Keywords
|
| wireless sensor network, fuzzy based rule. |
INTRODUCTION
|
| Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) have attracted much attention in recent years. The potential applications of WSNs are immense. They are used for collecting, storing and sharing sensed data. WSNs have been used for various applications including habitat monitoring, agriculture, nuclear reactor control, security and tactical surveillance. |
| Over the years there has been lot of research in area of agriculture. Lately we came to explore importance of soil, which was very important for agriculture Soil plays very key role for growth of plants and crop. Soil as medium for growth has come under lot of stress due to availability of land and demand of food and fiber. Plants mine soil for 13 nutrients and out of which 3 primary nutrients required are Nitrogen (N), Phosphorous (P) and Potassium (K). With increasing in mining this has resulted in increase in depletion of essential nutrients from soil which can be fulfilled by applying fertilizers. |
| Moreover Fertilizer application is required to replace crop land nutrients that have been consumed by previous plant growth. One way to redeem deficiency of essential nutrients for soil is application of fertilizers to soil. These fertilizer however if applied in adequately can cause huge concern for environment which are discussed below. So our initiative is to provide such a system which will provide exact recommendation of fertilizers for a crop. The three main components of fertilizer that are required for soil are nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) and Potassium (K). |
FUZZY EXPERT SYSTEM
|
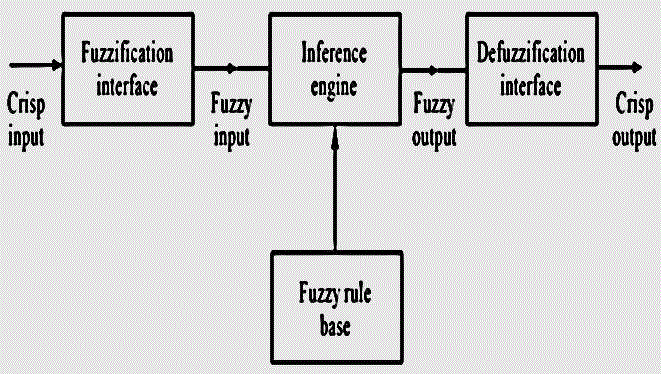
| Over the years various expert systems have been developed some of them like an expert system for weed control decision making in sunflower, Integrated Pest Management System using Fuzzy Expert System, CALEX Cotton: an integrated expert system for cotton production and management etc. Architecture of Fuzzy expert system architecture is shown in Fig. 1. |
| Here in this research a fuzzy based expert will be developed for fertilizer optimization with following implementation steps. |
| Soil test For this purpose firstly soil test is done by taking samples of soil in 250 Grams each from four corners and from extreme middle coordinate of field, further mixing together and taking 250 Grams. Further this sample is lab tested to know present levels of NPK in soil. After soil test being implemented, we can use a proposed Fuzzy Based Expert System to get optimize values of NPK fertilizers. |
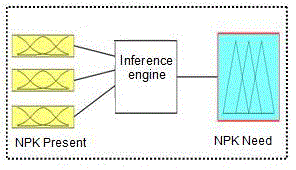
| Fuzzy based expert system for fertilizer Expert system is computer program that basically stimulates decision making power of human expert. In expert system there two parts knowledge base where facts and figure are recorded and secondly inherence system which uses knowledge base, to come to new facts from users query given at input. The block diagram of Fuzzy Expert system developed is illustrated in Fig 2. The mamdani system of fuzzy is being used for this application. The mamdani inherence system is useful when applying fuzzy logic to control of system[9] .The expert system is given crisp value as input i.e. fuzzification via membership functions, rule base , rule evaluation, aggregation and defuzzification for purpose of creating the crisp values at output. Here three input variables are taken i.e. present levels of nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium level in soil. The need of nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium levels were defined as output variables. |
| The range of input and output variables were selected by examining data. The universe disclosure were taken as for input nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium i.e. (0-1 Kg/Ha), (0-50 Kg/Ha) and (0-100 Kg/Ha) taken respectively. Similarly at output needed levels of nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium that were taken are (0-130 Kg/Ha), (0-100 Kg/Ha) and (0-50 Kg/Ha) respectively. The interrelation between inputs and outputs, both are crisp values, is made by linguistic transformation of input membership functions, implication and aggregation using the rule base, and defuzzification of the linguistic output to values representing need of amount of each fertilizer. |
| MembershipFunctionsThe membership functions that are adopted either trapezoidal or triangular membership accordingly needed. The rules are formulated here using MATLAB fuzzy tool, a simple Mamdani system which is very useful when applying fuzzy logic to control of system. There are three input variables taken nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium present already in soil which are partitioned into three, four and two sets respectively each. |
| Fuzzy rules used |
| The 24 basic fuzzy rules are taken to describe very useful relations between the three inputs of NPK present in soil and three outputs of NPK needed in soil. Here below few of them given in following |
| 1. If (Nitrogen is Low) and (Phosphorous is Low) and (Potassium is Low) then (Nitrogen is High needed) (Phosphorous is Very high needed) (Potassium is High needed) |
| 2. If (Nitrogen is Low) and (Phosphorous is Low) and (Potassium is High) then (Nitrogen is High needed) (Phosphorous is Very high needed) (Potassium is Low needed) |
| 3. If (Nitrogen is Low) and (Phosphorous is Medium) and (Potassium is Low) then (Nitrogen is High needed) (Phosphorous is High needed) (Potassium is High needed) |
| 4. If (Nitrogen is Low) and (Phosphorous is Medium) and (Potassium is High) then (Nitrogen is High needed) (Phosphorous is High needed) (Potassium is Low needed) |
| 5. If (Nitrogen is Low) and (Phosphorous is High) and (Potassium is Low) then (Nitrogen is High needed) (Phosphorous is Medium needed) (Potassium is High needed) |
| 6. If (Nitrogen is Low) and (Phosphorous is High) and (Potassium is High) then (Nitrogen is High needed) (Phosphorous is Medium needed) (Potassium is Low needed) |
| 7. If (Nitrogen is Low) and (Phosphorous is Very High) and (Potassium is Low) then (Nitrogen is High needed) (Phosphorous is Low needed) (Potassium is High needed) |
| 8. If (Nitrogen is Low) and (Phosphorous is Very High) and (Potassium is High) then (Nitrogen is High needed) (Phosphorous is Low needed) (Potassium is Low needed) |
| 9. If (Nitrogen is Medium) and (Phosphorous is Low) and (Potassium is Low) then (Nitrogen is Medium needed) (Phosphorous is Very High needed) (Potassium is High needed) |
| 10. If (Nitrogen is Medium) and (Phosphorous is Low) and (Potassium is High) then (Nitrogen is Medium needed) (Phosphorous is Very High needed) (Potassium is Low needed) |
| 11. If (Nitrogen is Medium) and (Phosphorous Medium) and (Potassium is Low) then (Nitrogen is Medium needed) (Phosphorous is High needed) (Potassium is High needed) eq.(3) |
RESULTS
|
| The results were taken for various levels of NPK values found during soil test and correspondingly required levels of NPK were calculated using Fuzzy Based Expert system. Following are some of input levels of NPK present that were taken, recommendation levels for NPK needed were calculated and are shown in TABLE II. |
| The Software result is here demonstrated in Table I, depicting when levels N,P,K in soil are found to be 0.5Kg/Ha, 25 Kg/Ha and 50 Kg/Ha correspondingly values of needed levels came out to be 100 Kg/Ha, 50 Kg/Ha and 35 Kg/Ha for N,P& K. |
CONCLUSIONFUTURE ENHANCEMENT
|
| This paper helped us a lot to get the needed Fertilizer for horticulture crops using Fuzzy System with programming in Dot Net. A Fuzzy Based system for fertilizer optimization is being developed and proposed where in are able to calculate that values of NPK fertilizers needed in soil for horticulture crop, knowing levels of NPK levels present in soil. Applying precise and almost exact amount of NPK fertilizers needed in soil accordingly into crop would help farmers to reap the maximum returns from his crop, while reducing his fertilizer costs. Reducing fertilizers intake accordingly will reduce fertilizers intake. And would prevent over fertilization which damages crop yield and make soil degraded. Overall benefit it prevents hazard effects that are caused to environment. |
| The methods used in the wireless sensor technology with Fuzzy System have advanced a lot over the farmers, especially with the production area. Even though the techniques are still not used very often in India, the options are never-ending. Several different methods exist and continue to be developed, while the ways of optimize the intelligent systems algorithm also advance quickly. |
Tables at a glance
|
 |
 |
| Table 1 |
Table 2 |
|
| |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
|
| |
References
|
- M. Manijeh Keshtgary1, AmeneDeljoo “An Efficient Wireless Sensor Network for Precision Agriculture” Canadian Journal on Multimedia and Wireless Networks, Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2012.
- K. Chuan Wang, Danielle George, and Peter R. Green “Development of Plough-able RFID Sensor Network Systems for Precision Agriculture” 2014 IEEE.
- K.Nirmal Kumar R.Prapakaran “Zigbee Wireless Sensor Network Technology Study for Paddy Crop Field Monitoring” International Conference on VLSI, Communication & Instrumentation (ICVCI) 2011 Proceedings published by International Journal of Computer Applications® (IJCA).
- N. Sakthipriya “An Effective Method for Crop Monitoring Using Wireless Sensor Network” Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 20 (9): 1127-1132, 2014 ISSN 1990-9233 © IDOSI Publications, 2014.
- AnujNayak, GeethaPrakash, AshishRao “Harnessing Wind Energy to power Sensor Networks for Agriculture” 2014 IEEE.
- Ana Laura Diedrichs†1, Germán Tabacchi†2, Guillermo Grünwaldt†3, Matías Pecchia†4, Gustavo Mercado†5 and Francisco González Antivilo_6 “Low-Power Wireless Sensor Network for Frost Monitoring in Agriculture Research” 2014 IEEE Biennial Congress of Argentina (ARGENCON).
- Pietro Catania1, Mariangela Vallone1*, Giuseppe Lo Re2, Marco Ortolani2 “A wireless sensor network for vineyard management in Sicily (Italy)” AgricEngInt: CIGR Journal.
- M. Rahmat 1,6, M. Azis 2, E. Rustami 2, W. Maulina 2, K.B. Seminar 3, A.S. Yuwono 4, H. Alatas 5 “Low Cost Configuration of Data Acquisition System for Wireless Sensor Network” International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol: 12 No: 02.
- Dr.K.Srinivasa Ravi*1, K.Tapaswi#2, B.Lokesh#3, G.Sai Krishna “Smart Sensor System for Agricultural Chronology” (IJCSIT) International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies, Vol. 2 (6) , 2011
- Santhosh Simon, K Paulose Jacob “Energy Optimized Secure Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks” International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT) Volume 3, Issue 4, October 2013.
- WichianSrichaipanya, PraminArtrit, and AnuchaSangrung “Fertilizer Quality Control of a Bulk-Blending Plant Using Intelligent Systems” Suranaree Journal of Science and Technology, January 20, 2014.
- BaljitKaur and Dilip Kumar “Development of Automated Nutrients Composition Control Fertigation System” International Journal of Computer Science, Engineering and Applications (IJCSEA) Vol.3, No.3, June 2013
- 1Bah, A., 2S.K. Balasundram and 1M.H.A. Husni “Sensor Technologies for Precision Soil Nutrient Management and Monitoring” American Journal of Agricultural and Biological Sciences 7 (1): 43-49, 2012.
- Georg Ruß1, Rudolf Kruse1, Martin Schneider2, and Peter Wagner2 “Data Mining with Neural Networks for Wheat Yield Prediction” ICDM 2008.
- A. Suyantohadi1,2*, M. Hariadi2, MH. Purnomo2, T. Morimoto3 “Dynamic neural network model for identifying cumulative responses of soybean plant growth based on nitrogen fertilizer compositions” Australian Journal of Agriculture Engineering, AJAE 1(5):188-193 (2010).
- Liming Chen1 Liming Xu2 Yanlong Hou3 “A Control System for the Mechanism of Feitilizer Proportioning and Mixing Based on the Nitrogen, Phosphate and Potassium Fertilizer” 2011 IEEE.
- WANG Xinzhong WANG Xi ”Design and Test of Variable-rate Fertilization Control Device of Precision Planter for Soybean” 2011 IEEE.
- 1Miss Maya V. Mawale, 2Dr. VinayChavan “Fuzzy Inference System for productivity and fertility of soil” 2014 IJEDR | Volume 2, Issue 3 | ISSN: 2321-9939.
- Rohit.K.Nikhade, S.L.Nalbalwar ”Monitoring Greenhouse using Wireless Sensor Network” International Journal of Advanced Computer Research (ISSN (print): 2249-7277 ISSN (online): 2277-7970) Volume-3 Number-2 Issue-10 June-2013.
- Kavi K. Khedo1, Rajiv Perseedoss2 and Avinash Mungur3 “A Wireless Sensor Network Air Pollution monitoring System” IJWMN International Journal Vol.2, No.2.
|