ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
| Aswini @ Bavani R 1, Athulya Das S2, Shubhasini Sugumaran3 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Hindustan Institute of Technology and Science, Chennai, India |
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
The novel approach is a centralized system that is being fed by the captured data obtained from various energy meters. The environmental variables like pressure, moisture, temperature also needs to be captured along with the energy for better control of the situation. In this article, temperature sensor communicates to the connected smart meter [1]. The temperature readings will be transferred along with the energy readings to the centralized system for further action in order to avoid the accidents in power plants, sub stations etc. The necessary operations are simulated using the IAR Embedded Workbench and controlled using microcontroller [11]. Since the energy meters already exist in power plants to measure the generated power, there is no need to establish a separate network to sense the temperature. So the existing network connection is used, thereby reducing the cost.
Keywords |
| Thermistor, Smart meter, GSM, Safety control, Cost effective. |
INTRODUCTION |
| In power plants, sub stations, energy transmission and distribution networks, energy meters are used for monitoring the import / export watt hours and the captured data has to be sent to the centralized system [3]. The environmental variables like pressure, moisture, temperature, etc. are calculated and maintained using the separate circuit and each variable has to be monitored manually in all the stations. This increases the cost and also delays the action, which during an emergency may result in malfunctioning of the machines. |
II. LITERATURE SURVEY |
| A smart meter is usually an electronic device that records consumption of electric energy in intervals of an hour or less and communicates that information at least daily back to the utility for monitoring and billing purposes. Smart meters enable two-way communication between the meter and the central system. Unlike home energy monitors, smart meters can gather data for remote reporting. Such an advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) differs from traditional automatic meter reading (AMR) in that it enables two-way communications with the meter. The sensors sense parameters such as temperature, pressure, humidity and send the output to the central system. The readings from the smart meter are also sent to the central system. The sensors and smart meter are no where connected to each other before reaching the central system. At the central system, the parameters are monitored. This increases the initial cost and the maintenance cost of the system. |
III. PROPOSED WORK |
| In this research, a sensor is used to measure the temperature for better control in power plants, sub stations, energy transmission and distribution networks. To measure the temperature, voltage divider circuit is used and Thermistor is connected to the microcontroller via the circuit [2]. The circuit is given below. |
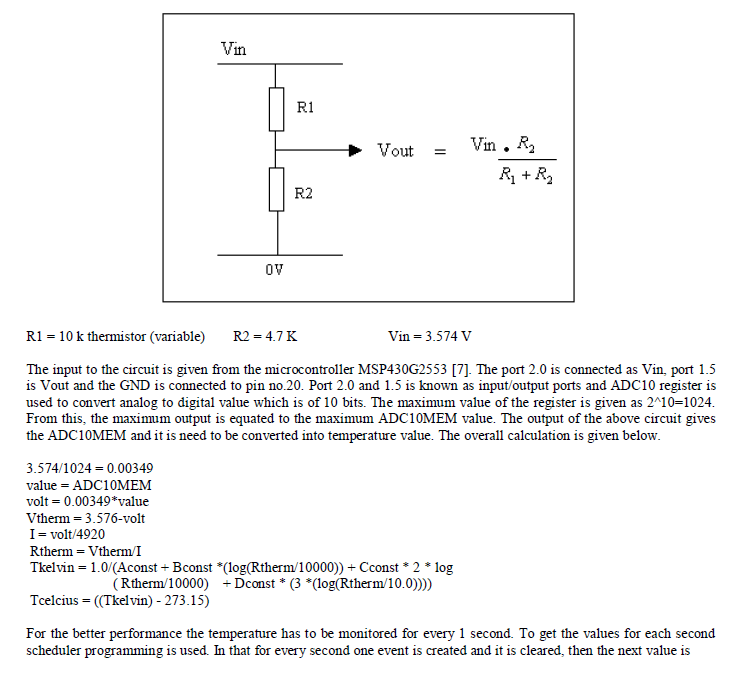 |
| stored in the event. Likewise for every 1 second event need to be created and cleared. By doing so, the temperature is monitored for every second. Then the microcontroller and the smart meter are connected through the line driver circuit. Here MK6E smart meter is used to display the temperature value along with the voltage and current. In this smart meter the default registers are available only to store the integer value. As we need to display the temperature as a float we need to build a script and a new register is created to store the temperature value. Then the script is needed to be uploaded to the meter and it is verified using the Eziview software [5]. The stored values are displayed in the lcd screen in the smart meter. |
 |
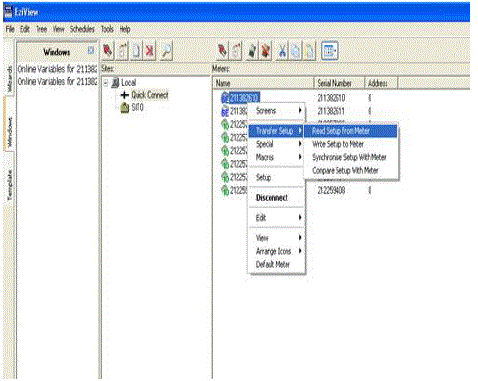 |
| The script for downloading the recent 100 records has been created and it is shown in the result. |
IV. EXPERIMENTAL RESULT |
| The proper execution of the code in workbench is indicated by the LED. The instant temperature value can be visible in the meter after building the script using script builder. The values of the meters can be sent to the central system using GSM. This needs to configure the GSM module with the system. The GSM modem is configured using the Eziview software. The processor will check the temperature value at certain intervals of time. These values are provided the smart meter and can be monitored both in smart meter as well as by taking log of recent values. When the temperature value exceeds a certain limit then the intimation of abnormal condition is sent to the control room along with time of the value and the same is sent to the respective member of control department. The log of recent 100 values is shown below which can be downloaded from the meter at any time. |
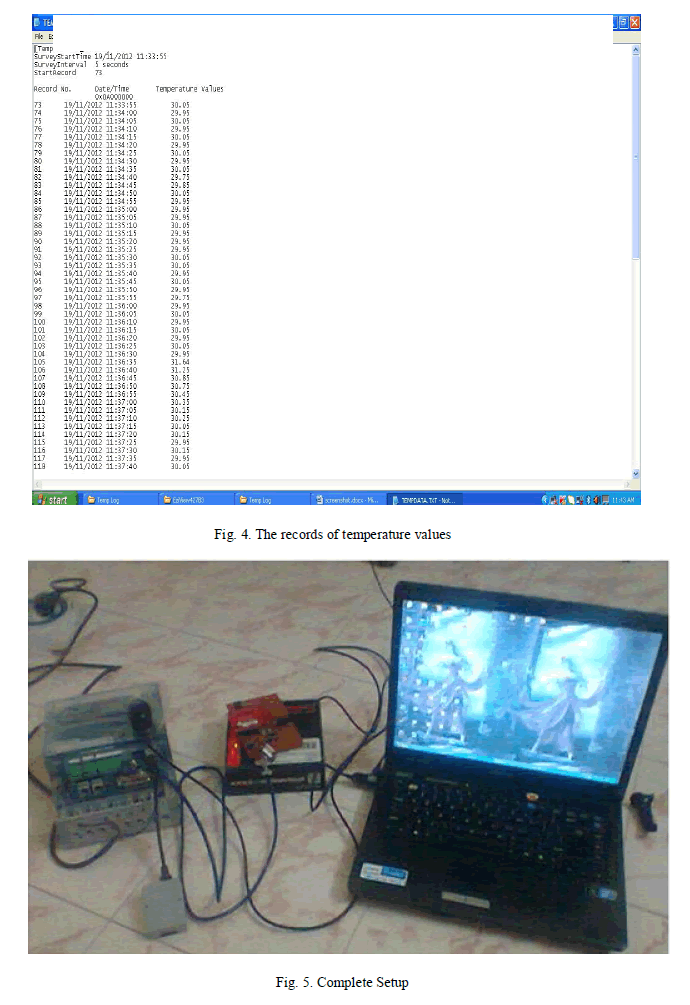 |
V. CONCLUSION |
| Thus the environmental parameters are monitored using Thermistor and the value is converted into temperature using MSP430 microcontroller. IAR Embedded Workbench is used to download and compile the code used for conversion. For every second the temperature value is monitored in the smart meter and if the value exceeds the limit a warning is send to the mobile as the message with the content of date and time. This can be done with the software tool “Eziview”. By doing so, the accidents which are caused by abnormal temperature can be minimized and the cost of maintenance will be reduced due to wireless access and existing meters. |
References |
|