Virtualization reduces the more Physical Machine (PM) requirement by sharing the resources which are utilized in cloud computing. Cloud service providers allocate a Virtual Machine (VM) to end users based on request by sharing the physical resources, but Machine gets overloaded if there is not enough or more VM resources shared to Virtual Machines on the average resources needed for utilizing the servers, shared to be able to handle the additional demand. In order to overcome the system load due to more Virtual Machine resources sharing on a single machine is automated the load balancing of virtual machine system by monitoring the High Load Prediction scheme and Resource Predication scheme. When the Overload identified Virtual Machines are migrated to another available Physical Machine. Load Balance monitoring system can bring down the low utilized or less resource usage Physical Machine by migrating Virtual Machine resources to another physical machine in order to save energy. This energy computing can be applied through low load predication scheme. To maximize the performance profit machine resources to VM should balanced and optimized. This paper proposes and analysis the utilization of the load balancing scheme and energy efficiency scheme for achieving effective optimal performance.
Keywords |
| Virtualization, cloud computing, resource management, green computing, migration, virtual machine. |
I. INTRODUCTION |
| Cloud computing has revolutionized the IT industry by giving computing resources based on user demands and payas-
you-go basis which are achieved through virtualization, Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) and Utility
Computing. Server virtualization is the masking of server resources for server end users to increase the overall
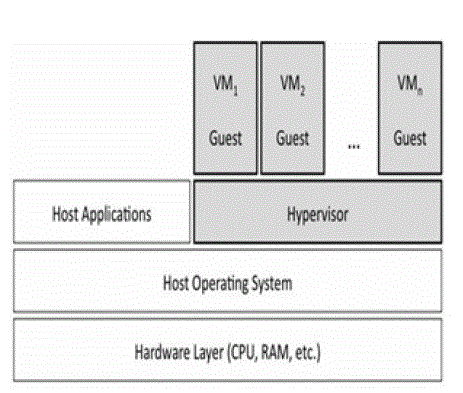
utilization of server[3]. Single Physical Machine can be sliced into various Virtual Machines as shown in Fig 1.1, each
VM typically reproduce a physical computing environment, but requests for CPU, memory, hard disk, network and
other hardware resources are managed in hypervisor layer which communicate these requests to the underlying
physical machine. The aim of the virtualization in cloud computing is to reduce the physical machine requirements,
data center risks and maintenances cost[2]. Virtual Machines are created within a hypervisor or a virtualization
platform that runs on top of a client or server operating system called as host OS, this virtualization layer is used to
create many individual, isolated VM environments. |
II. RELATED WORK |
| Zhen Xiao, Senior Member, Weijia Song, and Qi Chen [1] have stated that load balancing based on processor load.
A scheme for centralized utility maximizes process resource usage based on allocation. The authors present an optimal
solution under the assumption that the demand of resources can be split over several machines. Their solution has
limited applicability in context based multiple resources that need to be allocated on the same machine and the demand
for further resources cannot be split on same machines when overloaded. |
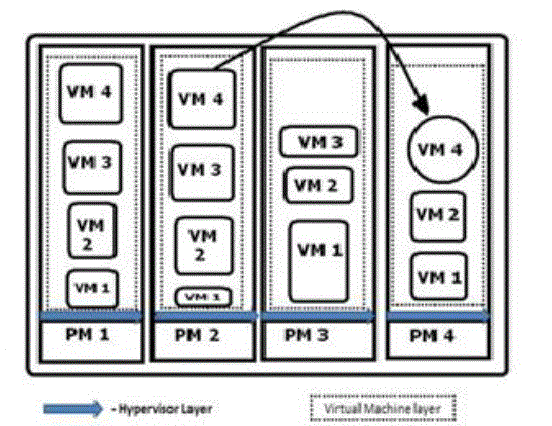
| Anton Beloglazov and RajkumarBuyya [2] Dynamic VM consolidation has been applied to minimize energy
consumption in a data center. They explored the energy benefits obtained by consolidating VMs using migration and found that the overall energy consumption can be significantly reduced. Problem of dynamic VM consolidation
proposed a heuristic that minimizes the data center’s power consumption, taking into account the VM migration as
shown in Fig 1.2.However, the authors did not apply any algorithm for determining when it is necessary to optimize the
VM placement. |
| Resource allocation for distributed systems are minimizes the migrations over consecutive load control [3]. The
study of physical resources and VMs non-stationary and unknown workloads, as observed in Infrastructure as a Service
(IaaS) environments, power and performance costs of VM migrations[6][8] and the large scale of Cloud data center
infrastructures. |
III. PROPOSED ALGORITHM |
A. Design Considerations |
| An automated system improves the utilization of server resources, so that reduce the power consumption in
virtualization of computing resources. Virtualization brings the hypervisor layer called abstraction layer between an OS
and hardware to communicate between VM and PM. Physical resources are sliced into more number of logical slices
called Virtual Machines. All Virtual Machine can hold an individual OS created for the users which ensures a view of a
dedicated physical resource, so that increases the performance and reduces the failure isolation between VMs sharing
with PM. Issue of host overload detection as a part of VM consolidation by dynamic move. Identify which VMs are
migrating from an overloaded host for VM consolidation by migrating dynamically which directly improves the
resource utilization and Quality of Service delivered to end users. |
| • Methodology of the module shows the balancing the load based on virtual machine migration when hot spot
of the system is overloaded. |
| • Resource performance also measured to conform the load is peak to initiate the migration to reduce the
physical machine load and increase the stability of machine. |
| • Whenever load is monitored to high VM consolidation raised by dynamic move between another PM which
holds the optimal load. |
| • Efficiently utilize the machines if the load is below cold spot and less resource usage are consolidated by
moving the VM process to another available optimal physical machine and bring down the machine with
cold spot load which energize the green computing. |
B. Description of the Proposed Algorithm |
| As virtualization expands deeper into the enterprise to include mission-critical and resource-intensive applications.
Virtualization vendors may still be touting the potential of putting more virtual machines (VM) on a single physical
machine (PM). But more VM on single PM ratios are dangerous in production environments and can cause
performance problems or worse, outages. In ordered to protect the overloaded machine from degrading the performance
following load balancer scheme automate the system load and guard the system resource usage. They are |
| • High Load Prediction Algorithm. |
| • Resource Prediction Algorithm. |
| • Low Load Prediction Algorit`hm. |
| Step 1: Overload Identification |
| System gets overloaded if more number of virtual machines is allocated to a single physical machine, so following
high load predication algorithm helps to predict the load before machine gets unworkable. |
| Step 2: High Load Prediction Algorithm |
| In ordered to identify the high load on physical machine, spot out the hotspot of CPU which are above the threshold
value. |
| Step 3: Resource Prediction Algorithm |
| Conforming the system load further by checking the Process and Memory load by its percentage of utilization. |
IV. PSEUDO CODE |
| Algorithm: High Load Monitoring |
| Input:Thermal reading of CPU to file cpu_sensor.txt |
| Initialization: |
| Φ defines the maximum hotspot threshold value of CPU load |
| Ω defines the average value of CPU Thermal reading at every 10 minutes |
| Output: Decision for migrating VM |
| Step 1: if average CPU thermal ‘Ω’ >‘Φ’then |
| Step 2: Invoke the Resource_Max(φ) usage of the PM |
| Step 3: ifreturn value ‘φ’ is true then |
| Step 4: Invoke the Migration module |
| Step 5: end if |
| Step 6: return the decision returned by Migration module |
| Step 7: end if |
| Step 8: return false. |
| Algorithm: Resource_Max Monitoring |
| Input: Process and Memory utilization status |
| Initialization: |
| P1 initials the process utilization percent |
| M1initials the memory usage percent |
| Output: return the value true if load detects |
| Step 1: if process P1>overall percent || memory M1 > overall percent then |
| Step 2: return true |
| Step 3: end if |
| Algorithm: Low Load Monitoring |
| Input: Thermal reading of CPU to file cpu_sensor.txt |
| Initialization: |
| σ defines the minimum threshold value of CPU load |
| ρ defines the average value of CPU Thermal reading at every 10 minutes |
| Output: Decision for migrating VM |
| Step 1: if average CPU thermal ‘ρ’ <‘σ‘then |
| Step 2: Invoke the Resource_Min(φ) usage of the PM |
| Step 3: ifreturn value ‘φ’ is true then |
| Step 4: Invoke the Migration module |
| Step 5: end if |
| Step 6: return the decision returned by Migration module |
| Step 7: Invoke the Shutdown module |
| Step 8: end if |
| Step 9: return false |
| Every physical machine is checked periodically to predict an overload by detection algorithm to migrate VMs when
necessary in order to avoid performance degradation and service level failing. For the host overload detection problem
several modules are proposed which identify the load and rectify. |
V. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK |
| In this load balancer system, the analysis of design and implementation of a physical machine resource monitoring
system for cloud computing services are proposed. Our system multiplex the virtual machine between physical
machines adaptively based on demand necessity. The load prediction algorithm and load balancer module can balance
the load by managing the resources dynamically. So our module and algorithm achieves the load balancing and green
computing for distributed system resources by dynamic move. |
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
|
| |
References |
- Zhen Xiao, Senior Member, Weijia Song, and Qi Chen “Dynamic Resource Allocation Using Virtual Machines for Cloud Computing Environment” IEEE Transaction on Parallel and Distributed Systems, June 2013, VOL: 24, NO: 6 PP: 1107 -1117.
- Anton Beloglazov and RajkumarBuyya., “Managing Overloaded Hosts for Dynamic Consolidation of Virtual Machines in Cloud Data Centers Under Quality of Service Constraints”, IEEE Transaction on Parallel and Distributed Systems, July 2013, VOL: 24, NO: 7, PP: 1366 – 1379.
- Patricia Takako Endo, André Vitor de Almeida Palhares, NadilmaNunes Pereira, GlaucoEstácioGonçalves, DjamelSadok, and Judith Kelner,“Resource Allocation for Distributed Cloud Concepts and Research Challenges” IEEE Networks,July/August 2011, VOL: 25, PP: 42 - 46.
- A. Verma, P. Ahuja, and A. Neogi, “pMapper: Power and migrationcost aware application placement in virtualized systems,”IFIP. Conf. onMiddleware, 2008,PP: 243–264.
- X. Wang and Y. Wang, “Coordinating power control and performancemanagement for virtualized server clusters,” IEEE Transactionson Paralleland Distributed Systems,Feb 2011, VOL: 22, NO: 2,PP: 245–259.
- Mayank Mishra, Anwesha Das, Purushottam Kulkarni, and AnirudhaSahoo “Dynamic Resource Management Using Virtual Machine Migrations”IEEE Communications, Sep 2012,VOL: 4, , PP: 97-110.
- Anala, M.R. “A framework for secure live migration of virtual machines“ICACCI International Conference, August 2013 PP: 243 – 248. Darsena, D “Live migration of virtual machines among edge networks viaWAN links” Future Network and Mobile Summit, July 2013 PP: 1 – 10.
|