ISSN ONLINE(2278-8875) PRINT (2320-3765)
ISSN ONLINE(2278-8875) PRINT (2320-3765)
R.Manikandan1 , M.Bhoopathi2
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
In deregulation power market system security is one of the challenging tasks due to competition and open access network. The security appraisal is an essential task as it gives knowledge about the system state in the event of contingency. In this paper presents contingency analysis of power system is to predict the line outage, generator outage and to keep the system secure and reliable by using full Newton‟s method. The full Newton‟s algorithm is more efficient for large power system. This result tends to be significantly more accurate and allow for gauging voltage/VAR effects. Whenever the maximum violation is occur in power system, that line and generator is outage element. So we find the maximum violation in the system network. IEEE-14 bus is the test system for contingency analysis by using power world simulator.
Keywords |
||||||||
| deregulation, contingency, appraisal, line outage, generator outage. | ||||||||
INTRODUCTION |
||||||||
| The power system consists of generation, transmission, distribution bundled together. In deregulation unbundling of power system network for efficiency, reliability and least price of power to the customer [1]. Under deregulation minimum price of power transfer to the utility, that time more number of buyers to buy the power from the generation. But all the transmission lines and generators have some limits [2]. Whenever the demand of power is maximum than compared with the transfer limits, the line will be damaged. The power demand is reduced then the generator is reliving from the power system network [3-6]. The system security will be collapsed. So the secured dispatch scheduling of power market is important due to open access and competition. Before security assessment the contingency analysis is needed [7]. The contingency limits are based on system operator experience. But this methodology not predicts the security limits. Before secured dispatch scheduling we have to analysis the contingency under single outage of line, generator and multiple outage of combination of both line and generator [8-10]. Whenever the maximum violation in the element some line and generator get damaged. So the contingency analysis is essential. Various methodologiesare used for contingency analysis such as fast decoupled method, DC power flow, neural network and fuzzy theory [10]. But full NewtonâÃâ¬ÃŸs method is high accurate, reliable and better solution. | ||||||||
| In this paper presents the contingency analysis of test system by using full NewtonâÃâ¬ÃŸs method in power world simulator and two important factor of line outage distribution factor and generation shift factor. In state estimation based contingency analysis more complex. So the student friendly software of power world simulator is used for analysis. The proposed algorithm of NewtonâÃâ¬ÃŸs method based contingency selection is presented. The mathematical formulation is in section II. The contingency analysis algorithm is in power world simulator in section III. The description of test system is in section IV. In section V includes simulation results with description and conclusion from the result in section VI. | ||||||||
PROBLEM FORMULATION |
||||||||
| The power world simulator can be set to use a full Newton solution or use a DC load flow method to analyse each contingency. The full Newton approach is not as fast as a DC load flow, but the results tend to be significantly more accurate and allow for gauging voltage/VAR effects. The Newton solution method (also called Newton-Rapson method) is more efficient for large power systems. The number of iteration required to obtain a solution is independent of a system size but more functional evaluation are required at each iteration. | ||||||||
| Equation for bus Admittance matrix | ||||||||
| In above equation j includes bus i expressing this equation in polar form, we have | ||||||||
| The complex power at bus | ||||||||
| Substituting from (2) for Ii in (3) | ||||||||
| Separating the real and imaginary parts | ||||||||
| Equation (5) and (6) constitute of nonlinear algebraic equation in terms of the independent variables, voltage magnitude in per unit and phase angle in radians. | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
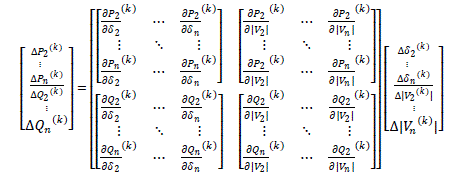
| In above equation, bus 1 is assumed to be slack bus. The jacobian matrix gives the linearized relationship between small changes in voltage angle Δδi(k) and voltage magnitude Δ|Vi(k)| with small changes in real and reactive power ΔPi(k) and ΔQi(k) elements of jacobian matrix are the partial derivatives of (5) and (6) evaluated at Δδi(k) and Δ|Vi(k)| | ||||||||
| Accordingly there are (n-1) real power constraints and (n-1-m) reactive power constraints and the jacobian matrix is the order of (2n-2-m) (2n-2-m). | ||||||||
| J1 is the order of (n-1) x (n-1) | ||||||||
| J2 is the order of (n-1) x (n-1-m) | ||||||||
| J3 is the order of (n-1-m) x (n-1) | ||||||||
| J4 is the order of (n-1-m) x (n-1-m) | ||||||||
| The terms ΔPi(k) and ΔQi(k) are difference between the schedule and calculated values, known as the power residuals, given by | ||||||||
| The new estimated for bus voltage is | ||||||||
| Another solution method in simulator is DC load flow. These factors can be derived in a variety of ways and basically come down to two types. | ||||||||
| a) Generation shift factors | ||||||||
| b) Line outage distribution factor | ||||||||
| The generation shift factors are designated Ali and have the following definition | ||||||||
| The line outage distribution factors are used in a similar manner, only they apply to the testing for overloads when transmission circuits are lost. By defining the line outage distribution factor has the following meanings. | ||||||||
PROPOSED APPROACH |
||||||||
| Before the secured dispatch scheduling the contingency analysis is the important one for selection of contingency element in the maximum violation of the system network. The following steps to involve in the contingency analysis. | ||||||||
A. CONTINGENCY ANALYSIS ALGORITHM |
||||||||
| Step 1: Draw the Simulink one line diagram in new case window of power world simulator for the given power System in edit mode. | ||||||||
| Step 2:Save the case with apt name. | ||||||||
| Step 3:Select run mode. | ||||||||
| Step 4:Play or Run the one line diagram in tool menu. | ||||||||
| Step 5:Select CONTINGENCY ANALYSIS in tool menu, then the contingency analysis dialogue box is open. | ||||||||
| Step 6:Right click on label and select auto insert contingencies through insert special option. | ||||||||
| Step 7:Verify that single transmission line or transformer is selected. | ||||||||
| Step 8:If can limit the contingencies inserted to only those meeting a definedfilter. | ||||||||
| Step 9:We want to insert contingencies for all branches and generators so nofiltering is desired. | ||||||||
| Step 10: To check the following conditions | ||||||||
| a) Remove the checkmark in use area/ zone filters. | ||||||||
| b) Verify no other options are selected. | ||||||||
| Step 11: Click do insert contingencies button to accept the all contingencies. | ||||||||
| Step 12: Click YES to get the contingencies. | ||||||||
| Step 13: Now the contingency analysis dialog shows contingencies. | ||||||||
| a) Right click on the list display on the contingency tap and select insert special and click auto insert to the local menu | ||||||||
| b) Select single generating unit then click the do insert contingencies button. Click YES to complete. | ||||||||
| Step 14:The auto insert tool did not insert a contingency for the generator connected to the slack bus. | ||||||||
| Step 15:Click „start runâÃâ¬ÃŸ on the contingencies tab click start on summary tab or Run contingency. | ||||||||
| Step 16:Select the maximum violation of contingency analysis taken for account in the secured dispatch of deregulation of power market. | ||||||||
TEST SYSTEM |
||||||||
| The contingency analysis of 14-bus test system is shown below when the power flow is running on the power world simulator. The percentage of power flow is mentioned in power flow diagram. It consists of five generators for dispatch of power. | ||||||||
SIMULATION RESULTS |
||||||||
| The contingency analysis is classified as single contingency, multiple contingency. In IEEE test system having 110 contingency. But in maximum violation of single contingency of line and generator is taken in account in table1.which depends on maximum branch percentage and minimum voltage the contingency element is taken in account for security dispatch of power. | ||||||||
| The combination of both generator and line contingency is also in security analysis. The maximum violation only taken in account in table 2. The L_ indicates line and G_ indicates generator. | ||||||||
| The generation shift factor describe a generator power sensitivity under the contingency condition is shown in table 3. It consists of 5 generators and their sensitivity. | ||||||||
| Line outage distribution factor (LODF) is used to approximate the change in the flow on one line caused by the outage of a second line. It is a real time operation. The percentage of LODF is tabulated in each line in table 4. | ||||||||
CONCLUSIONS |
||||||||
| The Full NewtonâÃâ¬ÃŸs method based contingency analysis algorithm is high accuracy and better efficiency. The contingency analysis in power world simulator is easy to run the power system and more reliable than compared with state estimation based contingency analysis. The security limits described from maximum violation of the element of test system and sensitivity analysis of both line outage distribution factor and generation shift factor. In feature power world simulator based contingency analysis is widely used for secured dispatch scheduling and the demand response improvement of deregulated power market. Voltage profile is varied which depends on violated and unviolated line is shown in Figure 2 and 3. | ||||||||
Tables at a glance |
||||||||
|
||||||||
Figures at a glance |
||||||||
|
||||||||
References |
||||||||
|