ISSN ONLINE(2320-9801) PRINT (2320-9798)
ISSN ONLINE(2320-9801) PRINT (2320-9798)
Kusum Rani1, Reecha Sharma2
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering
Image fusion is processes of combining complementary information from a set of input images. The resultant fused image give large and reliable information. In this paper we study about Discrete wavelet and Discrete Multiwavelet and there use in image fusion. Discrete wavelet transform (DWT) technique is used for multi Resolution fusion. Multi Resolution fusion uses wavelet transform at multi scale for the representation of the source images. Multiwavelets are extension of scalar wavelets, and have many advantages over scalar wavelets. Multiwavelet analysis can provide a more absolute image analysis than wavelet multiresolution analysis.In this paper DWT and DMWT are qualitatively compaired with each other
Keywords |
| Image fusion, multiwavelet transform,wavelet transform . multisensor image . |
INTRODUCTION |
| Image Fusion is defined as the task or technique of combining two or more images into a single image. The new single image retains important information from each input image. Image fusion is a powerful tool used to increase the quality of image. Image fusion increases reliability, decreases uncertainty and storage cost by a single informative image than storing multiple images Image fusion can take place at three different levels pixel feature,decision level Image fusion technique can be classified into two categories – Direct Image Fusion and Multi resolution Image Fusion. Multiresolution Image fusion techniques based on pixel level fusion methods. Multi Resolution fusion uses wavelet and multiwavelet transform at multi scale for the representation of the input images. Image fusion based on the DWT can provide better performance than fusion based on other multiscale methods such as Laplacian pyramid, morphological pyramid. Wavelet transform in multiresolution can provide good localization in both frequency and space domains. In comparision with other multiscale transforms, the discretewavelet transform is more compact, and give detail about directional information in the low-low, high-low, low-high, and high-high bands, and contains unique information at different resolutions. The main dwarback of the scalar wavelet functions is time-frequency localization property. Multiwavelets have more than two scaling and wavelet functions. The multi-wavelet has many outstanding properties like orthogonality, short support, symmetry, and high degree of vanishing moments which is desirable for image processing . A multiwavelet system provides perfect reconstruction also preserve length (orthogonality), good performance at the boundaries , and a high order of approximation . By this multiwavelets gives superior performance for image processing applications as compared with the scalar wavelets. |
II.IMAGE FUSION: SCALAR WAVELETS |
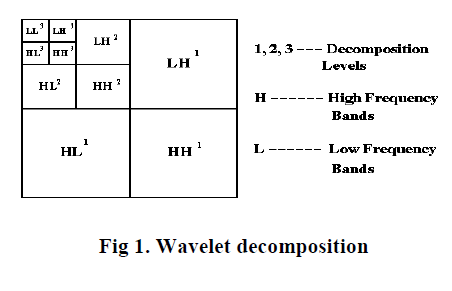
| The wavelet transform is use to detect local features in a signal process. It also used for decomposition of two dimensional (2D) signals such as 2D gray-scale image signals for multiresolution analysis. In wavelet transforms a signal is decomposed in lower frequency band and high frequency bands. In discrete wavelet transform (DWT), twochannel filter bank is used. When decomposition is performed, the approximation and detail component can be separated 2-D Discrete Wavelet Transformation (DWT) converts the image from the spatial domain to frequency domain. The image is divided by vertical and horizontal lines and represents the first-order of DWT, and the image can be separated with four parts those are LL1, LH1, HL1 and HH1. [10] |
 |
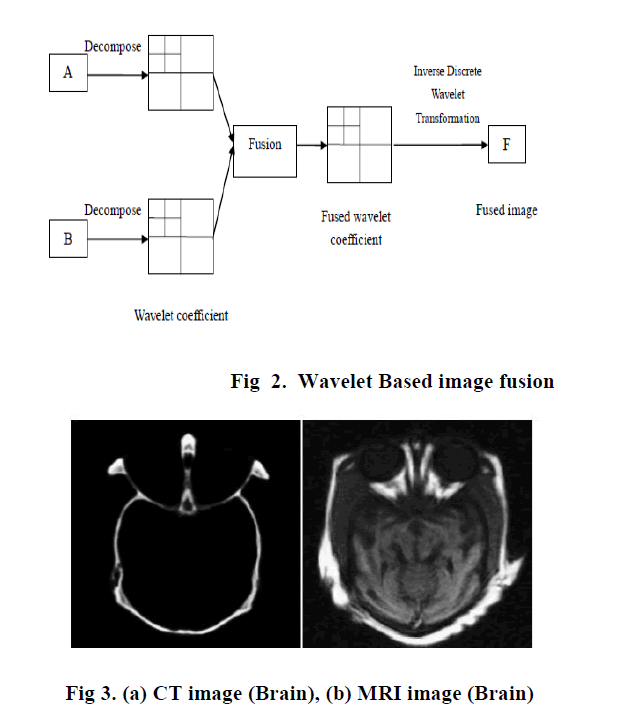
| General process of image fusion using DWT |
| Step 1. Implement Discrete Wavelet Transform on both the source images to create wavelet lower decomposition. |
| Step 2. Fuse each decomposition level by using different fusion rule like simple average , simple maximum ,simple minimum ,etc . |
| Step 3. Carry Inverse Discrete Wavelet Transform on fused decomposed level, for reconstruction of final fused image F. |
 |
 |
III.IMAGE FUSION: MULTI WAVELET TRANSFORM |
| Multiwavelets are similar to scalar wavelets but have some important differences. Scalar wavelets, which are used in multiresolution analysis with a single scaling function and a wavelet function, multiwavelets may have two or more scaling and wavelet functions. Goodman and Lee [1] are among the earliest to develop a multiresolution theory of multiwavelets. In his PhD work, Strela [2] further extends the theory of multiwavelets. He successfully presented it in terms of perfect reconstruction multifilter banks in both time and frequency domains. |
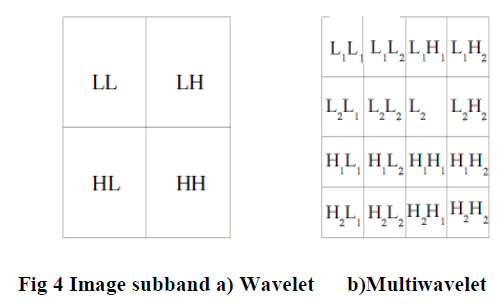
| Unlike scalar wavelets, in multiwavelet each decomposition level consists of 16 subbands. In 2D-DMWT prefilter is first used on each row of the image. Then resultant rows are then decomposed by using 1D DMWT. The same steps are used on the columns. Result of 2D-DMWT decomposition is 16 subimages containing multiwavelet coefficients related to lowpass and highpass filters as shown in figure (4). |
 |
| In image fusion process a registration step is required before applying 2D-DMWT. The registration step is used to overcome imaging parameter differences between two source images. After prefiltering and apply 2D-DMWT to the registered input images, an activity level measurement (AL) step is used for appoint different weights to multiwavelet coefficients. These weights will be used in coefficient selection. The activity level of an MSD coefficient indicates the local energy in the space spanned by the term in the expansion corresponding to coefficient. There are three methods including coefficient-based, window-based, and region-based [7] for computing the AL for an image I. |
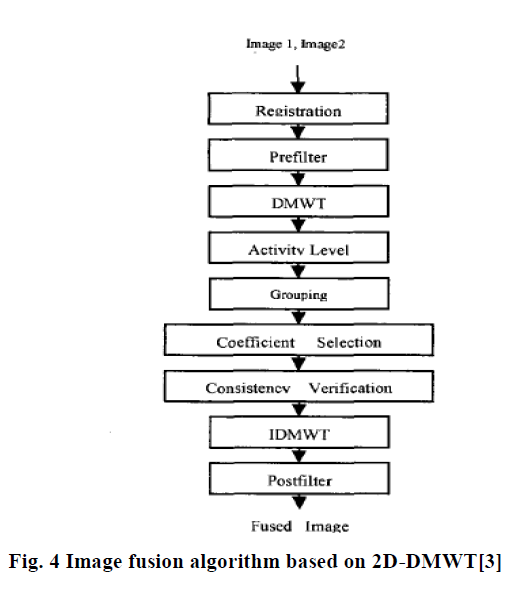 |
| Because of Unsupervised selection of DMWT coefficients from both the image coefficient sets degraded the output fused image. So that resolution level and for each location, only one DMWT coefficients should be selected from one of image Coefficient set. The grouping algorithm uses the AL assigned to each coefficient in order to select the best coefficient set from two images. To select correct coefficients for image fusion, the average AL of grouped coefficients in each level are calculated. Then, the group which has largest average AL is selected. The final step for coefficient selection process is consistency verification. The consistency verification attempts to ensure that the neighbouring coefficients in the composite MSD are obtained . |
 |
IV CONCLUSION |
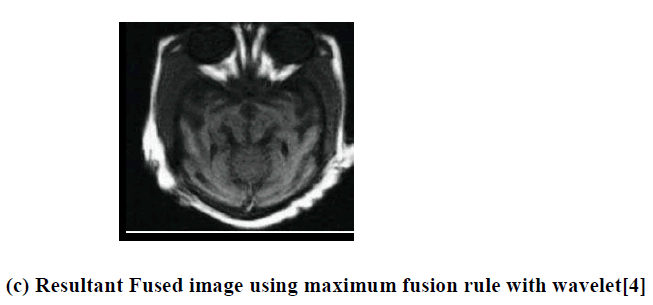
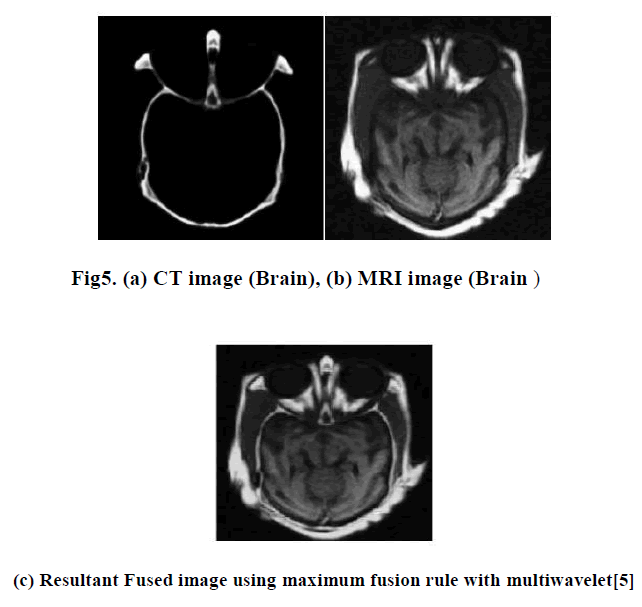
| In this paper two different modality images are fused using the maximum fusion rules based on the Multi-Wavelet and wavelet transforms. Qualitatively multiwavelet transform give better performance than wavelet . Multiwavwlet gives fine edge and boundary details. With proper selection of multiwavelet transform and coefficient may help to improve the quality of the image fusion results. |
References |
|