HISTORY
|
| The first 3G network offered for commercial use was launched in Japan by NTT DoCoMo. The network had the brand name FOMA and was introduced in May 2001 on a W-CDMA technology pre-release. The initial commercial launch of 3G was also done by NTT DoCoMo in Japan. This happened on October 1, 2001, although the technology was still very limited in terms of scope at the beginning. The broad availability, due to inadequate reliability had to be delayed. SK Telecom from South Korea was the second network that was released commercially live. Isle of Man by Manx Telcom was the first pre-commercial network released from Europe. At that time, the operator went by the name British Telecom. Telenor opened the first commercial network in Europe for business in December 2001. There were no commercial handsets, so there was also zero clients. These wereontheWCDMAtechnology. |
| 3G IN THE UNITED STATES |
| The first 3G network in the United States that was released commercially was by Monet Mobile Networks. This was on CDMA2000 1x EV-DO technology. Later on, the network provider had to shut down operations. Verizon Wireless released the second 3G network operator in the United States in October 2003. This was on CDMA2000 EV-DO, with a strongly growing network since more and more countries adopted the changing technology and incorporated the use of 3G with mobile phones and handsets. Today, 3G is a very common feature among modern models and designs, with more innovations and heightened efficiency being introduced every year. |
| 1.1 INTRODUCTION |
| 3G services for mobile devices have been introduced by various handset creators and cellular carriers. |
| DEVELOPMENTS |
| The HSDPA is a new technology, which may also be called 3.5G, offers fasters speeds of up to 7.2 Mbps and also promises the likes of 14.4 Mbps. The interface is very much different on a cellular phone, but other experiences like downloading, streaming, web browsing and sending messages and email can be very comparable to a computer broadband connection. As of the present, there are 3 big carriers that introduced and launched 3G services. |
| THE ACCESSES |
| Currently, 3G technology is the most recent in mobile communications. 3G is the shorter term for third generation, making analogue cellular technology generation one and digital/PCS generation. The 3G technology is planned and devised for the real multimedia cellular phone, also known as smart phones. These tools feature higher bandwidths and transfer rates to cater to web-based applications and phone-based video and audio data files. The most common include CDMA2000, which is based on code division multiple access, TD-SCDMA |
| 3GNETWORKS |
| 3G networks have the capability of transferring speeds up to 3 Mbps which is equivalent to around 15 seconds for every download of a 3-minute MP3 song. To compare, the speediest 3G cellular phones can move speeds up to 144 Kbps, which is equivalent to around 8 minutes to download a 3-minute MP3 song. The high data rates of 3G are recommended when downloading or acquiring information online, as well as sending and receiving huge multimedia files. |
| 3G phones are comparable to small laptops that can cater to several broadband applications like browsing the internet, receiving streaming videos online, video conferencing and sending and receiving faxes. The soaring towers are among the most important element of the group, allowing the data to be transferred from one Phone to another. 3G basically is a cellular phone network protocol. |
| 1.2 CHARACTERISTICS OF 3G TECHNOLOGIES |
| 3G technologies make use of TDMA and CDMA. 3G (Third Generation Technology) technologies make use of value added services like mobile television, GPS (global positioning system) and video conferencing. The basic feature of 3G Technology (Third Generation Technology) is fast data transfer rates.3G technology is much flexible, because it is able to support the 5 major radio technologies. These radio technologies operate under CDMA, TDMA and FDMA.CDMA holds for IMT-DS (direct spread), IMT-MC (multi carrier). TDMA accounts for IMT-TC (time code), IMT-SC (single carrier). FDMA has only one radio interface known as IMT-FC or frequency code. Third generation technology is really affordable due to the agreement of industry. This agreement took pace in order to increase its adoption by the users. 3G (Third Generation Technology) system is compatible to work with the 2G technologies. 3G (Third Generation Technology) technologies holds the vision that they should be expandable on demand. The aim of the 3G (Third Generation Technology) is to allow for more coverage and growth with minimum investment |
3GTECHNOLOGIES
|
| There are many 3G technologies as W-CDMA, GSM EDGE, UMTS, DECT, WiMax and CDMA 2000. Enhanced data rates for GSM evolution or EDGE is termed to as a backward digital technology, because it can operate with older devices. EDGE allows for faster data transfer than existing GSM.EDGE was introduced by AT& T in 2003. EDGE has increased the GSM coverage up to three times more. EDGE is a 3G Technology (Third Generation Technology). Therefore it can be used for packet switched systems. Universal mobile telecommunications systems .UMTS conforms to ITU IMT 2000 standard. It is complex network and allows for covering radio access, core network and SIM (subscriber identity module). It is a relatively expensive technology for the network operators because it requires new and separate infrastructure for its coverage. The GSM is the base of this technology. CDMA is also referred to as IMT-MC. This technology is close to 2G technology GSM because it is also backward compatible. Digital enhanced cordless telecommunications (DECT) is another 3G Technology (Third Generation Technology). DECT was developed by European telecommunications standards institute however it is now widely popular in the other countries of the world as well. It runs over a frequency of 1900Mhz. WiMax is a 3G Technology (Third Generation Technology) and it is referred to as worldwide interoperability for microwave access. It is a wireless technology. It transmits variety of wireless signals. It can be operated on the multi point and point modes. It is a portable technology. This technology is based on the wireless internet access. This technology removes the need for wires and is capable enough to provide 10mbits/sec. speed to connect hotspot. |
| 2.1 RECENT TECHNOLOGIES |
| 3G technology includes UMTS and 1xEV-DO ranging from 144 Kbps up to 2 Mbps. Some of the included features are full-motion video, quick web browsing, 3D games and streaming music.3.5G technology includes HSDPA which is an upgrade for UMTS and 1x EV-DV, with speeds ranging from 384 Kbps up to 14.4 Mbps. Features include video conferencing and on-demand video. 4G and more features speeds from 100 Mbps up to 1 Gbps. Some of the outstanding features include high quality video conferencing, high quality streaming video and voiceover- IP telephony. |
 |
COMPARISION OF 1G, 2G, 3G:
|
| 1G Systems: These are the analog systems such as AMPS that grew rapidly in the 1980s and are still available today. Many metropolitan areas have a mix of 1G and 2G systems, as well as emerging 3G systems. The systems use frequency division multiplexing to divide the bandwidth into specific frequencies that are assigned to individual calls. |
| 2G systems: These second-generation systems are digital, and use either TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) or CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) access methods. The European GSM (Global System for Mobile communications) is a 2G digital system with its own TDMA access methods.The 2G digital services began appearing in the late 1980s, providing expanded capacity and unique services such as caller ID, call forwarding, and short messaging. A critical feature was seamless roaming, which lets subscribers move across provider boundaries. |
| 3G systems : |
| 3G has become an umbrella term to describe cellular data communications with a target data rate of 2 Mbits/sec. The ITU originally attempted to define 3G in its IMT-2000 (International MobileCommunications- 2000)specification, which specified global wireless frequency ranges, data rates, and availability dates. However, a global standard was difficult to implement due to different frequency allocations around the world and conflicting input. So, three operating modes were specified. According to Nokia, a 3G device will be a personal, mobile, multimedia communications device that supports speech, color pictures, and video, and various kinds of information content. Nokia's Web site (http://www.Nokia.com) provides interesting information about 3G systems.3G systems will certainly support more phone calls per cell |
| The five charts below quickly compare the differences between the generations of wireless telecommunications. Each chart covers a different aspect of the standards: |
| 1. Dates & Cool New Features |
| 2. Technology in Use |
| 3. Speeds |
| 4. Frequencies and Carriers |
| 5. Primary Countries |
| 3.1 PARAMETERS IN 3G WIRELESS COMMUNICATION |
| a) TRAFFIC |
| b) BER (BIT ERROR RATE) |
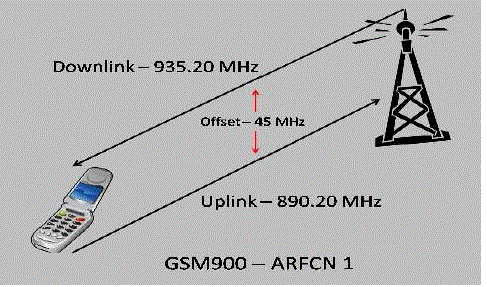
| c) UPLINK FREQUENCY |
| d) DOWNLINK FREQUENCY |
| The following diagram illustrates an ARFCN with paired uplink and downlink frequencies for ARFCN 1 in the GSM 900 band. |
 |
| 6) CODE ASSIGNMENT IN 3G |
| a) WALSH CODE |
| A system and method for expanding traffic channels in a wireless communications system, such as CDMA2000, includes a method for generating a forward link signal including encoding each of a first set of channels with a mutually corresponding channel code, such as a Walsh code, selected from a predetermined set of channel codes, and encoding each of a second set of channels with the same mutually corresponding channel codes. |
| b) SCRAMBLE CODE |
| A scramble code is applied to the encoded second set of traffic channels, which is combined with the encoded first set of traffic channels to form an extended forward link signal. Each channel code corresponds to two forward link channels, which are selectively decoded using the scramble code |
| c) ORTHOGONAL VARIABLE SPREADING FACTOR CODES |
| CDMA provides support for variable spreading factor codes. These codes have different lengths and it is required that these variable length codes be orthogonal to each other. Since during spreading, each information bit is multiplied by an entire codeword, it means that longer codes are associated with lower bit rates. When two messages with different code words and spreading factors are transmitted at the same time, the shorter codeword, modulated by its information message, will get repeated a number of times for each transmission of one longer codeword. This means that the longer code that is derivable from a smaller code is not orthogonal.[5] In terms of the tree structure of the codes, this translates to the condition that a code is not orthogonal to all the codes below it in the code tree. The codes in the tree are generated recursively by generating two codes from one code at each level[6]. |
| d) Turbo Code |
| Turbo codes are finding use in 3G mobile communications and (deep space) satellite communications as well as other applications where designers seek to achieve reliable information transfer over bandwidth or latencyconstrained communication links in the presence of data-corrupting noise. Turbo codes are nowadays competing with LDPC codes, which provide similar performance.[2],[3]. |
| 3.2 ADVANTAGES OF 3G TECHNOLOGY |
| 3G Internet or Third Generation Internet Technology is the fastest mode of data communication today. It is a wireless technology and can be used anywhere and everywhere. 3G improves the efficiency of data transfer over the 3G device, such as cellular phone or a data card. The data transfer rates for third generation mobile telecommunications is much more than 2G or 2.5 in use. |
| Previously mobile phones were using GPRS or EDGE technology for data transfers. The rate of transfer was so slow that it indeed tested the user's patience. The chief advantage of 3G is that all data transfer over the phone can now take place at a much faster speed. 3G internet has not only made our mobile handset better equipped but our PC or laptop also. 3G Data Cards or 3G USB Modems have been launched by most of the leading Internet Service Providers. We just need to plug in our 3G modem into the USB slot, and access internet on our computer at lightening speed. |
| 3G technology is basically all about speed and high data transfer rate. We can conduct video-conferencing, and also we can see the person to whom we are talking when we make calls, provided the other person also is using a 3G enabled device. This is in contrast to conventional voice calls where we are restricted to hearing only the voice of the person at the other end. |
| The 3G enabled handset can determine its current location on the inbuilt map, and can give directions to go to a certain place from its present location. It can even give driving directions. |
| Using 3G enabled cell phone we can do online shopping, online banking, and even watch the ups and downs in the share market, to name a few. |
| By virtue of 3G Internet, we no longer need to wait to go to the cinema or even get into our drawing room to watch on the television the latest movie released. To have a 3G enabled phone is like carrying the world in our pocket. |
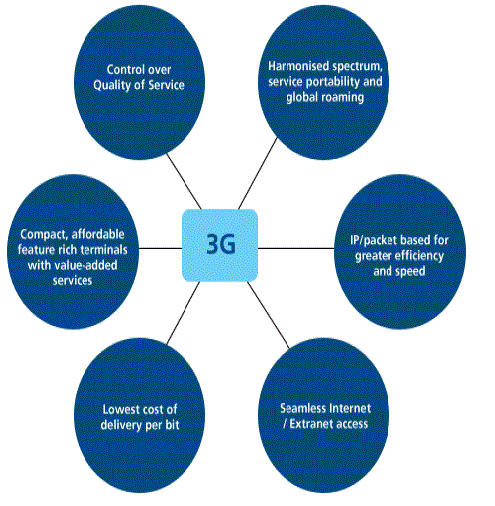
| A summary of advantages and key attributes of 3G over the conventional 2G are diagrammatically illustrated below: |
 |
CONCLUSION
|
| Despite the fact that 3G technology provide new changes and advanced methods in telecommunication, there are a number of things that may make the technology consequential. These new 3G cellular phones are actually a lot pricier, compared to traditional models. People can also do video conferences only with other 3G subscribers. There are several enhancements to features and applications, to determine if the technology is the best one our needs. |
| Newer technologies are also in the works, such as 4G and 3.5G. A major issue in 4G systems is to make the high bit rates available in a larger portion of the cell, especially to users in an exposed position in between several base stations. In current research, this issue is addressed by macro-diversity techniques, also known as group cooperative relay, and also by Beam-Division Multiple Access (BDMA). User can be simultaneously connected to several wireless access technologies and can seamlessly move between them. These access technologies can be Wi-Fi, UMTS, EDGE, or any other future access technology. |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
|
| I would like to thank esteemed Bharath university management |
References
|
- Theodore S. Rappaport, Wireless Communications Principles and Practice, Second Edition.
- C. Berrou, A. Glavieux, and P. Thitimajshima, “Near Shannon Limit Error-Correcting Coding and Decoding:Turbo- Codes”, Proc. of ICC’93, Geneve, May 1993, pp.1064–1070.
- C. Berrou and A. Glavieux, “Near Optimum Error Correcting Coding And Decoding: Turbo-Codes,” IEEE Trans. on Communications, vol. 44, pp. 1261–1271.
- http://www.schema.com.
- www.3gpp.org
|