Keywords |
| MANETs; Energy awareness; Stability; Protocol; Neighbour discover; Glomosim; |
INTRODUCTION |
| The history of wireless networks started in the 1970s and the interest has been growing ever since. During the last
decade, and especially at its end, the interest has almost exploded probably because of the fast growing Internet. The
tremendous growth of personal computers and the handy usage of mobile computers necessitate the need to share
information between computers. The information is difficult, as it users performed to static, bi-directional links
between the computers. It motivates the construction of temporary networks without wires, communication
infrastructure and administrative intervention required. Such interconnection between mobile computers is called an Ad
hoc Network. In such environment, it may be necessary for the mobile computers to take help of other computers in
forwarding a packet to the destination due to the limited range of each mobile host’s wireless transmission. Figure 1
shows the basic structure of Ad hoc Network. |
 |
| Ad hoc networks is rising for the future propagation by networks and formed for an appeal by mobile nodes
constituting an irregular intuitive network without the assist of any centralized administration or standard support services. Incoming emotional, ad hoc intend mean “for this,” more intending “for this purpose only”, and so generally
irregular. An ad hoc network is usually retrieved by for a network on nodes that is comparatively mobile equated to a
wired network. Thus the network topology from the network are often more dynamical and the transfers are frequently
irregular match to the online which comprises a wired network. These info makes more difficult explore outcomes, for
the targets from however routing should come about lives much ambiguous as from other resources as if bandwidth,
battery power and demands like latent period. The routing communications protocol utilized in average wired networks
is not easily fitted as these sorts of dynamical environments. |
RELATED WORK |
| MOBILE wireless networks are receiving an increasing interest due to the possibility of ubiquitous
communications they offer. In particular, mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) enable users to maintain connectivity to
the fixed network or exchange information when no infrastructure, such as a base station or an access point, is visible.
These are accomplished by multihop communications, which provide a node to accomplish far-off destinations by
using intermediate nodes while relays. The survival and sustainment by a multihop route, however, is a underlying
trouble in MANETs. Proposed an integration trust management scheme that raising the security of MANETs.
Applying modern raises in uncertain reasoning Bayesian inference and Dempster-Shafer theory, we evaluate the trust
values of observed nodes in MANETs. Misbehaviours such as dropping or modifying packets can be detected in our
scheme through trust values by direct and indirect observance. Nodes with low trust values will be excluded by the
routing algorithm. Therefore, secure routing path can be established in malicious environments. Based on the proposed
scheme, more accurate trust can be obtained by considering different types of packets, indirect observation from onehop
neighbours and other important factors such as buffers of queues and states of wireless connections, which may
cause dropping packets in friendly or neighbours nodes. Node mobility, signal Preventive, and power failure attain the
topology often alter; for a issue, the connects on a route might betray and a interchange path must be determined. To
keep off the abasement by the scheme operation, many results receive made up advised in the lit, allowing several
metrics of concern. A process that's comprised recommended to better routing efficiency is to select the most stable
path so as to avoid packet losses and limit the latency and overhead due to path reconstruction. So our propose work
focus on with proposed system we address selection of stable path among the neighbours which not only describes the
selection of correct position neighbours but also best link stability neighbours. Thus overcome the adversary or
malicious and also link failures. In this work, we study both the availability and the duration probability of a routing
path that is subject to link failures caused by node mobility in terms of malicious activities. |
EXISTING WORK |
| Prevention-based approach is studied comprehensively in MANETs. Unspecified emerge by this preventionbased
advances is that a centralized key management infrastructure are demanded, which might not represent truthful
inwards administered networks such as MANETs If the infrastructure is required. Which power not act realistic in
administrate. |
| Detection-based approaches can effectively help identify malicious activities. Although some excellent work has
been done on detection based approached trust in MANET’s most existing observance. At the same time to evaluate the
trust of an observed node. Therefore, inaccurate trust values may be derived. In addition, most methods of trust
evaluation from direct observance do not differentiate data packets and control packets. However, in MANETs, control
packets usually are more important than data packets. Some are mentioned this technique. |
| • This protocol exhibit least desirable behavior when presented with a highly dynamic interconnection topology. |
| • This protocol place a too heavy computational burden on each mobile computer in terms of the memory-size,
processing power and power consumption. |
| • Increased average end-to-end delay and overhead of messages. So a method that has been advocated to
improve routing efficiency is to select the most stable path so as to reduce the latency and the overhead due to route
reconstruction. |
| This routing protocol takes a lot of time for convergence upon the failure of a link, which is very frequent in ad hoc
networks |
| Using recent advances in uncertain reasoning, Bayesian inference and Dempster-Shafer theory, we evaluate the trust values of observed nodes in MANETs. Misbehaviours such as dropping or modifying packets can be detected in
our scheme through trust values by direct and indirect observance. Nodes with low trust values will be excluded by the
routing algorithm. Therefore, secure routing path can be established in malicious environments. Based on the proposed
scheme, more accurate trust can be obtained by considering different types of packets, indirect observance from onehop
neighbours and other important factors such as buffers of queues and states of wireless connections, which may
cause dropping packets in friendly or neighbours nodes. |
PROPOSED WORK |
| A fundamental issue arising in mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) is the selection of the optimal path between
some two nodes. Assuring a data path to comprise legitimate as sufficiently longer period of time is a very difficult
problem in MANET due to its highly dynamic nature. Variable link conditions are intrinsic characteristics in most
mobile adhoc networks. Rerouting amidst mobile nodes efforts network topology and traffic load conditions to change
dynamically. Given the nature of MANET, it is difficult to support real-time applications with appropriate QoS. In
some cases it may be impossible to guarantee strict QoS requirements. But at the same time, QoS is of great importance
in MANETs since it can improve performance and allow critical information to flow even under difficult conditions.
Unlike fixed networks such as the Internet, quality of service abides in mobile ad hoc networks depend not only on the
available resources in the network but also on the mobility rate of such resources. A method that has been advocated to
improve routing efficiency is to select the most stable path so as to reduce the latency and the overhead due to route
reconstruction. |
| In mobile ad hoc networks, knowledge of neighbours is a requirement in a number of administered secure
neighbour discovery, suitable for highly mobile ad hoc environments, are described in the proposed system under
discovery of neighbour by detecting malicious neighbours. |
SYSTEM DESIGN |
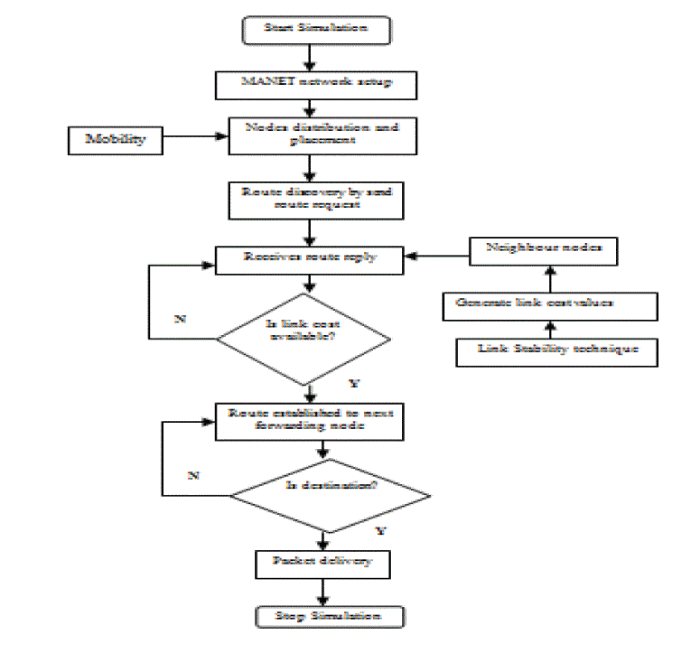 |
SYSTEM MODELS |
| A. MANET Framework Setup |
| We are going to give structure for our routing Process in an ad hoc network that includes setting up of node
Placement, node partition etc. Simulation framework is formulated by linking all layers and sub layers into a single
process because we can’t get results by running each and every layers. Framework includes topology design like grid
based or random or uniform or user specification. |
| B. Path Stability Value Based Prediction Technique |
| We propose an algorithm to predict the link lifetime in MANETs by the path stability value. The algorithm
recursively computes the nodes mobility states, modelled as a nonlinear system, using periodically measured node
current stability value as inputs. The technique states are then utilized to compute the estimates of the remaining link
lifetime. A host or node willing to send a message to a recipient or any host in the multihop path to it uses a prediction
technique to choose the best next hop or forwarding node for the message. The use of this technique is at strategic
network locations to allow predictions of emerging network congestion. The proceed is that well-informed factors can
apply much predictions to work context of use cognizant, cognitive operation as caring communicating in mobile
networks. |
| C. NVPQP Routing Protocol |
| Neighbour’s verification and path quality protocol (NVPQP) is our proposed protocol. It is very evident that two
major factors mobility and energy efficiency need to be considered to assure better network performance. Specially
while assuring QoS in MANET environment nodes should not die due to power constraint or the links should not
expire due to mobility in the middle of the transmission. So our target is to choose a more stable path considering
higher link stability and less cost along predicted higher life path. In this paper we combine the idea of link stability
calculation based on mobility prediction and best path in terms of cost and lifetime along with QoS support. To achieve
QoS path along with prolonging the network life time and to reduce packet loss we need to calculate three parameters
for a path: |
| i. Path Stability |
| ii. Lifetime prediction and |
| iii. Ratio of QoS support and requirements |
| To calculate the above parameter for path selection we define the network model first and then we will subsequently
describe the process of calculation for each the parameters. |
| D. Protocol Configuration Setup |
| We need to configure some attributes which is supported to execute our routing protocol like Number of nodes,
Mobility, Mac protocol, Simulation time, Band width, Transmission range etc… by setting these kinds of attributes we
execute out routing protocol with layers interaction. We setup the layer wise results in the configuration process.
The sequence of events at run time: |
| • The main function in driver.pc is run. This is the C main Function, where GloMoSim starts. |
| • The main function calls parsec main () to start the Parsec Simulation engine, initialize the simulation runtime
variables And create the driver entity. The parsec main function is used When the user wants to write own main and is
found at PCC DIRECTORY/include/pc api.h (since the function is part of the Parsec runtime system, it is not possible
to access the source for it). |
| • When the simulation ends, parsec main () returns, and the rest of the main function is executed. In GloMoSim,
the driver entity (in ./main/driver.pc) reads the input file descriptor, establishes partitions, allocates memory for node
information, calls appropriate functions depending on the read input values such as simulation time and node
placement, and finally starts simulation by sending a StartSim message to the partitionEntityName instance of the
GLOMOPartition entity type (defined in the glomo.pc file).every layers. Framework includes topology design like grid
based or random or uniform or user specification. |
| E. Performance Evaluation |
| First, we need to specify the necessary input parameters in the Config.in file as said above. For our simulation
procedure, we have been specific about certain parameters as mentioned below to enable hassle free simulation Terrain range – (500,500) |
| Number of nodes – 20 (This is a scalable simulator. Hence number of nodes can be increased at will.)These
parameters cost bound to as the entirely process of experimentation with the new protocol. The performance of the
proposed algorithm is evaluated via Glomosim simulator. Performance metrics are utilized in the simulations for
performance comparison: |
| a) Packet arrival rate: The ratio of the number of received data packets to the number of total data packets sent by
the source. |
| b) Average end-to-end delay: The average time elapsed for delivering a data packet within a successful transmission. |
| c) Communication overhead :The average number of transmitted control bytes per second, including both the data
packet header and the control packets. |
| d) Energy consumption :The energy consumption is for the total network admitting, transmitting energy consumption
for both the data and control packets. |
CONCLUSION |
| We studied the duration and availability probabilities of trust management and routing paths selection in
MANETs a fundamental issue to provide reliable routes and short route disruption times. Coordinating the large,
always increasing number of devices that populate mobile ad-hoc networks has been recognized as a major challenge.
In order to simplify application programming, the earlier works has presented a coordination model that fosters the
engineering of trust-based collaborations, by means of long-lived, asymmetric, trusted groups of interest. |
| In further we will focus on the random direction mobility model and derived both exact and approximate (but
simple) expressions for the probability of path duration and availability. We will use these studies to determine the
optimal path in terms of route stability; in particular, we will show some properties of the optimal path and we will
provide an approximate yet accurate expression for the optimal number of hops. |
| |
References |
- Zhexiong Wei, Helen Tang, F. Richard Yu, Maoyu Wang, and Peter Mason,”Security Enhancements for Mobile Adhoc Network with TrustManagement using Certain Reasoning” Citation information: DOI 10.1109/TVT.2014.2313865, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology.
- Y. Wang, F. R. Yu, H. Tang, and M. Huang, “A mean field game theoretic approach for security enhancements in mobile ad hoc networks,”IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 13, pp. 1616–1627, March 2014.
- F. R. Yu, H. Tang, S. Bu, and D. Zheng, “Security and quality of service (QoS) co-design in cooperative mobile ad hoc networks,” EURASIP J. Wireless Commun. Networking, vol. 2013, pp. 188–190, July 2013.
- Q. Guan, F. R. Yu, S. Jiang, and V. Leung, “Joint topology control and authentication design in mobile ad hoc networks with cooperative communications,” IEEE Trans. Veh. Tech., vol. 61, pp. 2674 –2685, July 2012.
- F. R. Yu, Cognitive Radio Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. New York: Springer, 2011.
- J. Loo, J. Lloret, and J. H. Ortiz, Mobile Ad Hoc Networks: Current Status and Future Trends. CRC Press, 2011.
- J. Chapin and V. W. Chan, “The next 10 years of DoD wireless networking research,” in Proc. IEEE Milcom’11, (Baltimore, MD, USA), Nov. 2011.
- S. Bu, F. R. Yu, P. Liu, P. Manson, and H. Tang, “Distributed combined authentication and intrusion detection with data fusion in high-security mobile ad hoc networks,” IEEE Trans. Veh. Tech., vol. 60, pp. 1025–1036, Mar. 2011.
- S. Corson and J. Macker, “Mobile ad hoc networking (MANET): routing protocol performance issues and evaluation considerations,” IETFRFC 2501, Jan. 1999.
- Y. Zhang, W. Liu, W. Lou, and Y. Fang, “Securing mobile ad hoc networks with certificateless public keys,” IEEE Trans. Dependable andSecure Computing, vol. 3, pp. 386–399, Oct.–Dec. 2006.
- S. Marti, T. Giuli, K. Lai, and M. Maker, “Mitigating routing misbehavior in mobile ad hoc networks,” in Proc. ACM MobiCom’00, (NewYork, NY, USA), Aug. 2000.
- G. Lim, K. Shin, S. Lee, H. Yoon, and J. Soo Ma, “Link Stability and Route Lifetime in Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks,” Proc. Int’l Conf. Parallel Processing Workshops (ICPPW ’02), p. 116, 2002.
- M. Gerharz, C. de Waal, M. Frank, and P. Martini, “Link Stability in Mobile Wireless Ad Hoc Networks,” Proc. IEEE 27th Conf. LocalComputer Networks (LCN), pp. 30-39, Nov. 2002.
- M. Gerharz, C. de Waal, P. Martini, and P. James, “Strategies for Finding Stable Paths in Mobile Wireless Ad Hoc Networks,” Proc. IEEE 28thAnn. Conf. Local Computer Networks (LCN ’03), pp. 130- 139, 2003.
- N. Meghanathan and A. Farago, “Looking at Protocol Efficiency from a New Angle: Stability-Delay Analysis,” Proc. Second Int’l Conf. Mobile Computing and Networking, pp. 51-55, 2004.
|