Education plays an important role in maintaining the economic growth of a country. Now a days the classroom teaching is changing and students are becoming more technology oriented and Therefore in his changing environment, it’s important that we think about the latest technologies to incorporate in the teaching and learning process. One of the latest technologies prevailing now days is Cloud Computing. By sharing IT services in the cloud, educational institution can outsource noncore services and better concentrate on offering students, teachers, faculty, and staff the essential tools to help them succeed. This paper focuses on the impact of cloud computing on the education system and how we can provide the quality education by using the above technology.
Keywords |
| Cloud computing, higher education, SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, virtualization. |
INTRODUCTION |
| India government is encouraging the parents to send their wards to join schools and colleges and has been providing
various schemes to promote education. The various schemes makes students reaches to the schools and colleges but lack of
facilities, good teachers, lack of latest books and labs facilities seriously affects their results and thus discourages them to
continue their education. One of the biggest challenges that the government faces in providing education is the lack of
infrastructure and if available then maintenance of that infrastructure and other issue is Procuring and maintaining a wide
range of hardware and software require ample, ongoing investment and the skills to support them. |
| Cloud computing can help provide those solutions. It’s a network of computing resources—located just about anywhere—
that can be shared. Thus by implementing cloud computing technology we can overcome all these short comes and
maintain a centralized system where all the authorities can check the education system from each and every aspects and
continue monitor and guide the system. They not only check the needs of the institutions but also ensure that quality
education is provide to every student and also his attendance, class performances etc can be effectively maintained without
worrying for the infrastructure issue. |
| The cloud helps ensure that students, teachers, faculty, parents, and staff have on-demand access to critical information
using any device from anywhere. Both public and private institutions can use the cloud to deliver better services, even as
they work with fewer resources. |
LITERATURE REVIEW |
| Cloud computing predecessors have been around for some time now [13, 14,15], but the term became “popular” sometime
in October 2007 when IBM and Google announced a collaboration in that domain [16,17].This was followed by IBM’s
announcement of the “Blue Cloud” effort [18]. Since then, everyone is talking about “Cloud Computing”. Of course, there
also is the inevitable Wikipedia entry [19]. |
| It is conceivable that August 24, 2006 will go down as the birthday of Cloud Computing, as it was on this day that Amazon
made the test version of its Elastic Computing Cloud (EC2) public [Business Week 2006]. This offer, providing flexible IT
resources (computing capacity), marks a definitive milestone in dynamic business relations between IT users and providers.
The term first became popular in 2007, to which the first entry in the English Wikipedia from March 3, 2007 attests, which,
again significantly, contained a reference to utility computing. Today, Cloud Computing generates over 10.3 million matches on Google. The scope of Cloud Computing grew from simple infrastructure services such as storage and
calculation resources to include applications. However, this meant that forerunners such as application service providing
and Software as a Service would also henceforth be included under the designation of Cloud Computing. |
CLOUD COMPUTING |
| Cloud computing is an extension of the concept of distributed computing – which is the process of running a program or
application over many computers connected by a network. The Internet makes this process easily achievable even for the
general user. NIST (US National Institute of Standards and Technology) defines cloud computing as: |
| “ a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing
resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with
minimal management effort or service provider interaction”. |
| Cloud computing is Internet-based computing in which shared resources, software and information are delivered as a service
that computers or mobile devices can access on demand. Cloud computing is already used extensively in education. Free or
low-cost cloud-based services are used daily by learners and educators to support learning, social interaction, content
creation, publishing and collaboration. Examples of cloud-based services include Google Apps, YouTube, Twitter and Drop
box. |
| The various types of services provides by the cloud are: |
| 1. Software as a Service (SaaS): Anytime Anywhere apps. This is currently of most interest in education. Not only is the
data stored in the cloud but the application too, with the user requiring only a web browser. The best known examples
are Google Apps for Education and MicrosoftLive@edu which provide communication and office applications such as
email and spreadsheets. |
| 2. Platform as a Service (PaaS): The operating environment in which applications run. With PaaS, one can develop new
applications or services in the cloud that do not depend on a specific platform to run, and can make them widely available
to users through the Internet. PaaS delivers cloud-based application development tools in addition to services for testing,
deploying, collaborating on, hosting, and maintaining applications. Examples of PaaS include Microsoft's Azure Services
Platform (Microsoft, 2012), Salesforce's Force.com development platform, Google Apps Engine, Amazon's Relational
Database Services and Rackspace Cloud services. |
| 3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): The on-demand data centers. Here customers can rent basic computing resources
such as processors and storage, and use them to run their own operating systems and applications. You pay for only what
you use, and the service provides all the capacity you need, but you’re responsible for monitoring, managing, and patching
your on-demand infrastructure. One big advantage of IaaS is that it offers a cloud-based data center without requiring you
to install new equipment or to wait for the hardware procurement process. This means one can get IT
resources at his school, college, or university that otherwise might not be available. For example Amazon’s Elastic
Compute Cloud; organizations can use this infrastructure to run Linux servers on virtual machines and scale up usage as
required. |
PRESENT EDUCATION SYSTEM |
| Most of the private educational institutions have become highly dependent on information technology to service their
requirements. These services are increasingly provided using Internet technologies to faculty and students and accessed
from web browsers. The services are offered cheaply or freely to education, often with much higher availability than can be
provided by the educational institution. |
| Are we therefore facing a future where the majority of educational services will be hosted in the cloud and institutions no
longer host their own data centers with expensive hardware, power bills, staff salaries and computing resources which are
rarely fully utilized? This policy brief has analyzed some of the emerging benefits and challenges of cloud computing for
the educational sector. But in most of the government schools and colleges in India IT plays very limited role. Most of the
work is done manually from attendance to classroom teaching to examination system. |
IMPLEMENTATION OF CLOUD TECHNOLOGY IN EDUCATION SYSTEM |
| Cloud computing technology can provide solutions for the above mentioned problems in education system. Cloud
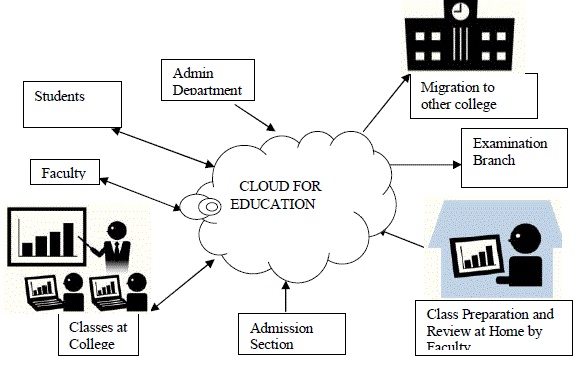
computing enables users to control and access data via the Internet.The main users of a typical higher education cloud
include students, Faculty, administrative staff, Examination Branch and Admission Branch as shown in Figure 1. All the
main users of the institution are connected to the cloud .Separate login is provided for all the users for their respective work.
Teachers can upload their class Tutorials, assignments, and tests on the cloud server which students will be able to access
all the teaching material provided by the teachers via Internet using computers and other electronic devices both at home
and college and 24X7. The education system will make it possible for teachers to identify problem areas in which students
tend to make mistakes, by analyzing students’ study records. In doing so, it will also allow teachers to improve teaching
materials and methods. |
| This will not only make it possible for students to use online teaching materials during class but they will also be able to
access these materials at home, using them to prepare for and review lessons. Utilization of cloud computing systems will
reduce the cost of operation because servers and learning materials are shared with other colleges. |
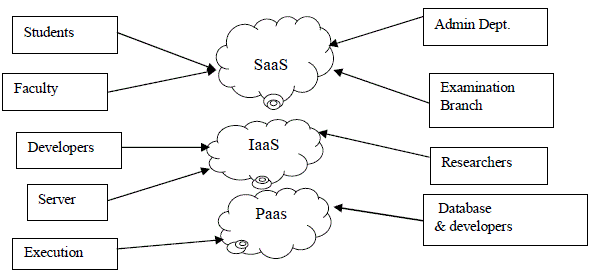
| In the traditional deployment model, all Information Technology resources are housed and managed in-house. Many
aspects of these services and tools may be migrated to the cloud and consumed directly over the Internet either as fully functional applications (SaaS), development platforms (PaaS) or raw computing resources (IaaS).Figure 2 shows how the
different categories of university users may consume cloud services. |
BENEFITS OF CLOUD COMPUTING FOR INSTITUTIONS AND STUDENTS |
| Personalized Learning: Cloud computing affords opportunities for greater student choice in learning. Using an
Internet-connected device, students can access a wide array of resources and software tools that suit their learning
styles and interests. |
| Reduced Costs: Cloud-based services can help institutes reduce costs and accelerate the use of new technologies to
meet evolving educational needs. Students can use office applications for free without having to purchase, install
and keep these applications up to date on their computers. It also provides the facility of Pay per use for some
applications. |
| Accessibility: Availability of the services is the most important and desired by the user using the education
cloud.24 X7 is the availability that is needed by this system without failure. From anywhere one can login and
access the information. |
| No Extra Infrastructure: Colleges and governments are now free to focus on their goals that is making more
research facilities available to the students and making the environment global in spite wasting time on worrying
about the buildings, labs, teachers etc. |
| Go Green: Education cloud will surely reduce the carbon footprint. |
| User Friendly: This new facility is user friendly and no need to worry about the complexity. It is easy to
understand and easy to operate. |
SECURITY ISSUES |
| In cloud computing we are saving our important and crucial data in one place and it will be easy for hack. Protection of data
is a major security issue. Educational Institutions may consider that their data is more secure if it is hosted within the
institution. Transferring data to a third party for hosting in a remote data Centre, not under the control of the institution on
and the location of which may not be known presents a risk. Some cloud providers now provide guarantees in their
contracts that personal data will only be stored in particular countries. It has been suggested that the provision of cloud
services through a single provider is a single point of failure and that it would be better to contract more than one cloud
provider in order to minimize risk. Another security issue is Unsolicited advertising in which cloud providers will target
users with unsolicited email or advertising. |
CONCLUSION |
| The cloud allows us to access our work anywhere, anytime and share it with anyone. It frees us from needing a particular
machine to access a file or an application like a word processor or spreadsheet program. In the present paper a cloud
education system is introduced and how it is beneficial for students, faculty and the educational institutes for providing
quality education. |
| |
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
|
| |
References |
- G.M. Muriithi,J.E.Kotze,âÃâ¬Ã Cloud computing in higher education: implications for South African public universities and FET collegesâÃâ¬ÃÂ, Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference on World Wide Web Applications Durban, 7-9 November 2012 (http://www.zaw3.co.za) ISBN: 978-0-620-55590-6
- Sunita Manro,Jagmohan Singh,Rajan Maro ,âÃâ¬ÃÂCloud Computing in Education: Make India Better with the Emerging TrendsâÃâ¬ÃÂ, High Performance Architecture and Grid Computing Communications in Computer and Information Science Volume 169, 2011, pp 131-139.
- Gaurav Bhatia, Mohnish Anand, Priya Shrivastava,âÃâ¬Ã Cloud Computing Technology In Education SystemâÃâ¬ÃÂ, International Journal of Advanced Technology & Engineering Research (IJATER), ISSNNO:2250-3536 Volume2,Issue2,March2012.
- Buyya, R. et al (2009). Cloud Computing and emerging IT platforms: Vision, Hype and reality for delivering computing as the 5th Utility. Future Generation Computer Systems. http://www.buyya.com/papers/Cloud-FGCS2009.pdf
- Sultan, N. 2010. Cloud Computing for Education: a new dawn? http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0268401209001170.
- https://education.alberta.ca/media/6884876/final%20cloud%20computing%20tech%20briefing.pdf
- http://www.thehindu.com/features/education/college-and-university/computing-in-the-cloud/article5433501.ece
- http://educationinjapan.wordpress.com/2014/01/06/yomiuri-shimbun-cloud-computing-to-be-used-in-schools-from-fy-14/
- http://iite.unesco.org/pics/publications/en/files/3214674.pdf.
- www.microsoft.com/educloud.
- Mladen A. Vouk,âÃâ¬Ã Cloud Computing âÃâ¬Ãâ Issues, Research and Implementations âÃâ¬ÃÅ,Journal of Computing and Information Technology - CIT 16, 2008, 4, 235âÃâ¬Ãâ246 doi:10.2498/cit.1001391
- White Paper Cloud Computing , Alternative sourcing strategy for business ICT. Published by:T-Systems Enterprise Services GmbH Mainzer Landstrasse 50 60325 Frankfurt, Germany.
- Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): http://www.amazon.com/gp/browse.html? node=201590011.
- IBM, âÃâ¬ÃÅNorth Carolina State University and IBM help bridge digital divide in North Carolina and beyondâÃâ¬ÃÂ, May7,2007,http://www-03.ibm.com/industries/education/doc/content/ news/pressrelease/2494970110.html
- E.NAONE,âÃâ¬ÃÅComputer in the CloudâÃâ¬ÃÂ, Technology,Review, MIT, Sept 18, 2007,http://www.technologyreview.com/printer friendly
- S.LOHR,âÃâ¬ÃÅGoogle and I.B.M. Join in âÃâ¬ÃËCloud ComputingâÃâ¬Ã⢠ResearchâÃâ¬ÃÂ, October
92a8c77c354521ba&ex=1349582400&oref=slogin&partner=rssnyt&emc=rss& pagewanted=print
- IBM, âÃâ¬ÃÅGoogle and IBM Announced University Initiative to Address Internet-Scale Computing ChallengesâÃâ¬ÃÂ,October 8, 2007, http://www-03.ibm.com/press/us/en/pressrelease/22414.wss
- IBM,âÃâ¬ÃÅIBM Introduces Ready-to-Use Cloud ComputingâÃâ¬ÃÂ,http://www 03.ibm.com/press/us/en/pressrelease/22613.wss, November 15,2007.
- WIKIPEDIA, âÃâ¬ÃÅCloud ComputingâÃâ¬ÃÂ, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud computing, May 2008.
|