Keywords
|
| Cloud Computing, Personal Health Records (PHRs), MyPHRMachines, Medical data, Virtual Machine |
INTRODUCTION
|
| Cloud computing offers unique opportunities for supporting long-term record preservation. MyPHRMachines [1], a patient owned health record system prototype based on remote virtual machines hosted in the cloud. MyPHRMachines is particularly promising for countries with a very heterogeneous architecture of systems across hospitals and other care institutions. In the view of developer PHRs should be portable. PHR systems typically offer functionality to share, visualize and analyze PHR data. Secure lifelong management of patient medical records since data are stored in the cloud and do not have to be carried around by patients. |
| The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Literature review of several techniques prevailing in literature aimed to secure the electronic methods over past 15 years are discussed in Section 2. Section 3 gives the architectural representation of cloud based PHR storage systems. Section 4 gives a broad overview of discussion of experimental results carried out. Section 5 concludes the paper and outlines the future work. |
LITERARY REVIEW
|
| Jeffrey J. Clawson (2000 b) [20] projected “Method and system for giving remote emergency medical counsel to choking patients” defined that Medical system provided for emergency medical counsel to choking patients remotely. Gather emergency medical information including medical dispatch services to choking victims and providing qualified emergency medical information to callers thereby permitting "zero time" response. Advantage of using this technique is a choking victim injuries can be treated with appropriate guidance. It is mostly useful for the remote emergency sufferers they provide a “zero time” response at the case of emergency. |
| Marc Edward Chicorel (2001) [21] proposes medical progress note a doctor can utilize the base of about 350,000 bytes of medical descriptive to paradigm particular medical progress note. During completion of the patient meeting, the doctor proceeds to write a short “code” should have at least two letters in the suitable box on a predesigned form. Basically this process uses approximately 15 to 90 seconds of the doctor's time. The code is then entered into the programmed processor and information corresponding to the code is printed, analyzed and signed by the doctor. The printed and signed text is then entered into the patient's medical chart. |
| Charlyn Jordan (2002) [22] proposed “Health analysis and forecast of abnormal conditions” said Health record signals are been stored and processed for the predetermined health function or parameter to define value in the abnormal range. Also future health signal record is to trend the predetermined function and assume a value in abnormal range and condition. Jeffrey J. Clawson (2003) [23] defined Standard process is involved in gathering and processing emergency medical information, categorizing such information into various basis levels for correct response and for providing qualified emergency medical information to callers thereby permitting “zero-time” response. Important function of this system is dispatcher is guided through the examination of callers, meeting the critical information dispatching the mobile care when needed and giving the appropriate guidance to the caller. It has universal entry protocol for accessing medical complaints. |
| PekkaRuotsalainen (2004) [24] in “A cross-platform model for secure Electronic Health Record communication” defined an Enhanced cross security platform is proposed which support a platform for communication through the adhoc network to access the distributed electronic health records. Roger J. Quy (2005) [25] in “Method and apparatus for health and disease management combining patient data monitoring with wireless internet connectivity” said the health related data is communicated from the WWD to a server using standard internet protocols. Server calculates the response time and further it reviewed by a physician or health care provider. User and server interaction takes place the server transmits a response to the WWD and the user may answer the response. |
| Avner Amir, Avner Man (2006 ) [26] in “System and method for administration of on-line healthcare” defined the endunit device is guided by the CMIP so that anamnesis, diagnosis treatment is provided, monitored, recorded and clinically investigated. This system is useful for the management of medical records. Christopher Alban, KhiangSeow (2007) [27] defines a single electronic database it stores clinical patient notes, provides multiple points of read/write access through user interface operating on single or more client computers that are in real time communication with the repository. Brian A. Rosenfeld, Michael Breslow (2008) [28] in “System and method for accounting and billing patients in a hospital environment” explored if the billable service is provided by a specialist, a specialist identifier is also associated with the billable service. The hospitalized patient is counted and a current procedural terminology (CPT) manager assigns CPT codes to the billable service. A bill generator receives all the details of the patient data, insurance information and CPT codes which generate a bill for the billable services provided to the hospitalized patient. Jacquelyn Suzanne Hunt, Joseph Siemienczuk (2009) [29] in “Process and system for enhancing medical patient care” explored the fact that a data warehouse receives the extracted information and reformats that information. Information’s are analyzed by a health care provider having that medical condition. It further collects the data of the selected patients for multiple health care providers and enables comparisons of health care provider’s success for such patients to promote advance of the treatment by less successful providers. |
| Richard J. Schuman (2010) [30] defines “Health care computer system” which define the A hospital bed, patient and nurse call system. A hospital network is provided. Communication is provided over a packet based communication network. Kanagaraj, G.Sumathi, A.C. (2011) [31] in “Proposal of an open-source Cloud computing system for exchanging medical images of a Hospital Information System” proposed clinical information system through the cloud can provide the essential details to the health care and the patient can seek the treatment in different hospital, reduce computational resource maintenance in the hospital also existing medical equipment’s can be reconstructed to be more efficient and low-cost. |
| J. Vidhyalakshmi, J. Prassanna (2012 b) [33] proposed “Providing a trustable healthcare cloud using an enhanced accountability framework” explored that Security and accountability of patient’s personal health record maintenance it handle the Privacy protection problem. They define Distributed accountability framework to control and monitor user data in cloud. It also handle the object centric which automatically trigger an object to create a log record and access over distributed data. Log file corruptions are handled, log manager maintenance and verify corrupted log records. With the introduction of cloud computing in medical data capital expenditure is converted to operational expenditure. |
| Carmelo Pino and Roberto Di Salvo (2013) [37] in “A Survey of Cloud Computing Architecture and Applications in Health” explained Cloud computing provide resource management and computation capabilities, hybrid cloud can increase the development of the health sector. Abhishek Kumar Gupta, Kulvinder Singh Mann (2014 b) [41] defined “Sharing of Medical Information on Cloud Platform” explored that basically hospitals store the patient details in paper format now in the migration to next level medical information are stored in cloud computing which provide a secure way to share. It results in the setting the platform for the exchange and collaboration of medical information. |
ARCHITECTURAL REPRESENTATION
|
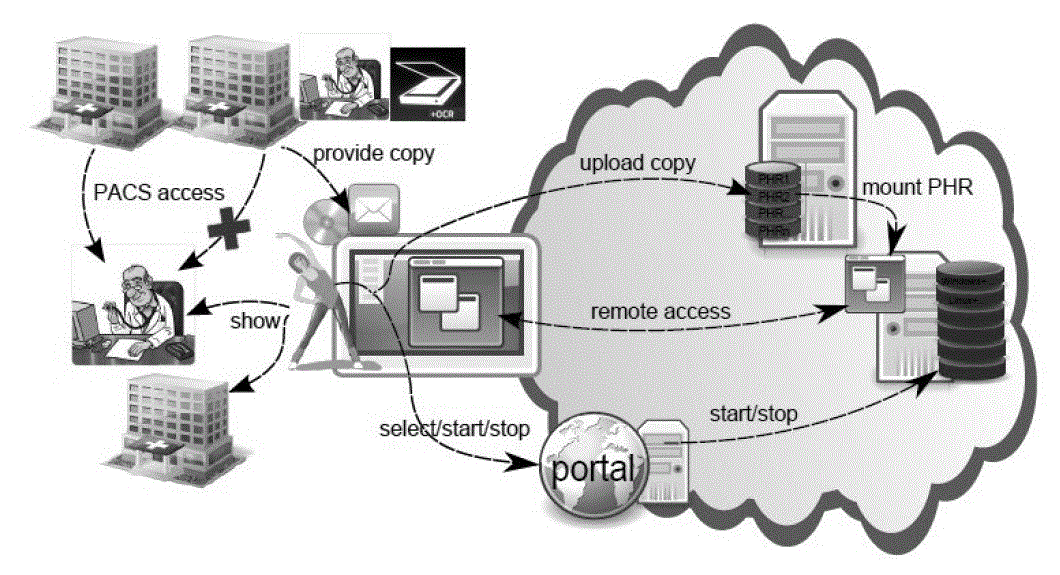
| The architectural representation of cloud based PHR storage is represented in Fig 1. The portal plays an important role in uploading copy of data, remote access maintenence, start/stop operation. PCAS access is used to provide and show copies. The cloud takes the responsibility of mounting the PHRs. |
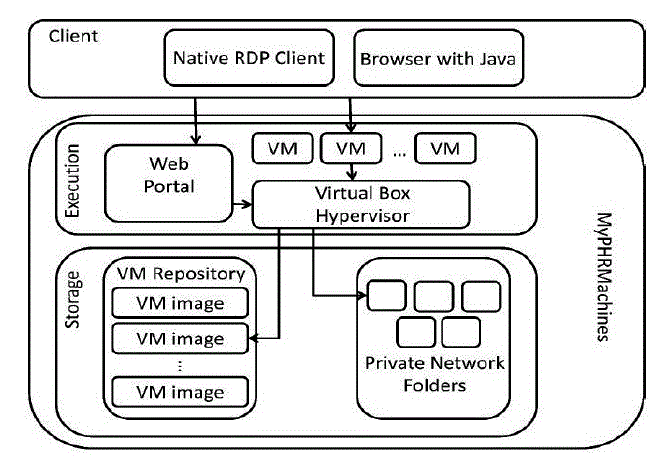
| Architectural representation of MyPHR Machine consists of two components evolution and storage with which client directly interacts with MyPHR Machine. The first component of MyPHR Machine consists of web portal which in turn interacts with Virtual Box Hypervisor. Virtual Machines are connected together with Virtual Box Hypervisor. The second component of MyPHR Machine, storage consists of VM Repository which houses VM Data and Private Network folders as indicated in Figure 2. |
DISCUSSION AND RESULTS
|
| MyPHRMachines allows patients to build PHRs which are robust across two dimensions namely: |
| i. Space Dimensions and ii. Time Dimensions |
| Two Use cases are also taken into consideration: |
| i. Spatial and Temporal pervasiveness and ii. Privacy related aspects. |
| The basic network model for the cloud data storage and four different network entities |
| 1. User |
| 2. Cloud Storage Server (CSS) |
| 3. Cloud Service Provider (CSP) |
| 4. Data owner |
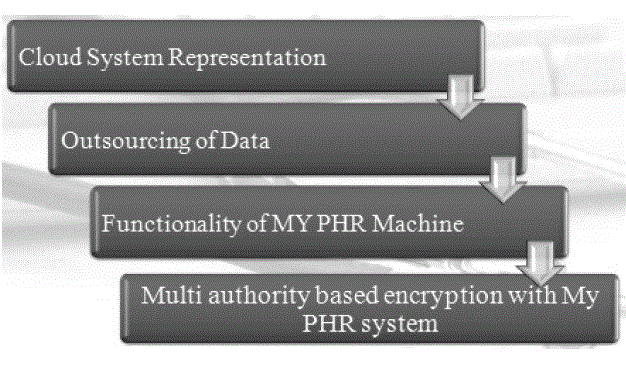
| The process of multi authority based encryption with MyPHR system starts with a cloud system representation. After outsourcing of data the functionalities of MyPHR machine are carried out. |
| The basic network model for the cloud data storage and three different network entities User: an entity, which has large data files to be stored in the cloud and relies on the cloud for data maintenance and computation, can be either individual consumers or organizations. Cloud Storage Server (CSS): an entity, which is managed by Cloud Service Provider (CSP), has significant storage space and computation resource to maintain the user data. The Data owner encrypted some keywords about his data, and service provider supported the owner to retrieve his data by keywords and not allow others to retrieve. |
| Cloud storage services to users, where users can have access to very large volume of storage. Data kept on clouds can also be shared by users giving that the sharing is authorized by the data owners Alice has a piece of data that is kept on the cloud. Secure data sharing needs to be achieved via an un trusted cloud storage provider. It is necessary that the cloud storage provider helps to enforce the authorization policy for data access but the enforcement should not reveal any information to the cloud storage provider or enable the cloud storage provider have excessive privileges to allow unauthorized access.Cloud storage services provide, very large volume of storage to outsource user data. Data kept on clouds can also be shared to users that the sharing is authorized by the data owners. Cloud storage provider helps to enforce the authorization policy for data access. |
CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
|
| In this paper, an extensive study is carried out on managing medical database in cloud for the past 15 years. Several approaches of cloud computing and high-performance computing models have been studied and the results were observed. Algorithms pertaining to ensuring security to electronic health records in cloud have been studied along with the computation overhead involved in implementing the algorithms for real and synthetic patient medical records. Also we have implemented the modular workflow based PHRs storage in Cloud Environment. |
| |
Tables at a glance
|
 |
| Table 1 |
|
| |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
Figure 5 |
|
| |
References
|
- Pieter Van Gorp and Marco Comuzzi “Lifelong Personal Health Data and Application Software via Virtual Machines in the Cloud” IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Healthcare Informatics, Vol. 18, No. 1, Jan 2014
- Lichtenstein Eric Stefan 1984 a, Computer control medical care system US4464172.
- ARalph R.Frerichs, Dr. PH.Robert A. Miller 1985, Introduction of a Microcomputer for Health Research in a Developing Country.
- Steven P.Brown 1986, Combinational Medical Data, Identification and health Insurance card.
- Peter P. Gombrich, Richard J. Beard, Richard A. Griffee, Thomas R. Wilson, Ronald E. Zook, Max S. Hendrickson 1989,A Patient care system,US4835372 A.
- Neil Bodick, Andre L. Marquis1990, Interactive system and method for creating and editing a knowledge base for use as a computerized aid to the cognitive process of diagnosis,US4945476 A.
- Angela M. Garcia, Dr.,Boca Raton 1991 a, System and Method for scheduling and Reporting Patient related services including prioritizing services,US5974389 A.
- Clark Melanie Ann, John Finley, Huska; Michael Edward, Kabel; Geoffrey Harold, Graham, Marc Merrill 1991 b,System and Method for scheduling and Reporting Patient Related services.
- Robert W. Kukla1992,Patient care communication system, US5101476 A
- Mark C. Sorensen 1993, Computer aided medical diagnostic method and apparatus, US5255187 A.
- Edward J. Whalen, San Ramon, Olive Ave Piedmont 1994,Computerized file maintenance System for managing medical records including narrative patent documents reports.
- Desmond D. Cummings 1994b,All care health management system, US5301105 A.
- Woodrow B. Kesler Rex K Kesslerin 1994 c,Medical data draft for tracking and evaluating medical treatment.
- Joseph P. Tallman, Elizabeth M. Snowden, Barry W. Wolcott 1995, Medical network management system and process, US5471382 A.
- Peter S. Stutman, J. Mark Miller 1996,Medical alert distribution system with selective filtering of medical information
- Edwin C. Iliff1997,computerized medical diagnostic system including re-enter function and sensitivity factors, US5594638 A.
- Timothy Joseph Graettinger, Paul Alton DuBose 1998, Computer-based neural network system and method for medical diagnosis and interpretation. US5839438 A.
- Melanie Ann Clark, John Finley Gold, Michael Edward Huska, Geoffrey Harold Kabel, Marc Merrill Graham1999,Medical record management system and process with improved workflow features, US5974389 A.
- Richard S. Surwit, Lyle M. Allen, III, Sandra E. Cummings 2000 a, Systems, methods and computer program products for monitoring, diagnosing and treating medical conditions of remotely located patients, US6024699 A.
- Jeffrey J. Clawson 2000 b, Method and system for giving remote emergency medical counsel to choking patients, US6010451 A.
- Marc Edward Chicorel 2001, Computer keyboard-generated medical progress notes via a coded diagnosis-based language, US6192345 B1.
- Charlyn Jordan2002, Health analysis and forecast of abnormal conditions.
- Jeffrey J. Clawson2003, Method and system for an improved entry process of an emergency medical dispatch system
- PekkaRuotsalainen 2004, A cross-platform model for secure Electronic Health Record communication.
- Roger J. Quy2005, Method and apparatus for health and disease management combining patient data monitoring with wireless internet connectivity, US6936007 B2.
- Avner Amir, Avner Man2006 a, System and method for administration of on-line healthcare, WO2006006176 A2.
- Paul C.Tang, Joan S. Ash, David W. Bates, J. Marc overhage and Daniel Z.Sands 2006 b, Personal Health Records: Definitions, Benefits, and Strategies for Overcoming Barriers to Adoption.
- Christopher Alban, KhiangSeow2007, Clinical documentation system for use by multiple caregivers.
- Brian A. Rosenfeld, Michael Breslow2008, System and method for accounting and billing patients in a hospital environment.
- Jacquelyn Suzanne Hunt, Joseph Siemienczuk 2009, Process and system for enhancing medical patient care.
- Richard J. Schuman2010, Health care computer system, US7831447 B2.
- Kanagaraj, G.Sumathi, A.C.2011,Proposal of an open-source Cloud computing system for exchanging medical images of a Hospital Information System
- AvulaTejaswi, NelaManoj Kumar, GudapatiRadhika, SreenivasVelagapudi 2012 a, Efficient Use of Cloud Computing in Medical Science.
- J. Vidhyalakshmi, J. Prassanna 2012 b, Providing a trustable healthcare cloud using an enhanced accountability framework.
- Carmelo Pino and Roberto Di Salvo 2013, A Survey of Cloud Computing Architecture and Applications in Health.
- K.S. Aswathy, G. Venifa Mini 2014 a, Secure Alternate Viable Technique of Securely Sharing the Personal Health Records in Cloud.
- Abhishek Kumar Gupta, Kulvinder Singh Mann 2014 sharing of Medical Information on Cloud Platform.
- D. C. Kaelber, A. K. Jha, D. Johnston, B. Middleton, and D. W. Bates, "Viewpoint paper: research agenda for personal health records (PHRs),”J. Amer. Med. Inform. Assoc., vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 729–736, 2008.
- J. Ahima, “Defining the personal health record,” vol. 76, no. 6, pp. 24–25, Jun. 2005.
- W. Currie and M. Guah. "Conflicting institutional logics: a national programme for it in the organizational field of healthcare:, Journal of Information Technology, 22:235–247,2007.
- M. Gysels, A. Richardson, and J. I. Higginson "Does the patient-held record improve continuity and related outcomes in cancer care: a systematic review", Health Expectations,10(1):75–91, Mar. 2007.
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO TR20514:2005 Health Informatics - Electronic Health Record Definition, Scope and Context Standard. International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Geneva, Switzerland,2005.
- S.Balamurugan, S.Charanyaa, "Principles of Social Network Data Security" LAP Verlag, Germany, ISBN: 978-3-659-61207-7, 2014.
|