Keywords
|
| Cross-layer design, minimum energy control, networks, optical communication equipment, traffic grooming, energy efficiency, IP-over-WDM, load adaptive, network optimization, routing stability, Packet switching, Packet–optical integration |
INTRODUCTION
|
| In this chapter discuss about Increase in internet traffic brings a significant issue of the energy consumption problem as well as the network capacity problem. Network equipment consumes 22 GW globally which is equivalent to 14 percent of energy consumption of the information and communication technology (ICT) sector in 2007. If internet traffic increases as predicted, the problem of energy consumption of networks will be the most critical issue that requires significant research effort for the energy-aware solution. In order to cope with such rapid increase in energy consumption in networks, a lot of research efforts are dedicated to solve the problem recently. Energy consumption analyses for network equipment have been also reported for understandings of the energy consumption of networks. Traffic grooming technique is one of the prime candidates to save energy consumption of networks, because it can maximally utilize a WDM optical layer that consumes relatively very little energy. Optical networks are a relevant part of transport infrastructure, because of their high capacity and effective low cost if compared with digital networks. Benefits of packet–opto integration could be summarized just by considering the ability of offloading pass-through traffic from the packet layer down to the WDM layer, so as to reduce the cost and power consumption, by eliminating unnecessary packet processing. |
LITERATURE SURVEY
|
| Chankyunlee [1, 2] says that Energy consumption measurement of network equipment has been studied in order to accurately model energy consumption of network equipment. Energy consumption of network equipment in an idle state is reportedly huge according to the energy proportionality index (EPI) of network equipment is proposed to model how much network equipment consumes energy proportionally to a network load. In addition to that energy savings impact by traffic grooming technique in network provisioning, and the equipment cost, operation cost, and energy consumption of networks Provisioning for dynamic traffic and investigates energy consumption by ILP with algorithm. Marce Caria has proposed load adaptive energy efficiency schemes are mechanisms to dynamically adapt the network’s capacity to the actual traffic demand in order to shutdown idle Equipment so that electrical power can be saved [2]. Benefits of packet–opto integration could be summarized just by considering the ability of offloading pass-through traffic from the packet layer down to the WDM layer, so as to reduce the cost and power consumption, by eliminating unnecessary packet processing [3].The analyze of the relationship between reliability, performance, and power consumption, with the result that using power consumption as the foremost parameter in network planning creates networks with concentrated connections, leading to reliability problems. The performance of IP link Switch-Off schemes was analyzed where not only idle links but also certain nodes can be completely switched off, since the authors assume that zero traffic is generated or terminated at some nodes. For the Switch-Off scheme, it is assumed that the network links consist of multiple cables whose capacities are aggregated and that individual cables can be powered down to save energy. |
PROPOSED SYSTEM
|
| In this paper, our proposed new algorithm is the discussed which provides better performance than that of the existing algorithm. However, from the literature survey, this work realized that current network equipment consume energy inefficiently due to poor energy-load proportionality of network equipment which causes a vast amount of energy consumption even in an idle state. To address this issue, this work is planned to introduce an efficient Traffic Grooming Framework called energy proportionality index (EPI) with Switch-On approach, which could optimize the energy consumption of IP/WDM but causes considerable computational complexity. This could be minimized, In our proposed system, if we are designing new mechanism which reduces the packet processing period. which will reduce the computational complexity, it also further improve the performance of Optical Network in terms of Power Consumption, Throughput, Router Utilization and Bandwidth Utilization. |
| A. System architecture design |
| B. Switch-On |
| However, the Switch-On scheme is not without challenges: the newly established circuits can also destabilize the IP routing, are often inadequate in size due to the established standards on circuit capacity, and require advanced planning and reconfiguration methods. In this architecture diagram represented a comparative study of Switch on and EP-Switch On scheme as shown in Fig.1 Switch off scheme Proposed load adaptive energy efficiency schemes are mechanisms to dynamically adapt the network’s capacity to the actual traffic demand in order to shutdown idle Equipment so that electrical power can be saved. |
| C. EP switch-On |
| Energy consumption measurement of network equipment has been studied in order to accurately model energy consumption of network equipment. Energy consumption of network equipment in an idle state is reportedly huge according to the energy proportionality index (EPI) of network equipment is proposed to model how much network equipment consumes energy proportionally to a network load. In addition to that energy savings impact by traffic grooming technique in network provisioning, and the equipment cost, operation cost, and energy consumption of networks Provisioning for dynamic traffic and investigates energy consumption by ILP with algorithm. In our EP SWITCH-ON system, the Load balancing concept is used to reduce the energy consumption by the network. |
| D. Proposed Technique Used |
| The objective of our algorithm is to optimize routing and to adapt the logical topology of IP layer to the variations of traffic in network. Different routing configurations lead to different logical topologies and different level of utilization in network links and channels. Based on the router utilization we have designed an algorithm for improving the energy consumption which is given below, |
| 1. If UR<=15% Make Router to |
| Sleep State |
| (Switch-OFF) |
| 2. Else If 60%< =UR<=80% Call Router From |
| Sleep State (If Exist) |
| (Switch-ON) |
| 3. If UR>80% Restrict New |
| (Admission Control Mechanism) |
IMPLEMENTATION AND RESULTS
|
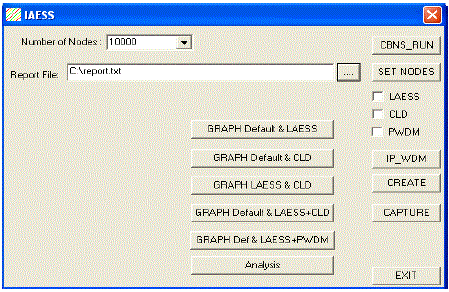
| Our implementation is based on Boson NetSim Network Simulator which are discussed as shown in Fig.2. To evaluate our Independent Energy Saving Scheme design with Packet switching and WDM technology to save energy consumption of optical networks. |
| A.Execution |
| The execution consists of four stages: setting the nodes, fixing the type of the network, creating infrastructure and running the tool. |
| B. Report |
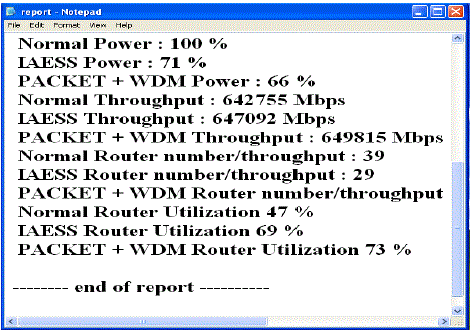
| After completing the execution, the report can be generated for Default, Combine with Load Adaptive Energy and Cross Layer Design system, combine with packet switching technology and WDM technology for proposed system. The report can be shown in the Fig.3 contains Power in percentage (%), Throughput in mbps, Number of router, Router utilization in percentage (%). |
| From the report window it shows that Indepentent energy saving scheme with packet and WDM switching technology outperforms in terms of power consumption, throughput, and router utilization. |
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
|
| The result comparisons with existing and proposed graph representations are shown as following sections. |
| A. Power Consumption |
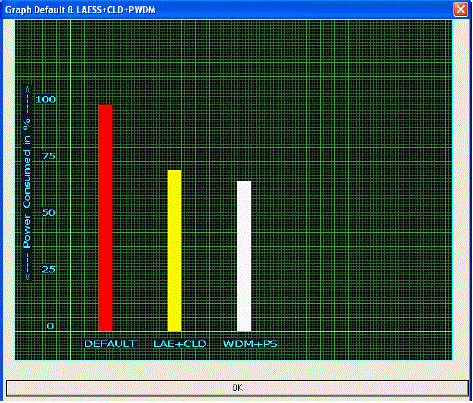
| The power consumption comparison is shown in Fig. 4. It shows that the power consumption for combines with WDM and PS (66%) which is less than the Default power consumption (100%) and LAE+CLD (71%), as to be the get reduced power in proposed system. |
| B. Throughput |
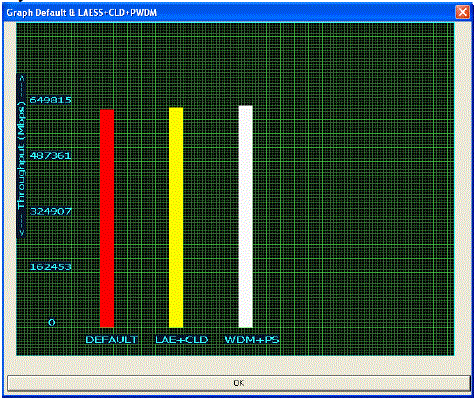
| The throughput comparison is shown in Fig. 5. It Shows that the throughput for combines with WDM and PS (649815 mbps) which is higher than the Default throughput (642755 mbps) and LAE+CLD (647092 mbps), as to be get increased throughput in proposed system. |
| C. Router Utilization |
| The Router Utilization comparison is shown in Fig. 6. It Shows that the Router Utilization for combines with WDM and PS (73%) which is higher than the Default Router Utilization (47%) and LAE+CLD (52%), as to be get increased Router Utilization in proposed system. |
CONCLUSION
|
| This tremendous growth rate of Internet faces a few challenges such as Enormous Energy Consumption, Communication Delay, Throughput and Bandwidth Requirement. The Enormous Energy Consumption causes Global Warming. To address this major issue, were Proposed and designed an Intelligent Adaptive Energy Saving Scheme (IAESS) for saving energy in Optical Networks but causes considerable computational complexity. This could be minimized, if we are designing an independent Energy Saving Scheme, which will reduce the computational complexity, which will further improve the performance of Optical Network in terms of Power Consumption, Throughput, Router Utilization and Bandwidth Utilization. |
| |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
|
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 4 |
Figure 5 |
Figure 6 |
|
| |
References
|
- Marcel Caria, MohitChamania, and AdmelaJukan, “A Comparative Performance Study of Load Adaptive Energy Saving Schemes for IP-Over-WDM Networks”, Journal of Optical Communication Networks, Volume 4, No. 3, March 2012.
- Yoontae Kim and Chankyun Lee, “IP-Over-WDM Cross-Layer Design for Green Optical Networking With Energy ProportionalityConsideration”, Journal Of Light wave Technology, Vol. 30, No. 13, July 1, 2012.
- Paola Iovanna, Francesco Testa, Roberto Sabella,“Packet–Optical Integration Nodes for Next Generation Transport Networks,’’ Journal ofOptical Communication Networks Volume 4, No. 10, October2012.
- WeigangHou, Lei Guo, “Robust and Integrated Grooming for Power and Port-Cost-Efficient Design in IP Over WDM Networks”, Journal OfLight wave Technology, Vol. 29, No. 20, October 15, 2011.
- Xin Liu, KerimFouli, Rui Kang, and Martin Maier, “Network Coding Based Energy Management for Next-Generation Passive OpticalNetworks”, Journal Of Light wave Technology,Vol. 30, No. 6, March15, 2012.
- Yi Zhang, Massimo Tornatore, and PulakChowdhury, “Time-aware Energy Conservation in IP-over-WDM Networks”, OSA / IPR/PS 2010.
- GangxiangShen and Rodney S. Tucker,“Energy-Minimized Design for IP Over WDM Networks”, Journal of Optical Communication Networks,Vol. 1, No. 1, June 2009.
|