. Computer Research and Development (ICCRD) 2011;3:198âÃâ¬Ãâ208.
- Wang C, Cao N, Li J, Ren K, Lou W. Secure ranked keyword search over encrypted cloud data. Journal of the ACM 2010; 43(3):431âÃâ¬Ãâ73.
- Sood SK, Sarje AK, Singh K. A secure dynamic identity based authentication protocol for multi-server architecture. Journal of Networkand Computer Applications 2011; 34(2):609âÃâ¬Ãâ18.
- Wang C, Wang Q, Ren K, Lou W. Ensuring data storage security in cloud computing, quality of service, 2009, IWQoS IEEE 17thinternational workshop, p. 1âÃâ¬Ãâ9, 2009.
|