This paper presents the work done on different modulation schemes for Single carrier frequency division multiple access (SC-FDMA).SC-FDMA has turned out to be a suitable solution for high data rate uplink communication systems. It has become the choice for uplink transmission in Long Term Evolution (LTE).OFDM was an excellent choice for a multipath fading channel. But it suffers from the major limitation of Peak to average power ratio problem. PAPR is highly detrimental to battery powered devices like mobile phones. SC-FDMA can overcome the PAPR limitation of OFDMA signals. In this paper we are finding out the best modulation scheme for PAPR reduction in SC-FDMA. Here we are using QPSK, QAM and CPM modulations for studying PAPR reduction. SC-FDMA uses 2 schemes for sub-carrier mapping. They are Interleaved (IFDMA) and localized (LFDMA) mapping. In this paper we are comparing PAPR of IFDMA, LFDMA and OFDMA. Similarly BER performance of the system will also be studied. The effect of pulse shaping on the signal will also be analyzed in the paper.
Keywords |
| Single carrier frequency division multiple access (SC-FDMA), Interleaved frequency division
multiplexing (IFDMA), Localized frequency division multiplexing (LFDMA) and peak to average power ratio (PAPR). |
INTRODUCTION |
| Cellular communication has grown rapidly through a sequence of generations which began with the progress in
technology with each new decade. The demand for higher data rate and throughput has been increasing tremendously
in recent years. To support these requirements of users third generation partnership project (3GPP) has developed a
new radio access technology called long term Evolution (LTE).The high data rate of LTE not only requires a wider
bandwidth but also an advanced modulation technique. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband
digital communication [1]. But this modulation scheme has a major limitation of high PAPR which can increase
complexity and power of transmitter (mobile) in uplink. The PAPR of a signal x (t) is given by, |
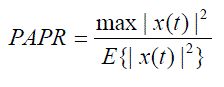 |
| PAPR becomes a major constraint in uplink communication because high PAPR of signal will degrade BER
performance of the system. For signals with large PAPR, the average input power must be reduced. If the input power is
not reduced then signal distortion will occur which can result in out-of-band spectral re-growth of signal as the signal
will be amplified in the non-linear region of high power amplifier. High power amplifiers are most efficient when they
are driven into saturation. So input power back off will reduce the efficiency of the power amplifiers. In order to
avoid distortion of the transmitted waveform, the power-amplifier at the transmitter front end must have a wide linear
range to include the peaks in the transmitted waveform. Building power amplifiers with wide linear ranges is a costly
affair [2]. So an uplink scheme should be designed with trade-off between low computation complexity and system
performance. The other limitations of OFDM signal includes high sensitivity to carrier frequency offsets and spectral null. So a solution to these limitations of OFDM was to use SC-FDMA which is similar to OFDM but has an additional
DFT pre-coding prior to OFDM modulation |
| The following sections are organized as follows. Section 2 provide an overview on SC-FDMA system. Section 3
highlights the modulation techniques used in the paper. Section 4 discuss the simulation results of BER and PAPR
obtained from SC-FDMA system for different modulation. Finally the work is concluded in Section 5. |
RELATED WORKS |
| A number of techniques were developed to overcome PAPR limitation of OFDM signal. These techniques can be
classified into two. They are distortion based and non-distortion based techniques. Distortion based technique can cause
spectral re-growth of signals. Clipping is a distortion based technique in which input OFDM signal is compared with a
set threshold value. If amplitude of signal exceeds the threshold then clipper will limit the signal. But it was a nonlinear
operation and had resulted in out-of band radiation of signals and degradation in bit error rate performance of
system. |
| The PAPR reduction techniques which do not distort shape and cause spectral re-growth of signals are called nondistortion
technique . It includes tone reservation and selected mapping .In tone reservation[3] a set of reserved tones
are selected to design a peak cancelling signal. But it had slower convergence toward optimal solution and has resulted
in bandwidth sacrifice as tones have to be reserved. Selected mapping multiplies the input data with a random series
and resultant series having lowest PAPR is chosen for transmission. This method has the advantage that it will not
eliminate peaks and can handle any number of subcarriers. But limitation of this technique was that it required
additional side information that has to be transmitted to the receiver to recover the information. This technique can
provide better PAPR reduction but is iterative in nature [4] .So transmitter complexity will increase with increase in
number of iterations. |
| Another method to overcome PAPR problem is based on signal transformation. The conversion of OFDM signal into a
constant envelope by phase modulation can ensure a very low PAPR level of 0dB [5]. It provides faster side-lobe rolloff
than OFDM. But orthogonality of subcarriers was not maintained in this method. |
SC-FDMA |
| The major reason for PAPR in OFDM is its multi-carrier structure. So conversion of multi-carrier OFDM signal into
single carrier can effectively reduce PAPR of the signals. Pre-coding of OFDMA signal with Discrete Fourier
transformation (DFT) can convert it into single carrier frequency division multiple access signal (SC-FDMA). SCFDMA
has similar performance and essentially the same overall complexity as that of an OFDMA system. It can
provide flexible bandwidth assignment for different users and was chosen for uplink in 3GPP Long Term Evolution
(LTE) due to its low PAPR property. SC-FDMA transmitter and receiver are given below |
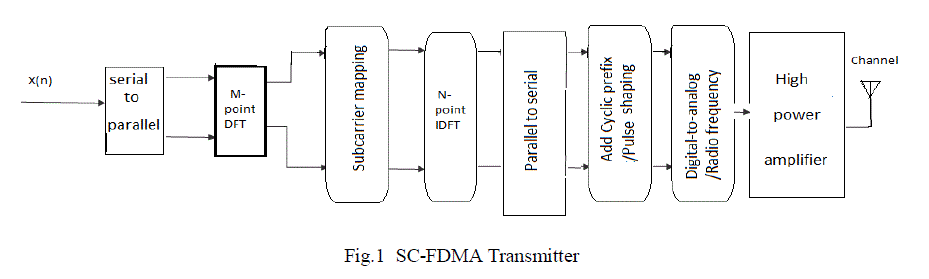 |
 |
| The information bits can be modulated using any of the modulation techniques like QPSK, QAM or CPM. The
complex modulated signal undergoes discrete time Fourier transformation. The number of DFT points (M) is defined
by the number of symbols to be transmitted [8].The DFT output are then mapped on to different sub-carrier using two
mapping schemes. The number of sub-carriers (N) allocated for the entire users is given by the following equation |
| N = M.Q |
| Where, M represents the number of DFT points and Q represents number of users. Sub-carrier mapping can be
classified into two. They are |
| 1) Localized Mapping (LFDMA) and |
| 2) Distributed Mapping. |
| In localized mapping each user is given a set of adjacent sub-carriers [10]. This scheme can provide multi-user
diversity even in the presence of frequency selective fading by assigning each user to subcarriers in the portion of the
signal band where that user has favourable transmission characteristics (high channel gain).This requires channeldependent
scheduling (CDS) of subcarriers. CDS requires the system (base station) to monitor the channel quality as a
function of frequency for each terminal, and adapt assignment of subcarriers according to changes in channel frequency
responses of all other user terminals. In distributed mapping each user is provided a set of sub-carriers that are
distributed over the entire signal bandwidth. This can ensure high frequency diversity. Interleaved sub-carrier mapping
(IFDMA) is a special case of distributed mapping where sub-carriers allocated for user will be equidistant to one
another. It was found that IFDMA was suitable for users transmitting at a moderate bit while LFDMA can work better
in a system using high-bit-rate. LFDMA can provide better BER performance than IFDMA. LFDMA are usually used
in LTE uplink applications. |
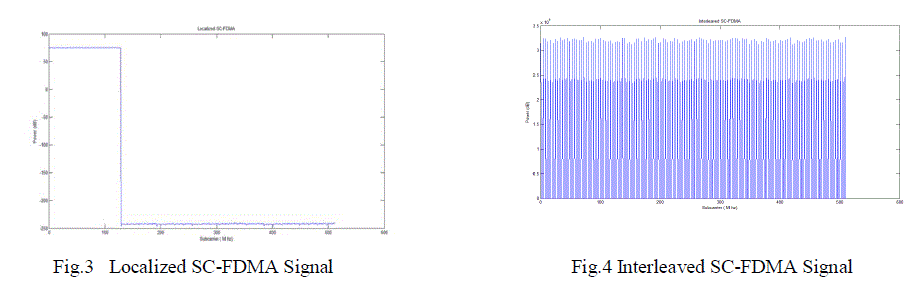 |
| The figures 3 and 4 shows localized and interleaved subcarrier mapping of 128 point DFT output on to 512subcarriers.We can observe that in localized mapping the signal have significant power level only over 128 subcarriers
and it reduces greatly after 128th sub-carrier. In interleaved mapping the signal is spread over the entire 512
sub-carriers. |
| The transmitter performs two important signal processing operation prior to transmission [11]. It inserts a set of
symbols referred to as a cyclic prefix (CP) to provide guard time against inter-block interference (IBI) arising from
multipath propagation. If CP length is greater than the maximum delay spread of the channel or is equal to length of
channel impulse response, there will be no IBI. It can convert discrete time linear convolution into discrete time
circular convolution. So the data transmitted through the channel can be modelled as a circular convolution between
channel impulse response and transmitted data block, which in frequency domain is a point-wise multiplication of the
same. Thus complexity of equalizer at the receiver can be reduced. The next operation done by transmitter includes a
linear filtering process referred to as pulse shaping for transmission of signal through a band limited channel [12].
Raised-cosine filters (RC) is one of the widely used pulse shaping filter in wireless communication systems. The
increase in roll off factor of filter will cause significant reduction in PAPR. But a trade-off between PAPR and out ofband
radiation is required because out-of-band radiation can increase with increase in roll-off. |
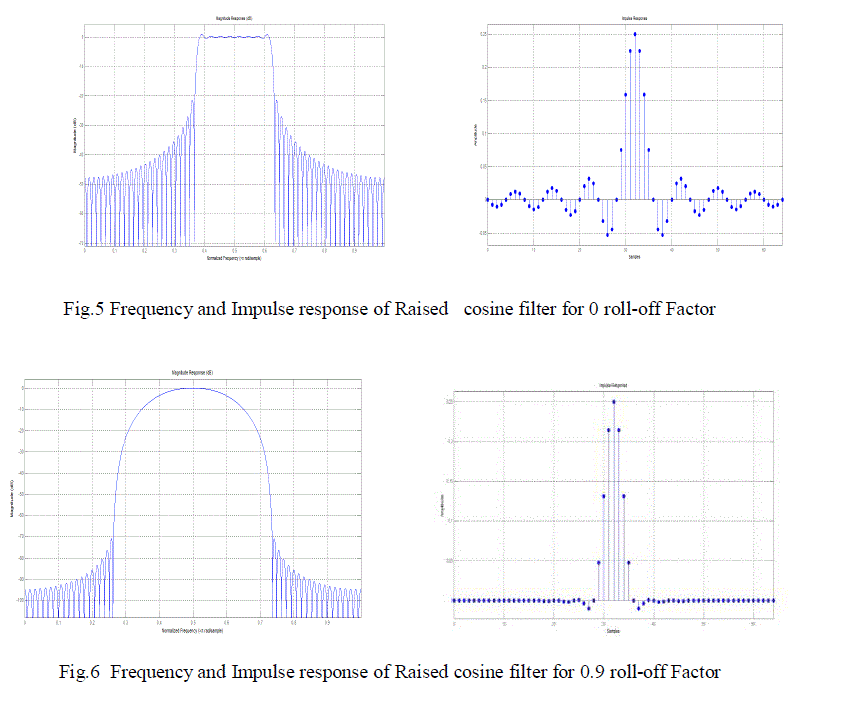 |
| The figures 5 and 6 shows frequency and impulse response of Raised cosine filter for roll-off factors of 0 and 0.9. We
can observe that as roll-off factor increases spreading of main-lobe will increase with reduction in power level of side
lobes. |
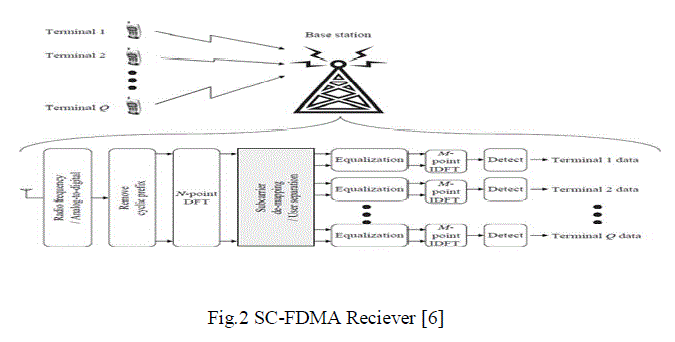
| The SC-FDMA receiver performs reverse operation of transmitter. The receiver transforms the signal into frequency
domain via DFT, de-maps the subcarriers and performs frequency domain equalization [13]. Equalization is done in
frequency domain because in broadband channels time domain equalizers are impractical as they have a very long
channel impulse response in time domain. For cellular systems with severe multipath propagation conditions, SCFDMA
signals will arrive base station with significant inter-symbol interference. The base station will use an adaptive
frequency domain equalization to cancel this interference. Most of the well-known equalization techniques like
minimum mean square error (MMSE) equalization, decision feedback equalization (DFE) and turbo equalization are
used. The equalized symbols are transformed back to time domain via IDFT and detection and decoding will be done
in time domain. |
MODULATION SCHEMES |
| In this paper we are using QPSK, QAM and continuous phase modulation (CPM) modulation scheme. The PAPR value
varies with the modulation schemes used. Constant envelope modulation like QPSK can ensure high power efficiency
and maintains low spectral side lobes. CPM have constant envelope and continuous phase which can provide high
spectral and power efficiency with better PAPR reduction. The modulation index can control spectral confinement of
CPM signal, smaller the index better will be the spectral confinement [7]. When modulation index increases BER
performance will be improved. But modulation and demodulation of CPM signal is complicated by the fact that initial
phase of each symbol will be determined by the cumulative phase of previously transmitted symbols which demands
receiver to have memory.CPM signals uses three types of pulse shaping for the signals namely rectangular, raised
cosine and Gaussian. When length of the pulse shape is equal to 1 (L=1), it is called full response signal [14]. When
length is greater than1 (L>1) it is called partial response signal. Full response signal will be having a better BER and
PAPR reduction than partial response signal. |
SIMULATION REULTS |
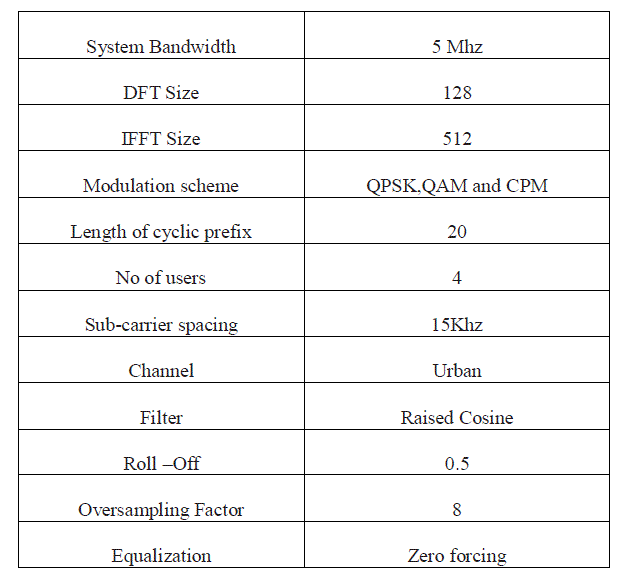
| The simulation of SC-FDMA system for QPSK, QAM and CPM modulation was done using monte-carlo method for
random bits of 100 (BER) and 10000 (PAPR) frames with each frame containing 128 symbols that are averaged over
the entire duration of transmission. The simulation parameters are given below |
 |
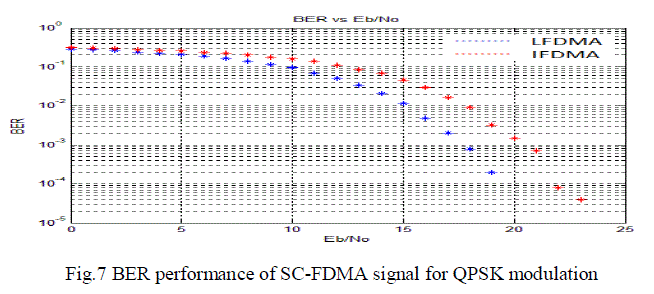 |
| The BER performance of LFDMA and IFDMA for QPSK SC-FDMA is done. It was observed that BER is better for
LFDMA than IFDMA. BER will decrease with increase in Eb/No. |
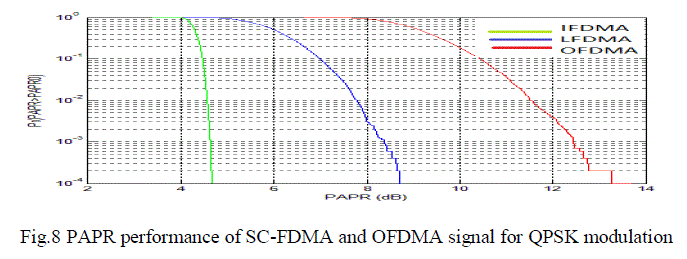 |
| The PAPR of QPSK signal is plotted against complementary cumulative distribution function(CCDF).The peak
power of a signal x(t) will be maximum of its squared envelope x(t)2. But for a continuous random process, max x(t)2 can be unbounded. For a random process with discrete values, max x(t)2 will be bounded but it may occur at
very low probability. The distribution of x(t)2 is a useful performance indicator and it will be better to be described
with complementary cut-off probability. From the graph it can be observed that SC-FDMA will be having lower PAPR
compared to OFDMA and PAPR reduction is higher in IFDMA than LFDMA. |
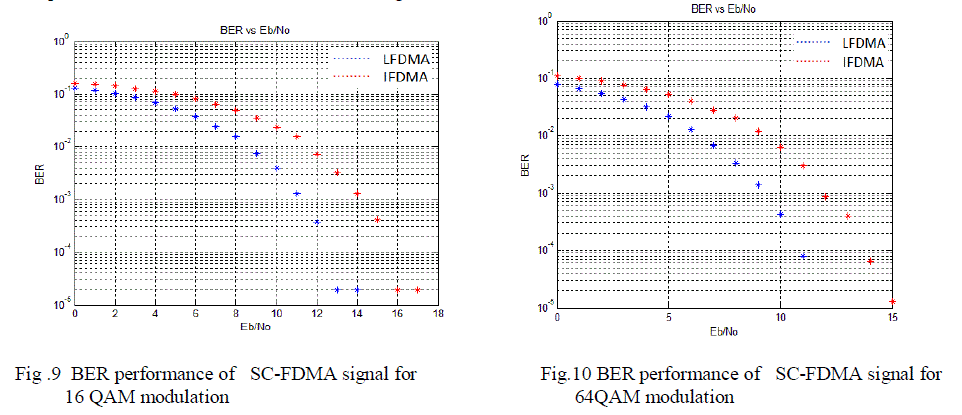 |
| The BER performance of 16 and 64 QAM modulation is given above. It was observed that as M value increases from
16 to 64 the BER performance of the system is improved. |
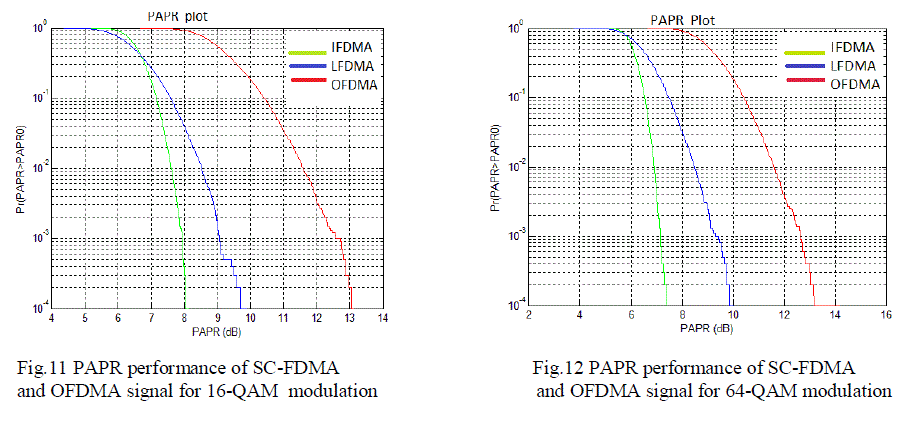 |
| The PAPR performance of 16 and 64 QAM is given above. It was observed that as alphabet size M value increases
PAPR of the signal will also increases. SC-FDMA has better PAPR reduction than OFDMA.It was also observed that
PAPR will be higher for QAM compared to QPSK . |
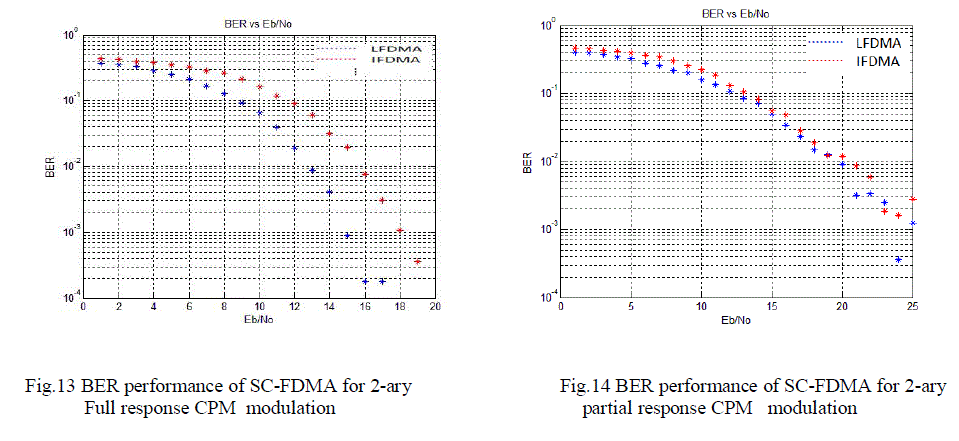 |
| The above simulation shows BER performance of 2-ary CPM signal for full and partial response. It was observed that
the BER performance is better for full response signal than partial response. |
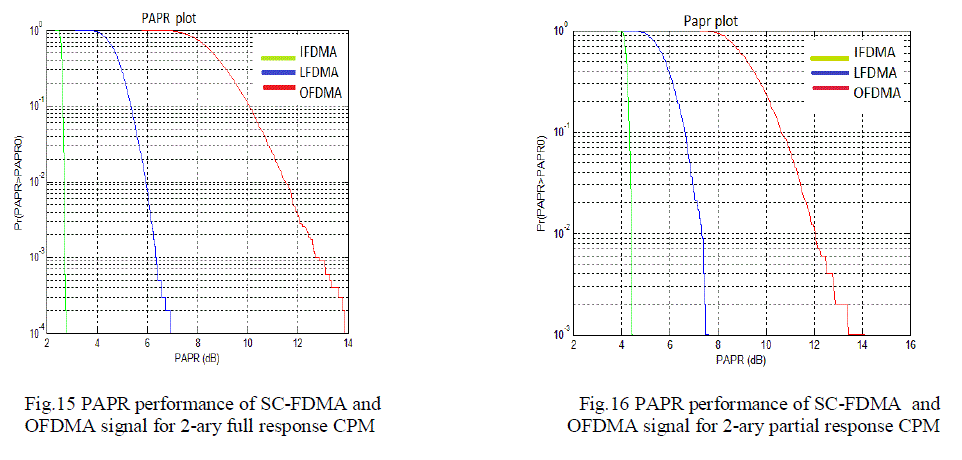 |
| The PAPR plot of 2-ary CPM signal was compared for full and partial response signal. It was observed that PAPR
will be less for full response than partial response because pulse length (L) will increase with partial response.CPM
modulation provided the best PAPR reduction than QPSK and QAM modulations. |
CONCLUSION |
| SC-FDMA was found to be the most suitable scheme for uplink communication than OFDMA. PAPR reduction is
significant in SC-FDMA system compared to OFDMA system. Among the various modulation schemes it was
observed that CPM was a better modulation technique for SC-FDMA for uplink communication. Full response CPM
signal has better BER and PAPR performance than partial response CPM signal. The BER performance was observed
to be better for LFDMA compared to IFDMA and PAPR reduction was better in IFDMA than LFDMA. Similarly rolloff
factor for pulse shaping must be chosen carefully. The PAPR reduces with roll-off factor but it can increase the
out-of radiation of signal. |
References |
- Ramjee Prasad, âÃâ¬ÃÅOFDM for wireless communication systemsâÃâ¬ÃÂ, Artech House, Inc.2004
- Mruthyunjaya, âÃâ¬ÃÅEffect of Peak-to-Average Power Ratio Reduction on the Multicarrier Communication System Performance ParametersâÃâ¬ÃÂ, International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, pp.779-786, 2009.
- B. S. Krongold and D. L. Jones, âÃâ¬ÃÅAn active-set approach for OFDM PAR reduction via tone reservationsâÃâ¬ÃÂ, IEEE Trans. Signal Process,vol. 52, pp. 495-509, Feb. 2004.
- A. D. S. Jayalath and C. R. N. Athaudage, âÃâ¬ÃÅOn the PAR reduction of OFDM signals using multiple signal representation", IEEE Commun. Lett, vol. 8, pp. 425-427, July 2004.
- S. Thompson, A. Ahmed, J. Proakis, J. Zeidler, and M. Geile, âÃâ¬ÃÅConstant envelope OFDM,âÃâ¬Ã IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 56, pp. 1300- 1312, Feb. 2002.
- Hyung.G. Myung and David. Goodman, âÃâ¬ÃÅSingle carrier FDMA - A new air interface for long term EvolutionâÃâ¬ÃÂ, Wiley Publications, 2008
- Marilynn P. Wylie-Green, Erik Perrins and Tommy Svensson, âÃâ¬ÃÅIntroduction to CPM-SC-FDMA: A Novel Multiple-AccessPower-Efficient Transmission SchemeâÃâ¬ÃÂ, 2011, IEEE
- Hyung G. Myung, Junsung Lim, and David J. Goodman, âÃâ¬ÃÅSingle Carrier FDMA for uplink wireless transmissionâÃâ¬ÃÂ,IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, pp.30-38, September 2006.
- WafaaRadi, HeshamElBadawy, SalwaElRamly, âÃâ¬ÃÅPeak to Average Power Ratio Reduction Techniques for Long Term Evolution- Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access System,âÃâ¬Ã International Journal of Advanced Engineering Sciences and Technologies, Vol No. 6, Issue No. 2, pp. 230 âÃâ¬Ãâ 236, 2011.
- Mohamed Salah, Gamal Abdel-Fadeel and Zaki B. Nossair, âÃâ¬ÃÅPeak to Average Power Ratio Reduction in Single Carrier OFDMA SystemsâÃâ¬ÃÂ, 13th International Conference on Aerospace Sciences & Aviation Technology ASAT- 13, May 26 âÃâ¬Ãâ 28, 2009
- Hyung G. Myung, âÃâ¬ÃÅIntroduction to single carrier FDMAâÃâ¬ÃÂ, 15th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2007), Poznan, Poland, pp.2144-2148,September 3-7, 2007.
- Ken Gentile, âÃâ¬ÃÅThe care and feeding of digital, pulse-shaping filters,âÃâ¬Ã www.rfdesign.com April 2002
- Hyung G. MyungJunsung Lim David J. Goodman, âÃâ¬ÃÅ Peak-To-Average Power Ratio of Single carrier FDMA signals with Pulse shapingâÃâ¬ÃÂ,17th Annual IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communication, 2006
- John G Proakis, âÃâ¬ÃÅDigital CommunicationâÃâ¬ÃÂ, Mc-Graw-Hill Higher Education,2008
|