Clustering is used to determine the intrinsic grouping in a set of unlabeled data. Subspace clustering is one type of clustering model that solves many normal clustering problems. The both novel subspace clustering algorithms known as fixed and optimal centroids are allows getting more profitable objects in database. But this also provides information with impurity data. So we proposed a new approach called Multi Objective and Evolutionary Subspace Clustering (MO&ESC) that provides statistic of the dimensions and the impurity measure within each cluster. This technique is used to provide Centroid-based Actionable 3D Subspace clusters and also returns the information based on impurity dimensional data value.
Keywords |
| Clustering; Data mining; Centroid; Multi Objective and Evolutionary Subspace Clustering |
INTRODUCTION |
| Clustering is a type of prewriting that allows exploring many ideas to get particular information. Like brainstorming
or free associating, clustering allows beginning without clear ideas. Clustering can be considered the most important
unsupervised learning problem so, as every other problems of this kind it deals with finding a structure in a collection
of unlabeled dataset. A data loose meaning of clustering may possibly be “the process of organize items or things into
group whose members are related in various approach” [1]. A clustering is a collection of objects which are “similar”
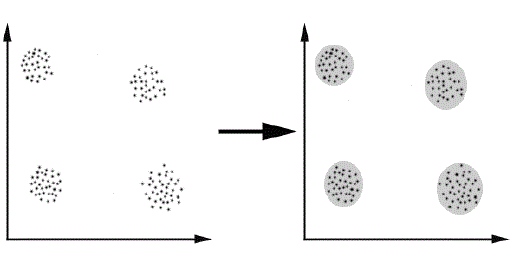
between them and are “dissimilar” to the objects belonging to other clusters. The below Fig: 1 shows a simple graphical
example. |
| In this above figure we simply recognize the four clusters divided into data. The similarity principle is distance
between two or more objects belong to the same cluster, if the clusters are “close” according to a given distance. This
way of action is known as Distance based clustering. Another one clustering model is conceptual clustering, i.e., the
two or more objects belong to the same cluster, if the cluster is one defines a concept common to all that objects. In
another definition, the objects are grouped according to their fit to descriptive concepts, not according to simple
relationship measures. So, the aim of cluster is to determine the fundamental grouping in a set of unlabeled dataset. But
how to decide what constitutes a good clustering? It can be shown that there is no absolute “best” principle which would be independent of the final plan of the clustering. Consequently, it is the user which should supply this measure,
in such a way that the results of the clustering will ensemble their needs. |
| For instance, we could be interested in finding representatives for homogeneous groups (data reduction), in finding
“natural clusters” and describe their unknown properties, in finding useful and suitable groupings (“useful” data
classes) or in finding unusual data objects (outlier detection). Here data mining is main part to analysis, maintain and
retrieve data from clustered data values. |
| In general, data mining is the course of action of analyzing data from different perspectives and summarizing it into
useful information that can be used to increase revenue, cuts costs, or both [2]. Data mining is the process to discover
interesting knowledge from large amounts of data. Data mining, also called knowledge discovery in databases in
Computer science department, the process of discover the interesting and useful patterns and relationships in large
volumes of dataset. |
RELATED WORK |
| The problems of helpfulness and usability of subspace clusters are very important issue in subspace clustering [3].
Subspace clustering is a division of clustering algorithm that is talented to find low dimensional clusters in very high
dimensional dataset values. This advance technique is used to clustering that allows system to find group of users who
share a regular interest in a particular field or sub filed regardless of differences in other fields. In high dimensional
datasets, the number of potential subspaces is enormous. For example, if there are ‘N dimensions’ in the data means,
the number of possible subspaces is ‘2N’ [4]. |
| In this existing paper, we recognize real time troubles, which encourage the need to launch subspace clustering with
actionability and users domain knowledge via centroids. This existing work particularly used to compare and find
datasets in Marketing, Land use, Insurance, City-planning and many others. |
| Existing work uses two types of centroids in clustering. They are, |
| A. Fixed Centroids, |
| B. Optimal Centroids |
Fixed Centroids: |
| Kelvin Sim et al. [5] uses the scheme called fixed centroids. In pattern based subspace clustering, the ideals in the
subspace clustering assure some distance or similarity based functions, and these functions usually want some
thresholds values. This regular process is obligatory fixed centroids. In existing the first approach is fixed centroids to
handle and prune the datasets. The subspace clustering problem using fixed centroids, however which the
understanding problem of threshold is mitigated as the clustering results is not sensitive to the optimization factor
values. Then center of attention on subspace clustering on two dimensional dataset (2D Dataset), and therefore it’s not
fitting for subspace clustering on 3D datasets. |
| So here we used 3D subspace clustering algorithms CAT Seeker with fixed centroids used to mine CATSs
(Centroid-based Actionable 3D Subspace clusters) subspace. This uses three-dimensional (3D) datasets, in the form of
object-attribute-time. The fixed centroids is a type of homogeneous representation i.e., similar type of data will be
manage and return. At this time we have known full area knowledge. So if we have only some knowledge of domain
means we cannot get proper outcome or result. |
| This algorithm focuses only on partition group of data items. As a result fixed centroids are focus on partitioning of
objects into separate groups to maintain the dataset. The main problem is if the article can be in multiple groups’ means
it cannot maintain properly. |
Optimal Centroids: |
| The second algorithm called CAT Seeker with optimal centroids for handling the many groups at same time. This
optimal technique can works on heterogeneous representation i.e., this compare the several groups of datasets and
provide the suitable result. For fear that we know only a few knowledge means that is enough to find out the related
user satisfied results. CAT Seeker uses SVD to prune the investigate space for using the SVDpruning algorithm to
detect high homogeneous values. CATS allowed incorporating their domain knowledge, by selecting their prefer
objects as centroids of the actionable subspace clusters. To indicate such cluster as the centroid-based actionable 3D
subspaces clusters (CATSs) and also denotes utility as a function measuring the profits or benefits of the objects. |
| GS-search [6] and MASC [7] ‘flatten’ the continuous valued 3D dataset values into a dataset with having the single
timestamp. They require the clusters to arise in every one timestamp, and it is difficult to find out clusters in dataset
that has a bulky number of timestamps. |
PROPOSED ALGORITHM |
| We propose a new approach called Multi Objective and Evolutionary Subspace Clustering (MO & ESC). The
Multi objective is used to identify the independent subspace clusters subject to the constraint that clusters in the Pareto
front have minimal overlap in the exemplars assigned to each other. |
| The general modern approach used here for Evolutionary Subspace Clustering (ESC) [8] assumes the bottom-up
method in which a traditional clustering algorithm is first applied to each attribute separately to set up the initial
‘lattice’ of candidate 1-dimensional clusters from which subspace clusters will then be composed. MO & ESC is the
new approach based on impurity centroids that can provides Centroid-based Actionable 3D Subspace clusters and also
returns the information based on impurity dimensional data value. |
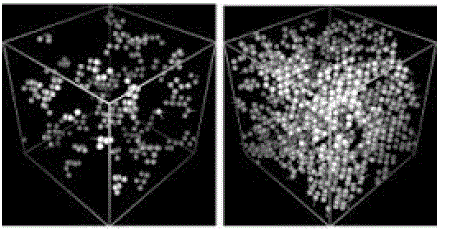
| In left side of Fig 2 shows the Evolutionary Subspace clusters and right side of Fig 2 shows the Evolutionary
Subspace clusters with impurity data. The Multi Objective and Evolutionary Subspace Clustering is search and
compare the data with impurity in 3D Subspace clusters and return to users. |
CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK |
| In Multi Objective and Evolutionary Subspace Clustering (MO & ESC) are impurity centroids that can provide
good efficiency. Previous works such as Fixed Centroids and Optimal Centroids are allows incorporating domain
knowledge with a sensitive way. But it is not considering the impurity data values. The MO & ESC approach is
provides Centroid-based actionable 3D Subspace clusters and also works based on the impurity levels of datasets. |
| In future, we research a new algorithm for support four dimensional (4D) datasets (like object-attribute-time-place)
works on the impurity levels in data mining. |
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
|
References |
- Agrawal.R, Faloutsos.C, and Swami.A, "Efficient similarity search in Sequential Databases", In Proceedings of 4th International
- Conference on Foundations of Data Organization and Algorithms, Chicago, 1993.
- Yanchang Zhao, “R and Data Mining - Examples and Case Studies”, Published by Elsevier in December 2012.
- Kriegel.H.P, Kroger.P and Zimek.A, “Clustering high dimensional data: A Survey on Subspace Clustering, Pattern based clustering, and Correlation clustering”, ACM Transaction Knowledge Disc Data, pp. 1–58, 2009.
- Nitin Agarwal, EhteshamHaque, Huan Liu and Lance Parsons, “A Subspace Clustering Framework for Research Group Collaboration”, Department of Computer Science Engineering, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85281.
- Kelvin Sim, Ghim-Eng Yap, David R. Hardoon, VivekanandGopalkrishnan, Gao Cong, and SuryaniLukman, “Centroid-based Actionable 3D Subspace Clustering”, IEEE transactions on knowledge and data engineering, vol. 25, no. 6, pp. 1-14, June 2013.
- Jiang.D, Pei.J, Ramanathan.M, Tang.C, and Zhang.A, “Mining coherent gene clusters from gene-sample-time microarray data”, In KDD, pp. 430–439, 2004.
- Sim.K, Poernomo.A.K, and Gopalkrishnan.V, “Mining actionable subspace clusters in sequential data”, In SDM, pp. 442–453, 2010.
- Ali Vahdat, Malcolm Heywood and NurZincir-Heywood, “Bottom up Evolutionary Subspace Clustering”, Department of Computer Science, Dalhousie University, Canada, B3H1W5.
|