Data and Information requirement is increasing with the Increase in the volumes of data in the repositories such as www etc, now question arises that out of this enormous data how to find the information which is required by the user and should be specific in nature. Information retrieval techniques solves the problem to an extent but they cannot help in a situation where only specific information pertaining to a question is required. Information retrieval engines will retrieve documents containing phrases and paragraphs which may have an answer to user query. This problem is addressed in this research paper which proposes a question answering system to satisfy users specific information need.
Keywords |
| QAS, PQC, Ontology, NE. |
INTRODUCTION |
| Question Answering systems are designed to satisfy the users specific information need. In these systems questions
are asked in natural language which is then used to identify keywords, named identities, question type which are then
used to formulate the database query. Ontology is the conceptualization of knowledge [1], Ontologies are written in
OWL and they exhibit the hierarchical structure, this paper presents a way to store the ontologies in the database in
such a way that they can be queried irrespective of their hierarchical nature, and also proposes an architecture of
question answering system which is used to process the natural language question and retrieve the answer from the
knowledge base. |
RELATED WORK |
| The question answering system proposed so far are completely based on document analysis, for example In [6]
author has proposed a system called BASEBALL which is one of the earliest question answering system, it is a
program for answering questions about baseball games played in the American league over one season. The system was
able to answer narrow-domain questions about statistics compiled over a season of American League play by using
shallow parsing techniques on the natural language query to identify the teams and statistics in question. In [7] author
proposed a question answering system named LUNAR was also based on narrow domain question answering, In [8]
during 8th TREC conference author first proposed the QA track, which required answering factoid questions by
returning a text snippet which contained an answer to the asked question. In [9], author proposed the first web based
question answering system which was different from earlier question answering system because this system was using
web as its corpus for extracting answers to the question unlike to earlier system which were based on fixed size corpus.
Some of the web based systems are START, Answer Bus, AskMAR etc. In [10] authors has proposed question
answering systems named Chinese QAS, which is language specific, morphological analysis and parsing is more
difficult in this systems because of its language specific annotations and symbols. |
PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE |
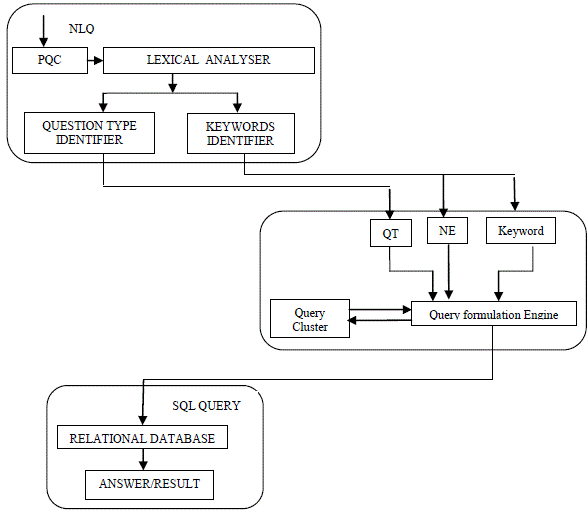
| The proposed architecture of OBQAS comprises of three functional components. They are Question Processing
module, query formulation module, Answer selection module. |
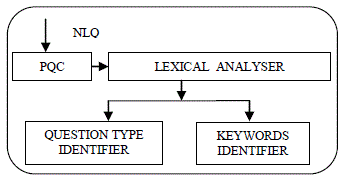
| A. Question Processing Module |
| Question Processing Module consists of two components PQC and Lexical analyser. Lexical analyser is further
consisting of two components Question type Identifier and keywords Identifier. A natural language question (NLQ) is
presented to this module which is directly fed to PQC. |
| PQC is Previous Question Cache whenever a natural language question is presented to the system it goes to this
cache which records the previously asked questions if the just arrived question matches the previously asked question
then answer to that question is retrieved directly from that cache otherwise it gets stored at the top of the list. Previous
question cache is maintained in linear list stack where stack pointer points to latest question asked. |
| The question is then presented to lexical analyser which parses it to identify the keywords and named entity in the
question. These identified keywords are then presented to query formulator. |
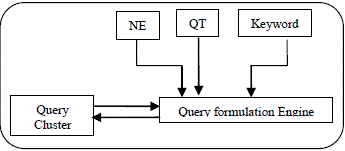
| B. Query Formulator |
| The query formulator consist of query formulation engine and query cluster the named entities identified, question
type and keywords extracted from NLQ are passed to query formulation engine, query cluster consist of query syntax depending upon the question type query is formulated using the syntax. Table 2 [2] consist of the various question
types for which the query syntax is present in the query cluster. |
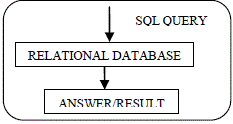
| C. ANSWER SELECTOR |
| The query formulated in the query formation module is presented to the relational database which returns the answer,
the answer to the question is returned to the user and also stored in the PQC along with the question on the top of the
list. |
| D. Database Creation |
| The system is ontology based and ontologies are written in OWL the documents pertaining to a specific domain are
in xml these documents have a hierarchical structure between the objects present in the document the xml document are
stored in the relational table in the form of xml schema. |
SIMULATION |
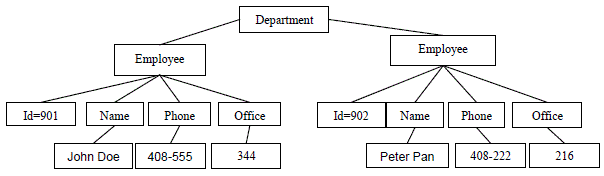
| Step 1: First of all the system is presented an XML document [4] from which an ontology is derived, |
| <dept bldg=“101”> |
| <employee id=“901”> |
| <name>John Doe</name> |
| <phone>408 555 1212</phone> |
| <office>344</office> |
| </employee> |
| <employee id=“902”> |
| <name>Peter Pan</name> |
| <phone>408 555 9918</phone> |
| <office>216</office> |
| </employee> |
| </dept> |
| Step 2: Hierarchical representation of above Ontology. |
 |
| Step 3: Database Creation for Department Ontology |
| • create table dept (deptID char(8), deptdoc xml); |
| Through this command a table will be created which is a relational containing 2 columns |
| They are dept id and deptdoc which is stored in its hierarchical structure as shown: |
| Step 4: User query in natural language: |
| NLQ: What is the name of employee with phone number 408-222 |
| This natural language query is parsed to identify: |
| i) Question Type: what |
| ii) Keyword: phone number 408-222 |
| iii) Named entity: name, employee |
| Query formulation is an internal process, the query formed by the formulator engine is |
| Select employee name from Dept |
| Where |
| Xmlexist (‘$ DEPTDOC/ department/ employee [phone number = ‘408-222’]’) |
| The retrieved answer is Peter Pan. |
CONCLUSION |
| The QAS proposed here not only serves the purpose of question answering but its architectures simplicity makes it
efficient in terms of answer retrieval. The system can be improved if the ontology can be updated automatically just as
web repositories are updated through page refreshing [5] techniques. |
Tables at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Table 1 |
Table 2 |
Table 3 |
Table 4 |
|
| |
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
|
| |
References |
- B. Chandrasekaran and John R. Josephson, “What Are Ontologies, and Why Do We Need Them?” IEEE Intelligent System Jan/Feb issue
pp. 20-26,1999.
- A New Model for Question Answering Systems, Mohammad Reza Kangavari, Samira Ghandchi, Manak Golpour , World Academy of
Science, Engineering and Technology 18 2008.
- IBM db2 9.7 pure xml information management cloud computing center of competence, ibm canada lab.
- http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/data/library/techarticle/dm-1006queriespurexml/dm-1006queriespurexml-pdf.pdf
- Rosy Madaan et. al. / (IJCSE) International Journal on Computer Science and Engineering Vol. 02, No. 03, pp. 753-758, 2010.
- Green, B., Wolf, A., Chomsky, C., and Laughery, K. "BASEBALL: an automatic question answerer," in: Readings in natural language
processing , Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., pp. 545-549, 1986.
- Woods, W.A. "Progress in Natural Language Understanding - an application to lunar geology," American
Federation of Information Processing Societies, pp. 441-450, 1973.
- E. Voorhees, “The TREC-8 Question Answering Track Report “, in NIST Special Publication 500-246: The Eighth Text Retrieval
Conference (TREC-8), pp. 77-82,1993.
- J. Lin and B. Katz. “Question answering from the web using knowledge annotation and knowledge mining techniques”, in CIKM '03:
Proceedings of the twelfth international conference on Information and knowledge management, New York, NY, USA,pp.116-123,2003.
- Gai-Tai Huang, Hsiu-Hsen Yao, “ Chinese question answering system”, Journal of computer science and technology Vol. 19, No. 4, pp
479-488, 2004.
|