Spatial Modulation (SM) provides many advantages when compared to other conventional Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) schemes in which multiple antenna transmit simultaneously. In SM only one antenna will be active during data transmission. This completely eliminates Inter Channel Interference (ICI) and reduces decoding complexity. In other coding techniques coding and modulation is done separately, but in Trellis Coded modulation (TCM), coding and modulation are combined together. In this paper the performance of SM-TC is compared to the performance of other techniques like Space Shift Keying (SSK), Spatial Modulation and Vertical Bell Labs Layered space time (VBLAST). SM-TC achieves better error performance when compared to previous MIMO techniques with minimum decoding complexity
Keywords |
| Spatial modulation, Multiple Input Multiple Output, Trellis coded modulation. |
I. INTRODUCTION |
| The increasing demand for the high data rate in wireless communication system needs transmission techniques,
which achieves high spectral efficiency.Recently, it was realized that the Multiple Input Multiple Output wireless
communication systems seems to be inevitable in the accelerated evolution of high data rates applications. This MIMO
communication systems, have received considerable attention of commercial companies and researchers due to their
potential to dramatically increase the spectral efficiency and simultaneously sending individual information to the
corresponding users in wireless system. In MIMO scheme, multiple antennas are used at the transmitter and receiver.
This will achieve diversity gain and antenna gain.The well-known vertical Bell Labs layered space-time (V-BLAST)
technique, in which multiple complex datasymbols are transmittedsimultaneously using multiple antennas, which
directly increases the achievable data rate and spectral efficiency. As this architecture uses multiple antennas at the
transmitter and receiver, it causes Inter Channel Interference (ICI). And the major drawback of this technique is that it
uses Maximum Likelihood decoder for achieving a good bit error rate performance, but it produces very high decoding
complexity, which increases exponentially with respect to the number of transmit antennas. When compared to V–
BLAST, SM does not have any restriction on the minimum number of receive–antennas, whereas in V–BLAST it has
to be greater than thenumber of transmit–antennas. Another classical MIMO technique is Space Shift Keying (SSK),
which uses only one information carrying unit. It map the block of information bits only to the antenna index rather
than transmitted symbols. |
| In order to reduce the decoding complexity at the receiver side, a new modulation technique called spatial
modulation has been recently proposed. Spatial Modulation is a novel data transmission technique for MIMO wireless
communication systemin which depending upon the input bits both a transmit antenna and a symbol will be selected.
The basic idea of spatial modulation technique is to map the input information to: 1) single antenna index chosen from
multiple transmit antennas and 2) a symbol selected from signal constellation diagram. Since only one antenna is active
during data transmission, ICI is completely eliminated and the decoding complexity at the receiver will be reduced.
Spatial modulation does not require synchronization between the antennas and it needs only one Radio Frequency chain
at the transmitter side. The receiver uses the antenna number and the data symbol to retrieve the original block of
information bits. |
| In wireless communication, in addition to spectral efficiency, energy efficiency is another eminent issue. TCM is a
well-known technique which is a combined effect of coding and modulation. TCM reduces power requirement without expanding bandwidth. The developers of SM developed a Spatial Modulation-Trellis coding (SM-TC), where the main
idea is to apply the concept of TCM to SM to achieve better performance in both correlated and uncorrelated
channels.In SM-TC, trellis encoder and SM mapper are jointly designed. In TCM, the block of information bit is
divided into two sequences; the first sequence enters into SM mapper after passing through convolutional encoder of
rate; and the second sequence directly enters into SM mapper. SM mapper selects the transmit antenna that is active by
modulating the bits that are coded and selects the symbol by modulating uncoded bits. TCM uses Ungerboeck set
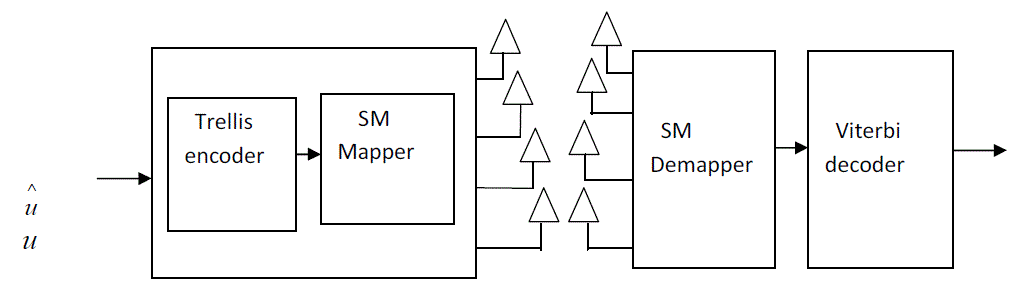
partitioning which partitions the signal constellation into subsets called cosets. The constellation must be partitioned in
such a way thatthe minimum Euclideandistance between the twopoints is increased. The decoding complexity reduces
as the Euclidean distance increases. At the receiver side soft decision Viterbi decoder is used for coded bits and then
combines with demodulated uncoded bits to produce the estimate of the input information sequence. |
| A. Literature Survey |
| a. New Trellis code design for spatial modulation |
| In this paper it is explained what is MIMO and Spatial Modulation with Trellis coding. Trellis encoder and SM mapper
are jointly designed. In this design a soft decision Viterbi decoder is used at the receiver.Pairwise Error Probability
upper bound derived for SMTC. SMTC scheme achieve better error performance than classical space-time trellis codes
and coded V-BLAST systems at the same spectral efficiency and with reduced decoding complexity. |
| b.Trellis coded spatial modulation |
| In this paper the idea is to apply TCM concept to antenna constellation points of SM. And the aim is to enhancing SM
performance in correlated channel condition. TCSM partitions the entire set of transmit antennas into subsets such that
the spacing between antennas within a particular subset is maximized. Performance and complexity of TCSM is
compared to performance of SM, coded V-BLAST and alamouti scheme combined with TCM.The complexity in this
scheme is 80 % less than V-BLAST complexity. |
| c. Space-Time Block Coded Spatial Modulation |
| STBC-SM combines both STBC and SM. In this paper, transmitted symbols are expanded not only on time and space
domain but also to the spatial (antenna) domain. A low complexity maximum likelihood is given for this scheme.
STBC scheme use MIMO because of their implementation simplicity as well as their low decoding
complexity.Orthogonal STBC have attached attention due to their single symbol ML receiver with linear decoding
complexity. But symbol rate of OSTBC is upper bounded by ¾ sumbols per channel use (pcu) for more than two
transmit antennas. |
II. SYSTEM MODEL |
| As shown in Fig.1, consider a SM-TC model which contains Nt transmit antennas and Nr receive antennas. Suppose
M-ary PSK modulation technique is used and then define n = log2 (MNt). |
| At the transmitter side, SM-TC system includes one trellis encoder (convolutional encoder) and SM mapper jointly
designed. The input sequence is first encoded by trellis encoder at a rate k/k+1 and mapped into a SM mapper. The SM
mapper first maps the index of the transmit antenna which can be determined by first log2(Nt) bits of the coded
sequence. Then it maps the left log2(M) bits of the coded sequence onto signal constellation. |
| The signal which is emitted by the active antenna then enters through a wireless channel. Due to the different spatial
positionsoccupied by the transmit–antenna in the antenna–array, the signal transmitted by each antenna experiences
different propagation conditions. Since only one transmit antenna will be active at any time instance, so only one signal
will be actually received. The other antennas will not radiate any power. |
| The receiver detects the signal which is coming from the transmitter. Channel impulse responses (NtNr) need to be
estimated which depends upon the number of transmitting and receiving antennas. At the receiver side, a soft decision
viterbi decoder is used which is fed with Soft information. The information is supplied by the SM decoder in order to
produce the estimated version of the input information sequence. |
| UngerboeckSet Partitioning |
| The functions of TCM is the combined effect of a convolutional coder of a code rate R = k / k +1 and an M-ary signal
mapper that maps M = 2k input points into a larger constellation of M = 2k+1 constellation points.For k = 2, and code
rate of 2/3that takes a QPSK signal(M=4) and put out an 8- PSK signal (M=8). So instead of expanding the bandwidth
As the signal goes from QPSK to 8PSK, it instead doubles the constellation points. Thus it conserves bandwidth by
doubling the number of constellation points of the signal. |
 |
| 3. To make all the signals to be used equally. |
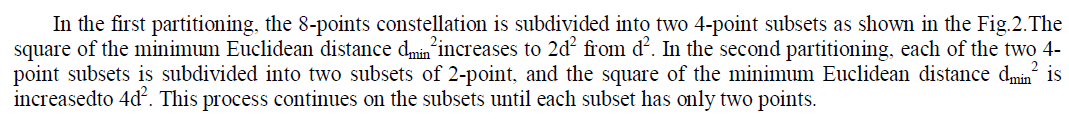 |
III. SPACE-TIME BLOCK CODED SPATIAL MODULATION (STBC-SM) |
| In the STBC-SM scheme, both STBC and SM are combined together to take the advantage of both.In this method, both
STBC symbols and the indices of transmit antennas from which these symbols aretransmitted carry information. A low
complexity Maximum likelihood (ML)is derived for the proposed STBC-SM system Alamouti’s code is chosen which
transmits only one symbol per channel use, which provides advantage in terms of spectral efficiency and simplified ML
detection.Furthermore, it is shown that this scheme achievesbetter error performance than OSTBC. |
IV. VBLAST versus SM |
| The use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiverside is shown to be an effective way of improving the
capacity and reliability of single antenna wireless systems. Two general MIMO transmission techniques, space-time
block coding and spatial multiplexing, have been proposed in the past decade. A novel concept called spatial
modulation has been introduced by Mesleh et al. as an alternative method to these two transmission techniques [2]. The
basic idea of SM is an extension of two dimensional signal constellations to a third dimension, which is called the
spatial dimension. |
V. TRELLIS CODED SPATIAL MODULATION |
| In TC-SM method, the trellis encoder and the SM mapper arejointly designed and a soft decision Viterbi decoder is
used at the receiver which is fed with the soft information supplied by the optimal SM decoder. For TC-SM, the general
conditional pairwise error probability (CPEP) is derived, and then for quasi-static Rayleigh fading channels, the
unconditional PEP (UPEP) of TC-SM is obtained with path lengths two and three. Code design criteria are used to
obtain the optimum codes with optimized distance spectra.Performance and complexity of TCSM is compared to
performance of SM, coded V-BLAST applying near optimum sphere decoder. |
VI.SIMULATION RESULTS AND COMPARISON |
| The simulation results and comparisons are shown in this section. Spatial Modulation technique is compared with
different techniques like STBC and SMTC. |
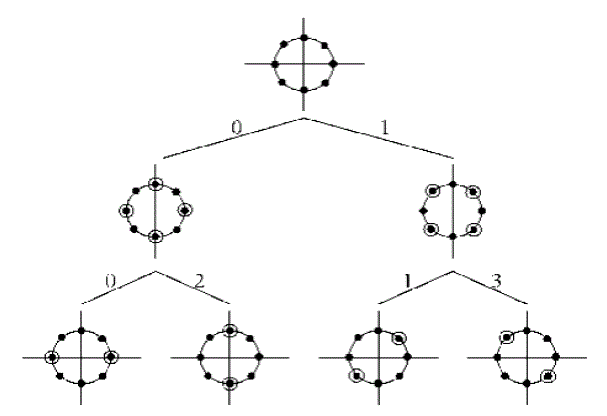
| A. Comparisonof SM and STBC-SM |
| It is shown in figure.3, Under Rayleigh fading conditions the STBC-SM provides SNR gains 3.5 dB over SM. This
result shows that one can optimize the error performance without expanding the spatial constellation to improve
spectral efficiency. |
| B. Comparison of SM and SMTC |
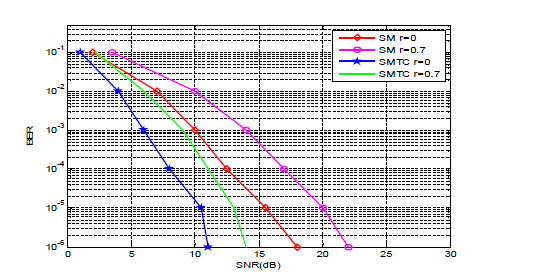
| The Graph shown in figure 4 shows the BER of a Spatial Modulation MIMO scheme for different scenarios. It is
shown that spatial modulation with trellis coding has outperformed conventional spatial modulation scheme. Thus we
can conclude that SMTC with higher r value gives better error performance which is very much necessary for wireless
communication system. |
VII. CONCLUSION |
| It has been shown via computer simulations and also supported by a theoretical upper bound analysis that the combined
effect of Spatial Modulation and Trellis coding offers significant advantages in BER compared V-BLAST and SM
systems. Set partitioned TCM achieves better error performance and improves spectral efficiency with reduced
decoding complexity compared to other classical MIMO schemes. |
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
|
| |
References |
- R. Mesleh, M. D. Renzo, H. Haas, and P. M. Grant, “Trellis coded spatial modulation,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 9, no. 7, pp. 2349– 2361, July 2010.
- Mesleh, R., Haas, H., Sinanovic, S., Ahn, C.W. and Yun, S., 2008. Spatial Modulation, IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., 57(4), 2228–2241.
- Ba¸sar, E., Aygölü, Ü.,Panayırcı, E. and Poor, H.V., 2010. New Trellis Code Design for Spatial Modulation, to appear in IEEE Trans. on Wireless Commun.
- Marco Di Renzo, Member, IEEE, Harald Haas, Member, IEEE, and Peter M. Grant, Fellow, IEEE 2011. Spatial Modulation for Multiple–Antenna Wireless Systems – A Survey, IEEE Communications Magazine, pp. 182-191.
- H. Wang, D. Wang, and X.-G. Xia, “On optimal quasi-orthogonal spacetime block codes with minimum decoding complexity,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, submitted June 9, 2004. Its short version is publishedinProc. IEEE Int. Symp. on Information Theory (ISIT), Sept. 2005.
- B. Hassibi and B. M. Hochwald, “High-rate codes that are linear in space and time,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 48, pp. 1804–1824, July 2002.
- G. Ganesan and P. Stoica, “Space-time block codes: a maximum SNR approach,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 47, pp. 1650–1656, Jan. 2001.
- C. Yuen, Y. L. Guan, and T. T. Tjhung, “Decoding of quasiorthogonal space-time block code with noise whitening,” in Proc. IEEE Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications Symp. (PIMRC), vol. 3, Sept. 2003, pp. 2166–2170.
- X. Li, T. Luo, G. Yue, and C. Yin, “A squaring method to simplify the decoding of orthogonal space-time block codes,” IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 49, pp. 1700–1703, Oct. 2001.
- M. K. Simon and M.-S. Alouini, Digital Communication over Fading Channels, 1st ed. New York: Wiley, 2000.56, no. 3, pp. 347–351, Mar.
|