Keywords
|
| Lung Sound, Vesicular breathe sound, Crakles, Coarse, Fine, Cepstrum Analysis |
INTRODUCTION
|
| This paper reviews about different techniques for lung sound analysis and diagnosis of disease. Lung sound signal is the random physiological signal that occurs during the ventilation process of the human respiratory system with the external environment. Lung sound signal is the random physiological signal that occurs during the ventilation process of the human respiratory system. Different sounds are present like tracheal breath sounds, vesicular breath sounds, inspiratory and expiratory stridor and stridor[2]. Research broadens the diagnosis purposes to various diseases possibly infects all respiratory sub-systems, specifically the lung organ. This is possible, because the recorded breath sound is processed and separated into lung sound and upper-respiratory sound, and compared with various adventitious/abnormal lung and respiratory sound data base, to identify what kind of disease infect the patient. In recent years, the data acquisition and signal processing technology accelerate the research development of lung sounds in some degree. The Lung Diseases Diagnosis Application consists of software and hardware components which formed a first-hand diagnosis tool of the lung diseases. |
| There are different techniques like Auscultation, Bronchoscopy, chest CT or chest scan [1] are present to detect and extract sound but due to variation in frequencies it is very important to develop tool which will work with dynamic frequency. Traditionally, normal and abnormal lung sounds have been analysed by the Spectrogram (SP) but it has disadvantages that it deals with only non-stationary signals. Effective acquisition, signal processing, and quantitative analysis have particular significance to the diagnosis of lung disease. |
| In the year 1967 Forgacs [19] gives quantitative analysis of crackles. Analysis based on intensity and spectral content of frequency domain signal. There are different techniques used for measurement of lung sound. In Auscultation includes listening of lung sound directly by using stethoscope. In Bronchoscopy, bronchoscope equipment is used to test and view the airways and diagnose in side lung. Chest CT scan uses an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of chest/upper abdomen. Routine sputum culture: a test of secretions from the lungs and bronchi tubes that carry air to the lung to look for organisms that cause infection. All the advantages and disadvantages of methods are tabulated below |
| There are some drawbacks by utilizing these methods only. Auscultation, which has been recognized as the most common and proven first-hand method, requires direct contact with the patients and cannot be applied when patients are remote from paramedics/doctors/hospitals. The examination also depends heavily on the listening skill and judgments of the doctors alone, therefore bias could exist. Bronchoscopy also requires direct contact with the patient, and insertion of bronchoscope equipment into the airways through the nose or mouth could cause discomfort, and usually this is for an advanced diagnosis. Chest CT scan is equipment which can give accurate diagnosis, however this equipment requires high cost investment. Chest X-ray although more common equipment, is also high cost in investment, and requires special laboratory. |
LITERATURE REVIEW
|
| Lung sound detection is very important because various diseases possibly infect all respiratory sub-systems, specifically the lung organ. Many researchers propose different techniques to analyse lung sound. |
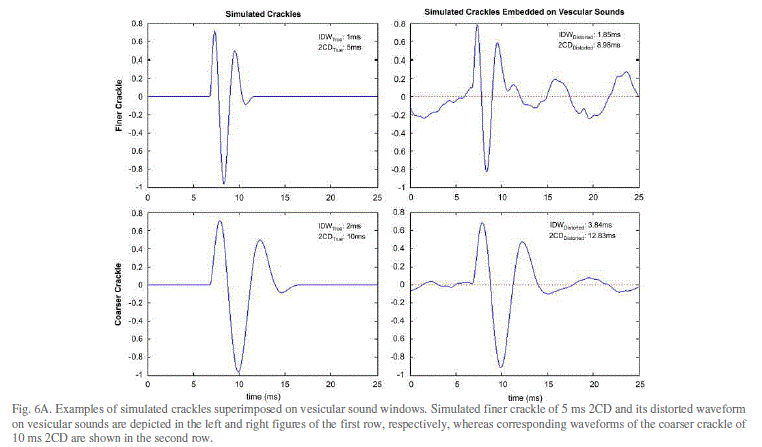
| Murphy et al. in 1977,[11] implemented an adventitious sound analysis through the time expanded waveform analysis (TEWA). In TEWA crackles displayed a short and more complex waveform than a sinusoidal sound. Later, Hoevers and Loudon described crackles by time-domain parameters such as the initial deflection width deflection width (IDW), the two cycles duration (2CD) and the largest initial deflection (LDW). |
| One of researcher proposes the time-frequency representation Hilbert-Huang (HHS) spectrum [18] as an appropriate analysis tool for fine and coarse crackles. HHS is selected after it has been demonstrated in a companion paper that for a signal with similar characteristics in time frequency. |
| Irina Hossain et al. [20] study the heart-noise reduction technique using wavelet transform which decompose frequency into different components and it is applied to different filters. Results show wavelet transform based filtering reduces the lung sound average power greatly over the whole frequency range. |
| Tiago H. Falk et al. [21] design a modulation filter to improve the separation of heart and lung sounds from breath sound recordings. Le Belvedere et al. use adaptive wavelets for lung sounds analysis and successfully detect pathological changes of the lung. |
| Benjin Wang et al. [2] multi-source estimation in the lung sound based on cepstrum .They study the relationship between the lung multi-source vibration and the delay time. From the perspective of digital signal processing, the cepstrum analyzes. Lung sound signal has a variety of superimposed components. Different compositions have their own particular time cycles. At the same time, normal and abnormal lung sounds show appropriate changes in frequency spectrum, time-domain waveform, the signal cycle, and the delay time. The number of multiple sound sources and the time delay contain rich case information, and reflect the physical characteristics of lung diseases. The method of cepstrum analysis in the application of typical lung sound source signal focuses on the relationship between the number of lung source and time delay of multi-source[2]. |
CLASSIFICATION OF LUNG SOUNDS
|
| A. Vesicular (normal) lung sounds |
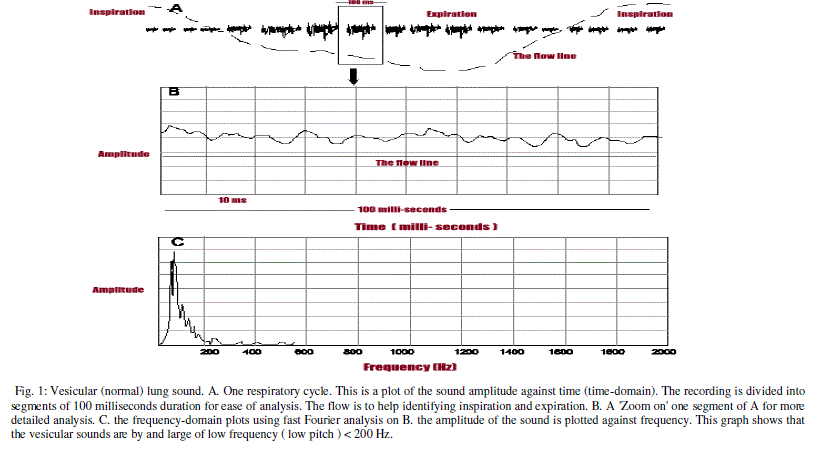
| Vesicular sound is a low pitched sound caused by the friction of the air with the walls of the airways. The sound is then 'modified' through passing numerous air filled alveolar spaces and the chest wall structures. |
| B. Abnormal Lung Sounds |
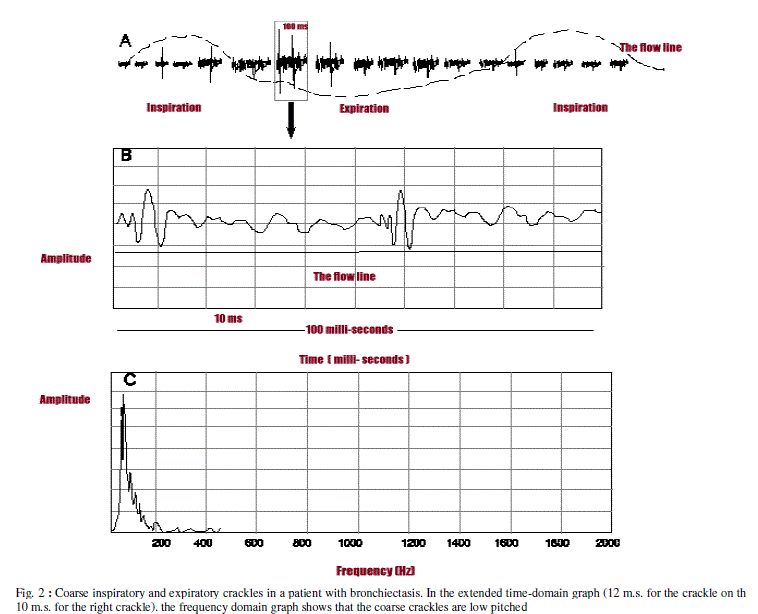
| 1. Coarse crackles: These are low pitched explosive sounds resulting from air bubbling through secretions. In bronchiect destruction of bronchial walls and cartlidges can account for coarse crackles that do not disappear or change after coughi after physiotherapy. |
| Coarse crackles can be heard over an area distant from the affected bronchi of the chest wall or by placing the stethosco the mouth. Coarse crackles normally disappear or reduce in number after coughing and after deep inspiration and expir Nath and Capel found that patients with coarse crackles have an obstructive defect of their lung function tests, which su an association with airway narrowing [14]. |
| When recorded by the time expanded wave form analysis crackles have a wide first deflection (also called initial def width) of >1.25 m.s. and two cycle duration of more than 9.32 m.s.[7]. |
| Coarse crackles are heard in chronic bronchitis, asthma, bronchiectasis, pulmonary oedema, and in prolonged bed rest. also heard in terminally ill patients. |
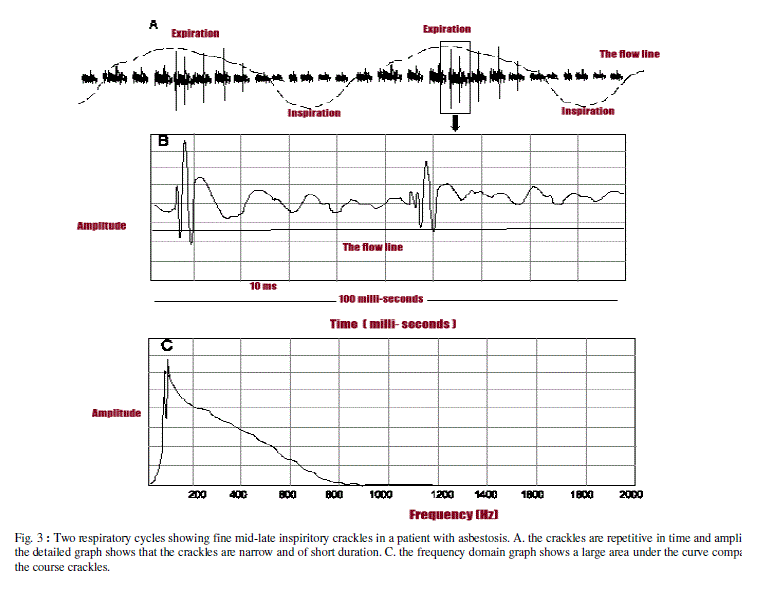
| 2. Fine Crackles: This is a high pitched discontinuous fine sound. Fine crackles is widely believed to be the resul sudden opening of partially closed and stiff small airways and alveoli. Coarse crackles are often audible in mid t inspiration, and they tend to be repetitive in time and place, which strongly suggests that they are due to changes in structures [15]. In computerised lung sound analysis crackles are narrow with an initial deflection width of < 0.92 m.s. an a two cycle duration of 6.02 m.s. [7]. |
| Fine crackles are heard in patients with interstitial lung disease, early stages of heart failure and in early stages of resol of pneumonia. Nath and Capel showed that fine crackles are associated with a restrictive default of lung functio interstitial lung fibrosis the number of crackles per respiratory cycle correlates with the severity of the disease [11]. |
PROPOSED SYSTEM
|
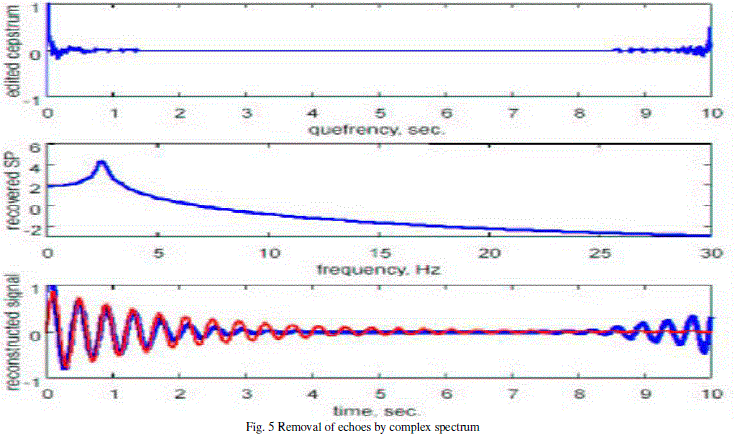
| Cepstrum Analysis can accurately capture the multi-source signal characteristics, amount of disease source and sound source interval. The cepstrum is usually used to determine the arrival times of fundamental wavelet and its echoes and their relative amplitude. |
| A signal coming out from a system is due to the input excitation and also the response of the system. From the signal processing point of view, the output of a system can be treated as the convolution of the input excitation with the system response. At times, we need each of the components separately for study and/or processing. The process of separating the two components is termed as deconvolution. The resulting sound can be considered as the convolution of respective excitation sequence and recorded characteristics. If e(n) is the excitation sequence and h(n) is the recorded sequence, then the resultant sequence s(n) can be expressed as follows: |
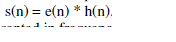 |
| This can be represented in frequency domain as, |
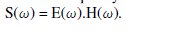 |
| The Eqn. (2) indicates that the multiplication of excitation and system components in the frequency domain for the convolved sequence of the same in the time domain. |
| From the Eqn. (2) the magnitude spectrum of the sequence can be represented as, |
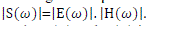 |
| To linearly combine the E(ω) and H(ω) in the frequency domain, logarithmic representation is used. So the logarithmic representation of Eqn. (3) will be, |
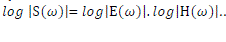 |
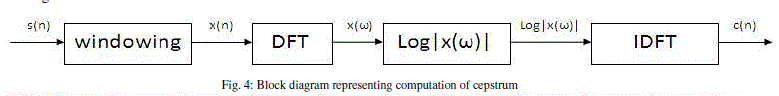
| As indicated in Eqn. (4), the log operation transforms the magnitude sound spectrum where the excitation component and recorded component are multiplied, to a linear combination (summation) of these components i.e. log operation converted the "*" operation into "+" operation in the frequency domain. The separation can be done by taking the inverse discrete fourier transform (IDFT) of the linearly combined log spectra of excitation and standard system components. It should be noted that IDFT of linear spectra transforms back to the time domain but the IDFT of log spectra transforms to quefrency domain or the cepstral domain which is similar to time domain. This is mathematically explained in Eqn. (5). In the quefrency domain the standard components are represented by the slowly varying components concentrated near the lower quefrency region and excitation components are represented by the fast varying components at the higher quefrency region. |
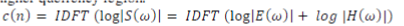 |
| Fig. 4 details the various steps involved in converting the given short term speech signal to its cepstral domain representation and Fig 5 shows the removal of echoes. |
EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS BY PROPOSED METHOD
|
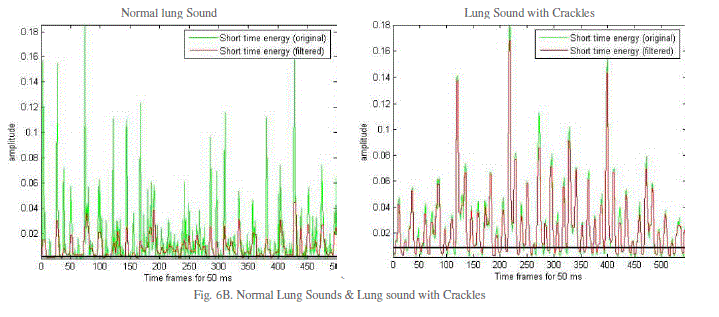
| The result of the proposed algorithm for lung sound analysis is shown in fig. 6A & fig. 6B. It gives idea of the amplitude values of crackle lung sound with respect to normal lung sound. The crackle sounds are repetitive, high pitch as seen in fig. 6B and are mostly associated with obstructive airway diseases like pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary edema and intestinal lung diseases like asthma, asbestosis etc. |
CONCLUSION
|
| There is a large variety of normal and abnormal respiratory sounds with characteristics which may be typical for a disease or for a certain pathological change in the respiratory system. Such deformities can be detected with our proposed method which has the ability to analyze and improve the knowledge of the physiology and pathophysiology of respiratory disorders that can be used in clinical assessment. |
Tables at a glance
|
 |
| Table 1 |
|
| |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 5 |
Figure 6a |
Figure 6b |
|
| |
References
|
- Ria Lestari Moedomo, M. SukrisnoMardiyanto, Munawar Ahmad, BachetiAlisjahbana, TjahjonoDjatmiko, The Breath Sound Analysis ForDiseases Diagnosis and Stress Measurement, ICSET, Bandung, Indonesia, Sept 2012
- Benjin Wang, LeiMiao, Huiying Dong, ZeguangZheng, The Research of Lung Sound Signals Based on Cepstrum Analysis, IEEE 2012; 978-0-7695-1706-0:12. 2012
- Murphy RLH, Del Bono EA, Davidson F. Validation of an automated crackles (rales) counter. Am Rev Resp Dis; 140:pp.1017-1020, 1989
- FatmaAyari, MekkiKsouri and Ali Alouani, A new scheme for automatic classification of pathologic lung sounds, IJCSI, pg 448-458,Vol 9,issue 4, No 1,July 2012
- AbhinavParkhi, Mahesh Pawar, Analysis of Deformities in Lung Using Short Time Fourier Transform Spectograph Analysis on Lung Sound, IEEE(ICCICS),2011; 978-0-7695-4587-5/11, 2011
- AratiGurung, Carolyn G Scrafford, James M Tielsh, Orin S Levine and William Checkley, Computerised Lung Sound Analysisas diagnosticaid for the detection of abnormal lung sounds:a systematic review and meta-analysis, Respir Med.2011 sept; 105(9):pp. 1396-1403, 2011
- American thoracic Society AdHoc Committee on pulmonary nomenclature for membership reaction. ATS News Fall1977;3:5-6, 1977
- Mitsuru Munakata, Hideaki Ukita, Isamu Doi, Yoshinori Ohtsuka, Yoshitaka Masaki, Yukihiko Homma, Yoshikazu Kawakami, Spectral andWaveform characteristics of fine and coarse crackles, Thorax 1991;46:pp. 651-657, 1991
- AmjadHashemi, HosseinArabalibiek and KhosrowAgin, Classification of wheeze sounds Using Wavelets and Neural Networks 2011 International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology, IPCBEE vol.11 (2011) © (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore
- Raymond l. H. Murphy, Stephen K. Holford and William C. Knowler,Visual lung-sound characterization by time expanded wave-form analysis, N Engl J Med 296:968-9 71, 1977
- Braughman RP, Loudon RG. Quantification for wheezing in acute asthma. Chest 1984;86:718
- FoadGhaderi, SaeidSanei, Localizing Heart Sounds in Respiratory SignalsUsing Singular Spectrum Analysis; IEEE TRANSACTIONS ONBIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 58, NO. 12, Dec 2011
- Nath AR. Capel LH. Inspiratory crackles and mechanical events of breathing.Thorax 1994;29:pp.695-698., 1994
- Al Jarad N, Davies SW, Logan Sinclair R, Rudd RM. Lung crackle characteristics in patients with asbestosis, asbestos related pleural diseaseand left ventricular failure using time expanded waveform analysis - a comparative study. Respiratory medicine 1994; 88:pp. 37-46, 1994
- Nath AR, Capel LH. inspiratory crackles, early and late. Thorax 1974; 29:223.
- Murphy RLH, Del Bono EA, Davidson F. Validation of an automated crackles (rales) counter. Am Rev Resp Dis 1989; 140:pp. 1017-1020,1989
- B.A. Rayes, S. Charleston-Villalobos, R. Gonzalez-Camarena, T.Aljama-Corrales, Analysis of Discontinuous Adventitious Lung Sounds byHilbert-Huang Specturm, IEEE EMBS Conference 978-1-4244-1815-2/08; Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada August 20-24, 2008
- Forgacs P. Crackles and Wheezes, Lancet; 2:pp. 203-205, 1967
- Hossain, I. and Z. Moussavi, Relationship between airflow and normal lung sounds, IEEE CCECE 2002, Canadian Conference, 2002
- Falk, T.H. and C.Wai-Yip, Modulation Filtering for heart and lung sound separation from breath sound recording, EMBS 2008, 30th Annual International Conference of IEEE 2008
- Donald G. Childers, David P Skinner and Robert Kemerait, The Cepstrum: A guide to processing, proceeding of the IEEE vol 65, No 10, oct1977.
|