| Discrete wavelet transform, Connected Component, Edge, Support vector machine, Discrete cosine transform. |
INTRODUCTION
|
| The image content is classified into two categories: perceptual content and semantic content [1]. Perceptual contents include colors, shapes, textures, intensities, and their temporal changes while semantic contents include objects, events, and their relations. Text content contains high level of semantic information as compared to visual information. Therefore text extraction from images is very significant in content analysis. It has many useful applications such as automatic bank check processing [2], vehicle license plate recognition [3], document analysis and page segmentation [4], signboard detection and translation [5], content based image indexing, assistance to visually impaired persons, text translation system for foreigners etc. |
| Text appearing in images is classified into three categories: document text, caption text, and scene text [6]. In contrast to caption text, scene text can have any orientation and may be distorted by the perspective projection therefore it is more difficult to detect scene text. |
| ? Document text: A document image (Fig. 1) usually contains text and few graphic components. It is acquired by scanning journal, printed document, handwritten historical document, and book cover etc |
| ? Caption text: It is also known as overlay text or artificial text (Fig. 2). It is artificially superimposed on the image at the time of editing, like subtitles and it usually describes the subject of the image content. |
| ? Scene text: It occurs naturally as a part of the scene image and contain important semantic information such as advertisements, names of streets, institutes, shops, road signs, traffic information, board signs, nameplates, food containers, street signs, bill boards, banners, and text on vehicle etc (Fig. 3). |
| A. Properties of Text in Images: |
| Texts usually have different appearance due to changes in font, size, style, orientation, alignment, texture, color, contrast, and background. These changes will make the problem of automatic text extraction complicated and difficult. Text in images exhibit variations due to the difference in the following properties [7]: |
| ? Size: The size of text may vary a lot. |
| ? Alignment: Scene text may be aligned in any direction and have geometric distortions while caption text usually aligned horizontally and sometimes may appear as non-planar text. |
| ? Color: The characters tend to have same or similar color but low contrast between text and background makes text extraction difficult. |
| ? Edge: Most caption and scene texts are designed to be easily read, hence resulting in strong edges at the boundaries of text and background. |
| ? Compression: Many images are recorded, transferred, and processed in compressed format. Thus, a faster text extraction system can be achieved if one can extract text without decompression. |
| ? Distortion: Due to changes in camera angles, some text may carry perspective distortions that affect extraction performance. |
| B. Process of Text Extraction: |
| The input image may be gray scale or color, compressed on uncompressed format. Text detection refers to the determination of the presence of text in the image while text localization is the process of determining the location of text and generating bounding boxes around it. After that, text is extracted i.e. segmented from the background. Enhancement of the extracted text is required as the text region usually has low-resolution and is prone to noise. Thereafter, the extracted text can be recognized using OCR. The block diagram of text extraction is shown in Fig. 4. |
TEXT EXTRACTION TECHNIQUES
|
| The various techniques of text extraction are as follow: |
| A. Region based Method: |
| Region-based method uses the properties of the color or gray scale in the text region or their differences to the corresponding properties of the background. They are based on the fact that there is very little variation of color within text and this color is sufficiently distinct from text's immediate background [20]. Text can be obtained by thresholding the image at intensity level in between the text color and that of its immediate background. |
| This method is not robust to complex background. This method is further divided into two sub-approaches: connected component (CC) and edge based. |
| i.) CC based Method: |
| CC-based methods use a bottom-up approach by grouping small components into successively larger components until all regions are identified in the image [9-12]. A geometrical analysis is required to merge the text components using the spatial arrangement of those components so as to filter out non-text components and the boundaries of the text regions are marked. This method locate locates text quickly but fails for complex background. |
| ii.) Edge based Method: |
| Edges are a reliable feature of text regardless of color/intensity, layout, orientations, etc. Edge based method is focused on high contrast between the text and the background [5,13-15]. The three distinguishing characteristics of text embedded in images that can be used for detecting text are edge strength, density and the orientation variance. Edgebased text extraction algorithm is a general-purpose method, which can quickly and effectively localize and extract the text from both document and indoor/ outdoor images. This method is not robust for handling large size text. |
| B. Texture based Method: |
| This method uses the fact that text in images have discrete textural properties that distinguish them from the background. The techniques based on Gabor filters, Wavelet, Fast fourier transform (FFT), spatial variance, etc are used to detect the textual properties of the text region in the image [16-19]. This method is able to detect the text in the complex background. The only drawback of this method is large computational complexity in texture classification stage. |
| C. Morphological based Method: |
| Mathematical morphology is a topological and geometrical based method for image analysis [16,17,20]. Morphological feature extraction techniques have been efficiently applied to character recognition and document analysis. It is used to extract important text contrast features from the processed images. These features are invariant against various geometrical image changes like translation, rotation, and scaling. Even after the lightning condition or text color is changed, the feature still can be maintained. This method works robustly under different image alterations. |
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
|
| A. Various parameters are used to analyze the performance of text extraction techniques and given as follow: |
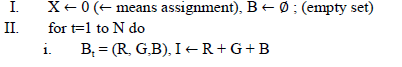 |
 |
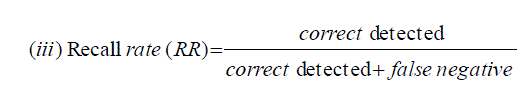 |
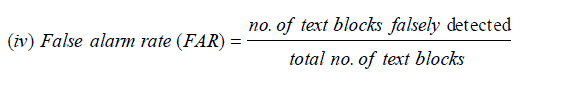 |
| B. Comparative Analysis of Related Work: |
| Many researches have been done on various text extraction techniques such as region based (CC based and edge based), texture based, morphological based or combination of these technique (i.e. hybrid approach). Researchers have used different type of images for their experimentation. The detailed analysis of text extraction techniques is shown in Table 1. |
CONCLUSION
|
| In this paper, various techniques such as region based, edge based, connected component (CC) based, texture based, morphological based etc. have been discussed and a detailed comparison of these techniques on the basis of various parameters such as precision rate, recall rate, accuracy etc. has been done. Every approach has its own benefits and restrictions. Even though there are many numbers of algorithms, there is no single unified approach that fits for all the applications due to variation in font, size, alignment, complex background of text etc. It is concluded that texture based method can detect and localize text accurately even when images are noisy, complex background and low resolution. |
Tables at a glance
|
 |
| Table 1 |
|
| |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
|
References
|
- H.K. Kim, Efficient Automatic Text Location Method and Content-Based Indexing and Structuring Of Video Database, Journal of VisualCommunication and Image Representation vol. 7, no. 4 ,1996, pp. 336–344.
- C. Y. Suen, L. Lam, D. Guillevic, N. W. Strathy, M. Cheriet, J. N. Said, and R. Fan, Bank Check Processing System, International Journalof Imaging Systems and Technology, vol. 7, No. 4 1996, pp. 392–403.
- D.S. Kim, S.I. Chien, Automatic Car License Plate Extraction using Modified Generalized Symmetry Transform and Image Warping,Proceedings of International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Vol. 3, 2001, pp. 2022–2027.
- A.K. Jain, Y. Zhong, Page Segmentation using Texture Analysis, Pattern Recognition, Vol. 29, No. 5, Elsevier, 1996, pp. 743–770.
- T.N. Dinh, J. Park and G.S. Lee, Low-Complexity Text Extraction in Korean Signboards for Mobile Applications, IEEE InternationalConference on Computer and Information Technology, 2008, pp. 333-337.
- Q. Ye, Q. Huang, W. Gao, D. Zhao, Fast and Robust Text Detection in Images and Video Frames, Image and Vision Computing, Vol. 23,No. 6, Elsevier, 2005, pp. 565–576.
- D. Ghai, N. Jain, Comparison of Various Text Extraction Techniques for Images- A Review, International Journal of Graphics & ImageProcessing, Vol. 3, No. 3, 2013, pp. 210-218.
- D. Zaravi, H. Rostami, A. Malahzaheh, S.S Mortazavi, Text Extraction using Wavelet Thresholding and New Projection Profile, WorldAcademy of Science, Engineering and Technology, Vol. 5, 2011, pp. 528-531.
- J.L. Yao, Y.Q. Wang, L.B. Weng, Y.P. Yang, Locating Text Based on Connected Component And SVM, International Conference OnWavelet Analysis And Pattern Recognition, Vol. 3, 2007, pp. 1418 - 1423.
- M. Kumar, Y.C. Kim and G.S. Lee, Text Detection using Multilayer Separation in Real Scene Images, 10th IEEE International Conferenceon Computer and Information Technology, 2010, pp. 1413-1417.
- Y. Zhang, C. Wang, B. Xiao, C. Shi, A New Text Extraction Method Incorporating Local Information, International Conference onFrontiers in Handwriting Recognition, 2012, pp. 252-255.
- H. Raj, R. Ghosh, Devanagari Text Extraction from Natural Scene Images, 2014 International Conference on Advances in Computing,Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), IEEE, 2014, pp. 513-517.
- A.N. Lai, G.S. Lee, Binarization by Local K-means Clustering for Korean Text Extraction, IEEE Symposium on Signal Processing andInformation Technology, 2008, pp. 117-122.
- H. Anoual, D. Aboutajdine, S.E. Ensias, A.J. Enset, Features Extraction for Text Detection and Localization,5th International Symposiumon I/V Communication and Mobile Network, IEEE, 2010, pp. 1-4.
- S.V. Seeri, S. Giraddi and Prashant. B. M, A Novel Approach for Kannada Text Extraction, Proceedings of the International Conference onPattern Recognition, Informatics and Medical Engineering, 2012, pp. 444-448.
- X.W. Zhang, X.B. Zheng, Z.J. Weng, Text Extraction Algorithm Under Background Image Using Wavelet Transforms, IEEE Proceedingsof International Conference On Wavelet Analysis And Pattern Recognition, Vol. 1, 2008, pp. 200-204.
- S. Audithan, RM. Chandrasekaran, Document Text Extraction from Document Images using Haar Discrete Wavelet Transform, EuropeanJournal of Scientific Research, Vol. 36, No. 4, 2009, pp. 502-512.
- S. A. Angadi, M. M. Kodabagi, Text Region Extraction from Low Resolution Natural Scene Images using Texture Features, IEEE 2ndInternational Advance Computing Conference, 2010, pp. 121-128.
- M.K. Azadboni, A. Behrad, Text Detection and Character Extraction in Color Images using FFT Domain Filtering and SVMClassification, 6th International Symposium on Telecommunications. IEEE, 2012, pp. 794-799.
- S. Hassanzadeh, H. Pourghassem, Fast Logo Detection Based on Morphological Features in Document Image, 2011 IEEE 7th InternationalColloquium on Signal Processing and its Applications, 2011, pp. 283-286.
- Y. Song, A. Liu, L. Pang, S. Lin, Y. Zhang, S. Tang, A Novel Image Text Extraction Method Based on K-means Clustering, SeventhIEEE/ACIS International Conference on Computer and Information Science, 2008, pp. 185-190.
- W. Fan, J. Sun, Y. Katsuyama, Y. Hotta, S. Naoi, Text Detection in Images Based on Grayscale Decomposition and Stroke Extraction,Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2009, pp. 1-4.
- N. Anupama, C. Rupa, E.S. Reddy, Character Segmentation for Telugu Image Document using Multiple Histogram Projections, GlobalJournal of Computer Science and Technology, Vol. 13, 2013, pp. 11-16.
|