ISSN ONLINE(2320-9801) PRINT (2320-9798)
ISSN ONLINE(2320-9801) PRINT (2320-9798)
Thivya.G1, Shilpa.G.V2
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering
Nowadays all illegal activities are happened using the communications in instant messages. Present framework for instant messenger have control over suspicious words but not in depth. It means present system could not find out all suspicious words. The proposed system is a framework, which predicts and highlights code words and short form of suspicious words with the help of association rule mining techniques and ontology concepts.Thus this proposed framework detects suspicious messages from instant messaging systems in early stage and helps to identify and predict the type of cyber threat activity and traces the offender details.
Keywords |
| Instant Messengers(IM); Social Networking Sites(SNS); Ontology;Association Rule Mining (ARM). |
INTRODUCTION |
| Social networks are essentially networks formed by individuals, groups and organizations. Social network analysis is about analyzing the behaviors of individuals, groups and organizations and determines its behavior patterns. Social network analysis is becoming an important tool for counter terrorism applications. |
| Social Networking Sites (SNS) are web-based services that facilitates individual to construct a profile, which is either public or semi-public. SNS contains list of users with whom we can share a connection, view their activities in network and also converse [1]. SNS users communicate by messages, blogs, chatting with video and music files. SNS plays very important role in human life.It is becoming a main communication media among the individuals and organizations. The other advantages include keeping contact with friends and family members. For entrepreneurs, it acts as a resource to set up a global presence. Employers nowadays use SNS as useful and effective recruitment tool. Some SNS provides low cost of advertising for business owners. However with all these advantages, SNS also have many disadvantages such as information is public, security problem, cyber bullying and misuse and abuse of SNS platform. |
| The medium of Instant Messaging on the Internet is a well-established means by which users can quickly and effectively communicate with one another. Long utilized by the public as a quick form of free communication, data mining tasks have not been attempted over Instant Messaging. Additionally, on a corporate or government level, people are just beginning to take notice of the potential that IM provides in terms of the type of information that can be collected from these networks. Many large Instant Messaging networks are of their own generally open to the public after registration, including Time Warner, Yahoo and Microsoft. |
| One of the biggest challenges in automated message surveillance is the recognition of messages containing suspicious content. A classic approach to this problem is constructing a set of keywords. In the event that a communication contains one or more of these words, the message is flagged as suspicious for further review. However there are two drawbacks to this particular approach. First, it is reasonable to assume that such relatively static keywords will not always be present in messages that would otherwise warrantsuspicion. Second, there is little guarantee that a sufficiently intelligent individual will not recognize such surveillance is in place and instead use substitute words in place of known keywords. |
| Internet evolutions led to the growth of innumerable cybercrimes. Cybercrime is a fast-growing area of crime. More offenders are exploiting the speed, convenience and anonymity of the Internet to commit a diverse range of offender activities that know no borders, either physical or virtual. Offenders adapted to send suspicious messages via mobile phones, instant messengers and social networking sites that are difficult to trace their offender activities dynamically. The E-crime department must be devised with the development of technology to find offenders. Many of the instant messaging systems restricted their limit for sending messages, video and audio conferencing. They are not well equipped to detect online suspicious messages, which lead to illegal activities. |
| This paper is organized as follows. Section II shows literature survey. Section III deals with proposed framework. At last section IV puts forward the conclusion and future works. |
LITERATURE SURVEY |
| Nowadays, it is difficult to survive without Instant Messaging Service (IMS) as users are addicted to. Trillions of messages are sent each day through emails and IMS. Popular IMS such as AOL, MSN, ICQ, Yahoo, Google Talk, Skype, Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn have changed the way of communication with friends, acquaintances and business colleagues. Understanding the dynamics behind the relationships between offenders can help an investigator identify suspects and understand offender activities [2]. Once limited to desktops, popular instant messaging systems are finding their way onto handheld devices and cellphones, allowing users to chat virtually from anywhere. |
| There are few works done in the area of SNS and content analysis. Julei Fu and Jian Chai [3] have proposed six-element analysis method for terrorist activities based on social network. However, this method analyzed on data obtained from previous year incidents, which is in the form of 420 web pages to get information of the terrorist events incited by East Turkistan. |
| Michael Robertson, Yin Pan and Bo Yuan [4] explained about the social approach to detect malicious web content for Facebook with security heuristics is limited to identify malicious URL links. Recently the Facebook static messages are scanned to identify criminal’s behavior [5]. Detection of suspicious emails from static messages using decision tree induction proposed which is purely dependent on highest information entropy that identifies the messages are deceptive or non-deceptive [6]. |
| John Resig and AnkurTeredesai [7] detect suspicious messages from the data gathered by anomaly detection, topic detection [8][9] and social network analysis, which will not disclose all suspicious messages. Hence new offenders will not be traced by this system. |
| Mohd Mahmood Ali and Lakshmi Rajamani [10] proposed framework with an idea of instant message secure system that identifies suspicious messages that leads to illegal activities by offenders. But it does not focus on securing messages by using encryption techniques and also does not concentrate on short form messages. This paper gives various ideas about stemming algorithm and apriori algorithm. |
| Sharath Kumar and Sanjay Singh [11] concentrates on cluster of users in SNS who perform illegal activity based on their messages with the help of past history of the user. But in present system, offenders are smarter than investigators. They are not using same way of writings. |
| Farkhund Iqbal, Benjamin C.M.Fung, MouradDebbabi [12] concentrate on entity such as name of a person and tries to find which group in social networks the person belongs to. It also focused on the messages sent by the same person in the group. But it never concentrates on suspicious words given by other offenders who are presently chatting with only one person. So it will focus on old group of offenders who are already in database. It is not providing full details to crime investigators. |
| Mohd Mahmood Ali, KhajaMoizuddinMohd and Lakshmi Rajamani [13] proposed framework for secure instant messaging system using ontology. This paper does not focus on code words and short form chat messages. Here, ontology construction means dividing the instant messages semantically with the help of Word Net [14] database into various topics such as murder, robbery and so on. But ontology is not updated regularly with new code words that are found using data mining techniques. |
| All the papers mentioned above are concentrated on security in instant messaging in the form of simple chat logs. But nowadays offenders are too smart to use code words and short forms of messages. And none of the paper focuses on proper ontology updates. Proposed work focuses on this area of messages and proper ontology based information extraction system. |
PROPOSED FRAMEWORK |
| Nowadays all illegal activities make use of the communications in instant messages. Present framework for instant messenger have control over suspicious words but not completely. |
| Thus existing system has several limitations as follows. |
| Cybercrimes have raised day by day, but the social networks are not having mechanisms to restrict them. |
| Offenders can easily convey their messages through the insecure social networks and internet. |
| Blackmails are also sent from one person to another person that could not be traced out. |
| Short form messages and code word messages in social networks are still worsen the case of disclosing the illegal activity. |
| Proposed system has the below mentioned salient features as objectives. |
| System tries to provide security for the stored chat messages by using encryption technique. Then it will find suspicious words by decrypting stored messages. |
| Detects the suspicious words from the message even the message is in short form or code form. |
| This determination of illegal activities is analyzed with the help of ontology. Even new code words that are not available in predefined database are also extracted with the help of data mining techniques and added into ontology database. |
| If the system finds some cyber threat it will report with the offender’s personal details to E-crime department. |
| System’s performance can also be evaluated with the help of execution of user generated content called test bed. |
| Thus the proposed system is a framework that predicts and highlights such suspicious messages along with suspected threat activity with offender’s personal details. All the instant messages will be faced by the system for any supposed cipher thread activity. This new framework uses association rule mining algorithm and ontology based information extraction technique which initiates the steps to capture and store the instant messages that are communicated between the users and identifies suspicious messages with predefined knowledge such as the keywords murder, kill and theft and so on. In addition the system also verifies code words and short form suspicious words. The system also uses encryption/decryption methodsto enhance security to the messages and figure out any suspicious messages present over there. |
| This proposed framework has the following components: |
| Data collection system |
| Suspicious word detection system |
| Both data collection and suspicious word detection systems have normal functionalities that are given by all instant messengers such as login module, change password etc., |
| In addition,suspicious word detection system has the following sub components: |
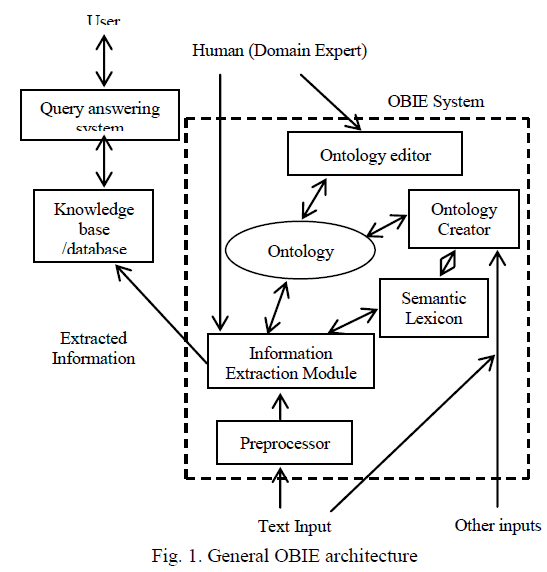 |
| A. Ontology management |
| Since ontologies are widely used to represent knowledge or meaning they are often seen as providing the backbone for the semantic web.In this framework, ontology database is created with suspicious word list such as murder, kidnap, terrorist, corruption and robbery. These processes can be implemented by OBIE [17] (Ontology Based Information Extraction).OBIE has recently emerged as a subfield of information extraction. Here ontologies - which provide formal and explicit specifications of conceptualizations - play a crucial role in the IE process. Because of the use of ontologies, this field is related to knowledge representation and has the potential to assist the development of the semantic web. |
| General OBIE architecture can be constructed as shown in below Fig 1. This architecture depicts ontology editor, ontology creator and IE module as major parts of ontology. Preprocessing of the text is important before IE. Semantic lexicon also acts major role in ontology creator. Thus the user can effectively extracts relevant information with the help of OBIE system. |
| B. Encryption / Decryption Module |
| Proposed system will encrypt the messages and store it in the database. Suspicious word detection can be done on the decrypted message along with short form and code words. |
| C.Suspicious word detection |
| Here, filtering of unnecessary words from messages is done; during this process, the suspicious words such as murder, kidnap, terrorist, corruption and robbery are identified using data mining techniques. |
| D.Short form management |
| A separate database will be maintained with short forms of suspicious words such as politician names, country names and short form of suspicious word such as kl (kill), att (attack), bom (bomb) and money ($).Again by using same detection algorithm these suspicious words are detected. |
| E. Code word management |
| Comparing several messages communicated within a same group can identify code words. If same word was used by different people in conversation within a group along with known suspicious words in database then these words are considered as code words and also added to suspicious list to detect suspicious words in future. |
| F. Ontology Update |
| New suspicious words that are not already in database are founded with the help of code words detection method and will be added back in ontology. Thus ontology used here is fully updated then and there. This ontology update helps in finding suspicious words in efficient manner and it saves time in detecting suspicious words in future. |
| G. Offender’s information module |
| After finding suspicious words from the conversation system can easily figure out the offenders names along with their personal details and IP address of their systems. This information is displayed with the help of database which was originated while creating the chat id. |
| The following Fig 2.shows the overall system structure of the proposed framework. As shown in the figure, data collection system follows ordinary web chat application’s features for group chat along with encryption techniques to facilitate security. Suspicious word detection system focuses on detecting suspicious words with the help of OBIE and data mining techniques. Short word, code word and suspicious word databases are maintained. Finally offender’s details are displayed with the help of user’s personal database. |
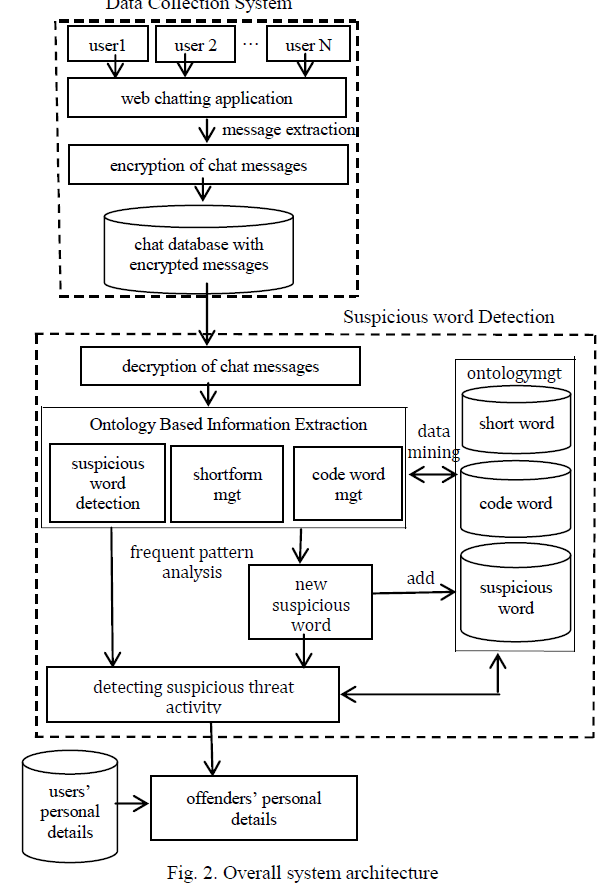 |
CONCLUSION |
| Framework of proposed system aids the E-crime department to identify suspicious words from cyber messages and trace the suspected culprits. Currently existing Instant Messengers and Social Networking Sites lack these features of capturing significant suspicious patterns of threat activity from dynamic messages and find relationships among people, places and things during online chat, as offenders have adapted to it. The testbed is proven to be useful, for monitoring terror and suspicious crimes in cyberspace, which provides national and international security. |
| If the proposed framework integrated with existing IM and SNS at server-side for surveillance will change the world of cyberspace to rest in peace without cybercrime. |
References |
|