Keywords
|
| DWT, DCT, Speech compression & decompression, MSE, SNR. |
INTRODUCTION
|
| Speech/Audio coding has been and still is a major issue in the area of digital speech processing. Speech coding is the act of transforming the speech signal at hand, to a more compact form, which can then be transmitted with a considerably smaller memory. The motivation behind this is the fact that access to unlimited amount of bandwidth is not possible. Therefore, there is a need to code and compress speech signals. Speech compression system focuses on reducing the amount of redundant data while preserving the integrity of signals. The different transformation of speech signals to the time frequency and time-scale domains for the purpose of compression aim at representing them with the minimum number of coding parameters. Digital audio compression allows the efficient storage and transmission of audio data. The various audio compression techniques offer different levels of complexity, compressed audio quality, and amount of data compression. Compression systems are designed to eliminate this redundancy. Speech coding is a lossy type of coding, which means that the output signal does not exactly sound like the input. The input and the output signal could be distinguished to be different. Coding of audio however, is a different kind of problem than speech coding. |
a) Wavelet Compression
|
| Different techniques were implemented each having its advantages and disadvantages. In general, they can be classified into two types, lossy and lossless. The original data will be totally restored without any modifications. Lossy compression does not completely retain the original signal; consequently some of the information is lost. For speech signals, this loss is acceptable since we are interested only in recognizing the signal. Wavelets compression technique is considered to be lossy where the reconstructed signal is not an exact match of the original signal. When applying the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to a given speech signal many coefficients of small values (depending on level we choose) are thus considered insignificant but ignoring them may cause more redundancy in recovered in sound signal. |
b) Wavelet Families
|
| It is very important to briefly introduce wavelets’ families, because they are the main tools. For anyone who wants to study wavelet theory must be familiar with these families, in order to get the best performance of his work. We can’t say that one type of wavelet is better than another, because every type has its own applications. So, a wavelet family may be good for one application, but not for another, this depends on the nature of the application. We will introduce, for each wavelet family, the scaling function Φ (t) in Eq. (1), the wavelet function Ψ (t) in Eq. (2) and its filters' values (for a filter back) in both of time-domain and frequency-domain representations. |
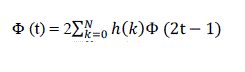 (1) (1) |
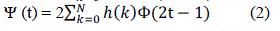 |
| Wavelet analysis is the breaking up of a signal into shifted and scaled versions of the original (or mother) wavelet. |
| Discrete Cosine Transform can be used for speech compression because of high correlation in adjacent coefficient. We can reconstruct a sequence very accurately from very few DCT coefficients. This property of DCT helps in effective reduction of data. |
IMPLEMENTATION
|
| In this paper hybrid model of compression and decompression by using DWT and DCT technique is used for the recorded signal. A different approach is being used for better compressed signal as well as less redundant signal is being recovered. |
| Set the compression and decompression flag at zero level. Then set the compression ratio i.e. up to what compression level is required. By using the frame size of the signal we can estimate the size (length) of the signal to be compressed. After the transformation of the signal, we arrange the transformed coefficient so that lower value of frequency of the signal is not eliminated. Whereas we are move the unnecessary zeros to other location. This provides a great help in compression with better result of MSE and SNR. In the above figure the signal which is used to compress using DWT then by DCT with different compression ratio generating the compressed signal. After the compression by removing the distortion or unnecessary coefficient the signal is reconstructed to the original form by taking inverse transform after adding the zeros which were generated in DWT & DCT. In method of compression the signal doesn’t lose any of its information. |
| In this paper compression of the speech signal is compared among the filters of the wavelet family such as haar, db4, sym, coif2. Now take the frame size of the signal to be 10 sec to analysis the different compression ratio in order to attain compressed signal with better result. Comparison is on the basis of mean square error (MSE) and signal to noise ratio (SNR). |
CONCLUSION
|
| Speech compression is used for transmission and storage. The speech compression is achieved by representing each sample of digitized data by lesser number of bits this paper shows the key advantageous features of different Wavelet filters in the field of speech Signal processing. It is found that the different wavelet filters significantly improves the reconstruction or fidelity assessments of the compressed speech signal. The SNR and MSE of signal show the high efficiency of the compression it is concluded that it can be very effectively used for the speech signal compression. |
RESULT
|
| Speech compression is achieved by using HAAR, DB4, SYM, COIF filter of DWT and DCT transform. In table 1 to 3 shows the MSE, SNR of the given speech signal of frame size as 10sec of the recorded speech signal. The compressed signal with compression ratio 2 of different filter of wavelet transform gives us the better result in terms of reconstructed speech signal. |
Tables at a glance
|
|
|
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
|
References
|
- Graps, A. “An Introduction to Wavelets”, 1997.http://www.amara.com/current/wavelet.html
- H. Elaydi “speech compression using wavelet”
- Jean-Marc Luneau, J´erˆome Lebrun, and SørenHoldt Jensen“Complex Wavelet Modulation Subbands for Speech Compression” in data compression conference in 2009.
- Polikar, R. “The Wavelet Tutorial” 1996. http://engineering.rowan.edu/~polikar/WAVELETS/WTpa rt4.html
- ZHAO DanïüÃÅMA Sheng-qian “Speech Compression with Best Wavelet Packet Transform and SPIHT Algorithm “Second International Conference on ComputerModeling and Simulation in 2010.
- Joebert S. Jacaba “AUDIO COMPRESSION USING MODIFIED DISCRETE COSINE TRANSFORM: THE MP3 CODING STANDARD” in October 2001.
- Mathworks Wavelet Toolbox. In: http://mathworks.com/access/helpdesk/help/toolbox/ wavelet.
- Russel Lloyd Lim “Speech Compression using the Discrete Wavelet Transform”
- Othman O. Khalifa, SeringHabib Harding & Aisha-Hassan A. Hashim “Compression using Wavelet Transform” in Signal Processing: An International Journal,Volume (2): Issue (5).
- “A Tutorial of the Wavelet Transform” by Chun-Lin, Liu in February 23, 2010.
- HarmanpreetKaur and RamanpreetKaur, “Speech compression and decompression using DCT and DWT”, International Journal Computer Technology &Applications,Vol 3 (4), 1501-1503 IJCTA | July-August 2012
|