Performance of a network is based on routing protocols. RIPv1, RIPv2, EIGRP and OSPF are the dynamic routing protocols being used in the practical networks to propagate network topology information to the neighboring routers. There have been a large number of static and dynamic routing protocols available but choice of the right protocol for routing is dependent on many parameters critical being network convergence time, Ethernet delay, security and bandwidth requirement etc. In this paper, we propose the idea of routing protocols, starting with an overview of the basics of Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP). Later, we describe the idea of Link State Routing Protocols (LSRP) and Distance Vector Routing Protocols (DVRP) while making a comparison which should determine the protocol needed for each network topology. The characteristics of each routing protocol will be also discussed. According to the designed simulation experiment scenarios compare the difference between RIPv1, RIPv2, OSPF and EIGRP routing protocols.
Keywords |
| Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP),
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), Link State Routing
Protocols (LSRP), Distance Vector Routing Protocols
(DVRP), Routing Information Protocol (RIP),
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
(EIGRP), Open Shortest Path First (OPSF). |
INTRODUCTION |
| A routing protocol works based on an algorithm.
Routing algorithm also based on metrics to find the path
to transmit data across two networks. Metrics also include
cost, bandwidth, Maximum Transmit Unit, delay, number
of hop count these metrics also save or store in routing
table. Routing protocol has two types. First one is an
interior gate way protocol and other one is an exterior
gateway protocol. OSPF is also interior gate way
protocol, other interior gate way Protocol are RIP,
EIGRP, IGRP. BGP and BGP4 is Exterior gate way
protocol. |
| The dynamic routing protocols keep the routing
tables updated. This paper specifies the Open Shortest
Path First (OSPF), Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
Protocol (EIGRP) and Routing Information Protocol
(RIP) TCP/IP internet routing. The network based on
TCP/IP protocol permits the efficient routing of data
packets based on their IP address. Routers are used in the
network to control and forward data. |
| In the packetized communication of information, the
function of routing is moving traffic across networks and
the routers should be aware of where they should forward
the traffic next in order to reach the final destination. In
order for routers to effectively and efficiently distribute
data, the choice of the routing protocol becomes very
critical factor to define the success of the network over
time. Factors that differentiate one routing protocol from
another include the speed that it adapts to topology
changes called as convergence, the ability to choose the
best route among multiple routes and the amount of
network traffic that the routing protocol creates. |
PACKET TRACER |
| Packet Tracer is a Cisco router simulator that can be
utilized in training and education, but also in research for
computer network simulations. The tool is created by
Cisco Systems and provided for free distribution to
faculty, students, and alumni who are all have participated
in the Cisco Networking Academy. Packet Tracer
supports users for creation of simulations, visualizations,
and animations of networking phenomena. Like any
simulation, Packet Tracer relies on a simplified model of
networking devices and protocols. It provides a simulated
environment where processes between various
networking devices, such as routers, switches, wireless
access points, computers, links and applications are
visible with animations and easy explanatory descriptions.
The purpose of Packet Tracer is to offer students and
teachers a tool to learn the principles of networking as
well as develop Cisco technology specific skills. |
 |
ROUTING PROTOCOLS |
| Most of the routing algorithms are possible to be
classified like one of two basic algorithms: |
A. Distance Vector characteristics |
| 1. The routing by distance vector collects data of the
information of the routing table of its neighbors. |
| 2. The routing by distance vector determines the best
route adding the metric value that receives as the
routing information happens from router to another
one. |
| 3. With most of the protocols of routing by distance
vector, the updates for the change of topology
consist of periodic updates of the tables. The
information happens from router to another one,
giving generally like result one more a slower
convergence. |
| RIP and EIGRP are examples of distance vector routing
protocols. |
B. Link state characteristics |
| The link state routing obtains a great vision of the
topology of complete internetwork accumulating all the
necessary LSA. |
| 1. In the link state routing, each router works
independently to calculate its own shorter route
towards the networks destiny. |
| 2. With the protocols of routing of connection state,
the updates are caused generally by changes in the
topology. |
| 3. The relatively small LSA that have gone to all the
others routers generally give like result faster times of convergence with any change of topology of the
internetwork. |
| OSPF is an example of link state routing protocol. |
 |
ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL (RIP) |
| The RIP allows that routers update their routing
tables at programmable intervals, generally every 30
seconds. One of the disadvantages of routers that use RIP
is that constantly they are connected with routers
neighboring to update his tables of routing, generating
therefore a great amount of network traffic. This makes
by means of a denominated concept vector-distance. A
jump is entered whenever the data cross to router that is to
say, happen through a new number of network, this is
considered equivalent to a jump. A route that has an equal
number of jumps to 4 indicates that the data which they
are transported must cross 4 routers before arriving at
their final destiny in the network. If there are multiple
routes towards a destiny, the route with the smaller
number of jumps is the route selected by router. |
| As the number of jumps is only metric of routing
used by the RIP, not necessarily it selects the fastest route
towards its destiny. A metric one is a measurement unit
that allows making decisions and next will learn that other
protocols of routing use other metric ones in addition to
the number of jumps to find the best route of data transfer.
Nevertheless, the RIP continues being very popular and it
is continued implementing widely. The main reason of
this is that it was one of the first protocols of routing that
were developed. |
RIP characteristics |
| 1. Distance vector routing protocol. |
| 2. It metric is the number of jumps. |
| 3. The maximum number of jumps is 15. |
| 4. One updates every 30 seconds. |
| 5. Not always it selects the fastest route for the
packages. |
| 6. It generates great amount of traffic of network with
updates. |
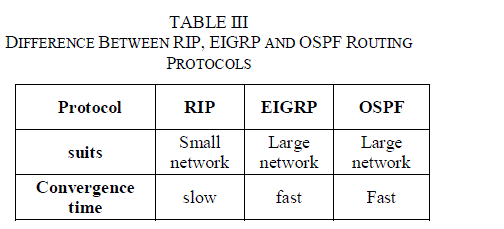
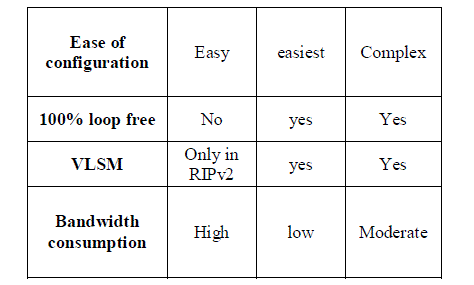
| There are two versions of RIP, namely RIPv1 and RIPv2.
The table below summarizes the differences between
these versions. |
 |
ENHANCED INTERIOR GATEWAY ROUTING
PROTOCOL(EIGRP) |
| EIGRP is an enhanced version of IGRP (Interior
Gateway Routing Protocol), an obsolete routing protocol
that was developed by Cisco. It is an advanced distancevector
protocol that implements some characteristics
similar to those of link-state protocols. Some Cisco
documentation refers to EIGRP as a hybrid protocol.
EIGRP advertises its routing table to its neighbors as
distance-vector protocols do, however it uses the hello
protocol and forms neighbor relationships similar to linkstate
protocols. |
| EIGRP sends partial updates when a metric or the
topology on the network changes. It does not send full
routing-table updates in periodic fashion as distancevector
protocols do. EIGRP is a classless protocol that
permits the use of VLSMs (Variable Length Subnet
Masks) and supports CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain
Routing) for a scalable allocation of IP addresses. |
| EIGRP uses the metrics like bandwidth, delay,
reliability, load, and MTU in making its routing decisions.
The default metrics used are bandwidth and delay. For a
more granular level of control, EIGRP multiplies each of
the metrics by 256 before performing the calculation of
the composite metric. EIGRP has been designed to make
much better use of bandwidth, and to allow routers to
have a much better awareness of neighboring routers.
Instead of sending its entire routing table out at regular
intervals, an EIGRP router sends out only partial updates,
and even then, only when a route changes. This makes a
better use of the available network bandwidth. |
| An EIGRP router also has a more complete view of
the network than a typical distance vector protocol as it
not only maintains its own routing table, but also keeps a
copy of the routing tables of neighboring routers. When
an EIGRP router cannot find a route to a network based
on all the information it currently has and it sends out a
query to other routers, which is propagated until a route is
found. |
OPEN SHORTEST PATH FIRST(OSPF) |
| Protocol OSPF proposes the use of shorter and
accessible routes by the construction of a map of the
network and data base maintenance with information on
local and neighboring systems, this way it is able to
calculate the metric for each route, and then the shorter
routing routes are chosen. In this process the metric of
state of the connection and distance are calculate in the
case of RIP calculates only the distance and not the link
traffic, by this cause OSPF is a routing protocol designed
for networks with growth constant and able to handle a
distributed routing table and fast propagation, between
routers. The Link State Database (LSDB) contains the
link state advertisements sent around the 'Area' and each
router holds an identical copy of this LSDB. The router
then creates a Shortest Path First (SPF) tree using
Dijkstra's algorithm on the LSDB and a routing table can
be derived from the SPF tree which now contains the best
route to each router |
OSPF characteristics |
| 1. Fast detection of changes in the topology and very
fast re-establishment of routes without loops. |
| 2. Low overload, use updates that inform about
changes on routes. |
| 3. Division of traffic by several equivalent routes. |
| 4. Routing according to type of service. |
| 5. Authentication. |
 |
 |
NETWORK ANALYSIS |
| In order to analyse the network in terms of network
convergence activity, Ethernet delay and protocol traffic
sent are chosen. |
| Network Convergence: Convergence is the process of
routers agreeing on optimal routes for forwarding packets
and thereby completing the updating of their routing
tables. Convergence occurs as a result of a change in
network topology, i.e., a link becoming available or
unavailable. When this occurs, each router independently
runs a routing algorithm to recalculate metrics and build a
new routing table based on this information. Once all the
routing tables have been updated, convergence is
complete. |
| The time required before all of the routers can reach
a consensus regarding the new topology, called
convergence time, depends on the number of routers in
the network that use dynamic routing protocols, the
distance of routers (measured in hops) from the point of
change, the bandwidth and traffic load on
communications links and the load on the routers. Among
the ways in which convergence time can be minimized
are using improved convergence algorithms and designing
the network so that fewer routers need to converge and so
that the load on any given router or communications link
is minimized. |
| Convergence is necessary because routers are
intelligent devices that are capable of making their own
routing decisions. This distributed intelligence is usually a
huge advantage, because it allows large networks to be
vastly faster, more robust and more efficient than would
be possible with direct human intervention. For EIGRP
protocol, the network convergence time is the shortest but
the OSPF network takes more time than the EIGRP
Network. |
 |
| Routing Traffic: Network traffic or data traffic is data
in a network. In computer networks, the data is
encapsulated in network packets. Data transmitted over a
network. Traffic is a very general term and typically
refers to overall network usage at a given moment.
However, it can refer to specific transactions, messages,
records or users in any kind of data or telephone network.
OSPF protocol provides higher traffic compared to
EIGRP and RIP. After failure/recovery happened, OSPF
protocol provides lower traffic than EIGRP. |
 |
| Ethernet Delay: Network delay is an important design
and performance characteristic of a computer network or
telecommunications network. The delay of a network
specifies how long it takes for a bit of data to travel across
the network from one node or endpoint to another. It is
typically measured in multiples or fractions of seconds.
Delay may differ slightly, depending on the location of
the specific pair of communicating nodes. Thus, engineers
usually report both the maximum and average delay, and
they divide the delay into several parts: Processing delay,
Queuing delay, Transmission delay and Propagation
delay. |
| Processing Delay- time routers take to process the packet
header |
| Queuing Delay- time the packet sends in routing queues
Transmission Delay- time it takes to push the packet’s
bits on the link |
| Propagation Delay- time for a signal to reach its
destination |
| There is a certain minimum level of delay that will be
experienced due to the time it takes to transmit a packet
serially through a link. |
| Onto this is added a more variable level of delay due
to network congestion. IP network delays can range from
just a few milliseconds to several hundred milliseconds.
EIGRP provides lowest delay and RIP provides highest
delay. |
 |
CONCLUSION |
| This paper demonstrated that CISCO Packet Tracer
can be employed by network planners to select the most
suitable routing protocol for various networks and to
design an optimal routing topology. Among the IGP types
the best protocol is EIGRP because it provides a better
performance than RIP and OSPF, it has a good impact in
the world of networking due to its fast convergence time, improved scalability and for sure the great handling of
routing loops and also EIGRP has a great impact in HTTP
application which gives it the power to be in the lead of
routing protocols. |
References |
- MaryAnne B. Taquiqui (2013) âÃâ¬ÃÅProtocol Data Unit (PDU): ASimulationâÃâ¬ÃÂ, Network and Complex Systems, Bahrain.
- AbdulrahmanAlkandari (2012) âÃâ¬ÃÅAn Anatomy of IGP and BGP Routing ProtocolsâÃâ¬ÃÂ, International Islamic University,Malaysia.
- Don Xu and LjiljanaTrajkovic (2011) âÃâ¬ÃÅPerformance Analysis of RIP, EIGRP and OSPF based on OPNETâÃâ¬ÃÂ, OPNETWORK2011, Washington DC.
- Shravan K. Naivety and Santosh K. Balsu (2011) âÃâ¬ÃÅPerformance Comparison of EIGRP and ISIS/RIP ProtocolsâÃâ¬ÃÂ, School ofComputing/Telecom, Karlskron, Sweden.
- Khalid Abu Al-Saud, Mohammed Saleh (2008) âÃâ¬ÃÅImpact of MD5 Authentication on Routing Traffic for the Case of EIGRP,RIPv2 and OSPFâÃâ¬ÃÂ, University Utara Malaysia
- Lemma.E, Hussain .S, Anjelo .W (2010) âÃâ¬ÃÅPerformance Comparison of EIGRP/IS-IS and OSPF/IS-ISâÃâ¬ÃÂ, BlenkingeTekniskaHogskolan, Sweden.
- Ayub,N., et al. (2011). Performance Analysis of OSPF and EIGRP Routing Protocols with Respect to the Convergence,European Journal of Scientific Research, ISSN 1450-216X Vol.61 No. 3, pp434-447.
- Farhangi, S. et al. (2012). Performance Comparison of Mixed Protocols Based on EIGRP, IS-IS and OSPF for Real TimeApplications, Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 12(11): 1502-1508, 2012 ISSN 1990-9233.
- Lammle, Todd. (2011). Cisco Certified Network AssociateStudy Guide, Wiley Publishing, Inc., Seventh Edition.
- http://cisco.netacad.net.
|