e-ISSN: 2320-0812
e-ISSN: 2320-0812
Rahul Kasar1*, Ashish Gogia2, Kartik Shah2, Vetriselvan1 and Chinmay Anand2
1Health Foods Research Lab, Phytochemistry, Research and Development, The Himalaya Drug Company, Makali, Bangalore 562 123, Karnataka, India
2Formulation and Development Department, Cadila Pharmaceutical Limited, Ahmedabad, Gujrat, India
Received date: 28/08/2013; Revised date: 10/09/2013; Accepted date: 17/09/2013
Visit for more related articles at Research & Reviews: Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis
Chromatography is one of the fast emerging tools by which the quality control and fingerprint of herbs can be maintained. Using this technique, the identification of various chemical markers of the herbal drugs can be easily done and it also helps to identify the same herbs in combination. Application of TLC/HPTLC methodology in testing of phytoconstituents from individual herbal drugs and fingerprint characteristic of the herbal plants are reviewed in this paper. Popularity of TLC/HPTLC analytical method for analysis of herbal drugs due to economic, rapid, simultaneously screening of large number of herbal samples and less time consuming methods. The different mobile phase, spraying reagent, property of herbal drugs and its phytoconstituents, TLC/HPTLC plates, trouble shooting of HPTLC, different developing solvents and chromatograms are pointed out in this paper.
Quality control, Phytoconstituents, TLC/HPTLC, Herbal industries.
Many aqueous extract or alcoholic extracts, hydro alcoholic extracts are used in manufacturing Ayurvedic and herbal formulations. If the phytochemical profile of the plant or its part is known an appropriate kind of extract can always be used by selection for a particular purpose. A TLC or HPTLC profile of the phytochemical can be employed for the similarity or dissimilarity or to find out the presence or absence of the certain phytochemicals [1]. TLC/HPTLC has excellent resolution and, therefore, permits simultaneous identification of a wide range of substances in a single run. In this paper, application of TLC/HPTLC methodology in testing, investigation, advantages of HPTLC for analysis of Medicinal plants, General guideline for the analysis by HPTLC, Trouble shooting in HPTLC, Typical tasks in the quality control of medicinal plant, Documentation are reviewed as table no 1, 2, 3.
Parameters of Planar Chromatography
The articles in this series are dedicated to the important steps of planar chromatography and their parameters, which influence the chromatographic result. Hints for optimization are given to help the reader to use planar chromatography most efficiently. General methodology for HPTLC is a guideline for the analysis by HPTLC. This SOP provides general guidance for HPTLC.
TLC/HPTLC Methodology [5]
The components of TLC/HPTLC methodology for drug testing and investigation are 1) Selection of TLC material, 2) use of appropriate developing solvents, 3) use of appropriate color reagent and 4) interpretation of TLC/HPTLC result. Various aspect of TLC/HPTLC methodology is reviewed in this section.
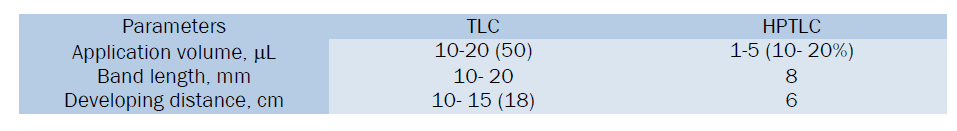
Conversion of methods from TLC to HPTLC
Types of TLC plate
HPTLC analysis was performed on a Camag HPTLC system .The plate used was HPTLC 254 silica gel 60 (E. Merck). Camag HPTLC system equipped with a sample applicator Linomat IV, Twin trough developing chamber, Integration software system, CATS V.4.06, TLC scanner III in absorbance/reflectance mode
Spray reagent
After the plate is developed, it is sprayed with various reagents for the development of color often the color reaction is not confined to a single compound but is produce by several compounds belonging to a particular group. Therefore along with using migration rates, various constituents of a sample are also identified their response to chemical treatment. The coloring reagents commonly used for drug testing are listed in table no.5 and the correlations of color response with particular aspect of drug structure are reviewed.
Acceptances of Chromatographic Techniques in Pharmacopoeia as Quality Control Methods [6]
As primary source for TLC fingerprint method for identity of Herbal medicinal products (HMPs) and starting materials such as plants material, crude drugs and extracts, the European Pharmacopoeia, the U.S. Pharmacopoeia/ National Formulary, the British Herbal Pharmacopoeia, and the Chinese Pharmacopoeia may be consulted. Although none of these methods represent the state-of-the-art in modern HPTLC, they still have the status of validated methods.
It is also observed that most of the Pharmacopoeias such as Indian Herbal Pharmacopoeia, European Pharmacopoeia, the U.S. Pharmacopoeia/ National Formulary, the British Herbal Pharmacopoeia, and the Chinese Pharmacopoeia consist of standard quantitative and qualitative tests for phytoconstituents. The commonly used quantitative method for analysis is HPTLC e.g. Diosgenin from Dioscorea composita, Emodine & Crysophanol from Rheum emodi, Glycyrrhizine from Glycyrrhiza glabra and Ecdysterone. Test for identification of phytoconstituents are also mentioned in these pharmacopoeia e.g. podophyllotoxin from podophyllum hexandrum, Solasodine from Solanum americanum
Far any other TLC/HPTLC method used in quality testing the EU guidelines “Note for Guidance on Validation of Analytical Methods; Definitions and Terminology”. Validation is required if Pharmacopeial method is optimized or adapted for specific tasks in quality control or if a method is taken from other reliable sources such as the American Herbal Pharmacopeia (AHP), the Indian Herbal Pharmacopoeia, or Plant Drug Analysis: A Thin Layer Chromatography Atlas Of all the sources, only the AHP monographs feature modern HPTLC methods for identification.
Typical Tasks in the Quality Control Of Medicinal Plant [7]
Identification
Identification can be considered as the dominating application of TLC. Identification is established by comparison of a sample with a reference on a same plate. It is an advantage of TLC that not only the entire sample can be seen but also several samples can be easily compared at the same time. The prevailing value of HPTLC fingerprints is the visual impression, which can be further expanded by multiple detection (visualization or derivatization). A broad spectrum of constituent can thus be detected and described without the need to know the chemical nature of each zone of the chromatogram. Finally fingerprint chromatograms with a visible pattern of bands provide fundamental data. Ideally, to achieve maximum information, several suitable methods should be used for fingerprinting different group of phytoconstituents.
In a cGMP environment, the identity of raw material must be documented. Electronic images of HPTLC fingerprints are conveniently generated and saved. They are typically evaluated based on number, color, sequence, and relative position of zones with respect to zone obtained on the same plate with chemical or botanical reference materials. General HPTLC methods followed for typical class of phytochemical are mentioned in Table no.4 and common spraying regent mention in Table no. 5. The methods used must be specific. That means only a sample properly identified will comply with the specification and any adulterant produces a significantly different fingerprint.
Semi quantitative assessments
In process control and stability tests, HPTLC fingerprints are often used during product and process development to establish proper extraction parameters, standardized extracts and detect any changes or degradation in the material during formulation. In a cGMP environment, it is essential to document how the raw material is converted/ preserved in the individual steps of the production process. Fingerprint of some medicinal plants [8] by TLC/HPTLC method are reported in table no. 6.
Quantitation of marker compound
Quantitation of marker compound is the most demanding application of TLC. Due to limited separation power of the technique, it is often not possible to obtained baseline separation of all components of such complex samples as medicinal plant materials. Therefore, most assays are typically based on HPLC. However, it often overlooked that with proper instrumentation and suitable methodology, quantitative determinations by HPTLC are no difficult. An example of quantitative determination [9] is shown in Figure 1 and screening of some phytoconstituents by TLC/HPTLC method reported in table No 7.
Documentation
Each developed plate is documented under UV light at 254nm, UV light at 365nm, and white light. If a type of light does not produce usable information, that fact must be documented. If plate is derivatized, images are taken out before and after derivatization. Image labels should include the plate number as well as the derivatization and the illumination mode. Video and digital documentation systems are widely used to document high-performance thin- layer chromatograms. The advantages of modern electronic documentation systems are instant images of the chromatogram/ fingerprint.
Trouble Shooting in HPTLC:
Fix the TLC problems before they cause trouble. Ideally all problems will be prevented by a good maintenance plan. One way to minimize problems is to anticipate them so they can be fixed at your convenience. Some problems, however, cannot be avoided, but good work practices will minimize the impact of such problems. Short remedies for trouble shooting in HPTLC are discussed in table no 8.
1. Quality control of herbal medicinal products (HMPs) is a challenging analytical task, because the entire herbal drug or herbal drug preparation is regarded as the active substances, regardless of whether constituents with defined therapeutic activity are known.
2. In herbal medicinal products the entire herbal drug or an herbal drug preparation is regarded as the active pharmaceutical ingredients
3. In quality control and stability testing of herbal medicinal products, fingerprint chromatograms are used as powerful tools to evaluate and compare the composition of compounds in such product [10]
4. Visualization (so- called fingerprint) of the entire pattern of compounds present in an herbal drug or preparation is therefore fundamental in the quality and stability testing of HMPs and the respective materials.
High- performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC, Planar chromatography) is an ideal tool for analysis of medicinal plant and offers several advantages. In its traditional form, thin layer chromatography has a long record in almost all pharmacopoeias for its use in identification of botanical raw materials [11,12]. However, HPTLC is not limited to identification. It can also be used for control of batch to batch consistency in stability testing of medicinal plants and for purposes of control throughout the entire manufacturing process of HMPs [12-14]. See Figure No. 1a. It helps to check quality control of batch to batch consistency. This can be done by well photodocumentation under light at 254 nm, 365 nm, and visible mode. Compare that scanned 3D chromatogram for further study.
The proposed HPTLC method provides an experimental procedure to identify the presence of phytochemical markers in the herbal dosage form and specifically to verify genuinity of plant material used which has direct correlation with the therapeutic efficacy of the finished product.
These methods were also employed to analyze commercial samples to illustrate their application in qualitative (fingerprint) and quantitative determination, demonstrating their feasibility in the quality control of phytoconstituents from mentioned Herbal drugs and formulations. This will help induced to come out uniform standard products, which will restore faith of product and Alternative herbal medicine therapy.