ISSN ONLINE(2320-9801) PRINT (2320-9798)
ISSN ONLINE(2320-9801) PRINT (2320-9798)
Akshatha M M, Lokesh B, Nuthan A C
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering
As the growth in the technology increases maintaining the security of visual information during its transaction has to be increased. Rapid growth in the techniques for doing so is also increasing. Internet has become most commonly used media for communication and hence text, voice, video, Images and many more are transmitted through Internet. These might include Military Secrets, Commercial Secrets and Information of individuals and therefore it has to be transmitted by safer means with enhanced security. In the process of Visual Cryptography a secret image is encrypted into shares which refuse to divulge information about the original secret image. In this paper, Chaotic Pseudo – Random Number generation, Zigzag Scan Pattern Method, Method to reduce the degradation of the resultant image is proposed by an extension from gray to colour image. Pixel Index Method is discussed to improve the security for images. An integration of this technique of Visual Cryptography with (n, k, p) gray image is also proposed.
Keywords |
| Security, Visual Cryptography, Visual Secret Share. |
INTRODUCTION |
| Cryptography refers to the study of mathematical techniques and related aspects of information security like data confidentiality, data integrity and of data authentication. In the process of Visual Cryptography a secret image is encrypted into shares which refuse to divulge information about the original secret image. Decryption is through a separate decryption algorithm. A basic model for Visual Cryptography for natural images was proposed by Naor and Shamir, where the resultant image is twice the size of secret image. |
| As the advent of electronic applications increases, providing the security for information in an open network environment is required. Encryption is a method of transforming original data, called plain text or clear text into a form that appears to be random and unreadable which is called Cipher text. Plain text is either in the form that can be understood by a person (document) or by a computer (executable code). |
| Once it is transformed into Cipher text, neither human nor machine can properly process it until it is decrypted. This enables the transmission of confidential information over insecure channels without unauthorized disclosure. When data is stored on a computer it is protected by logical and physical access controls. When this same sensitive information is sent over a network,the information is in much more vulnerable state. Naor and Shamir introduced the new concept of Visual Cryptography in 1994[1], requiring no computation except human Visual System to decrypt. They proposed a basic (2,2) Visual Cryptography scheme where a secret image is divided into 2 shares, revealing the secret image through Share Stacking. |
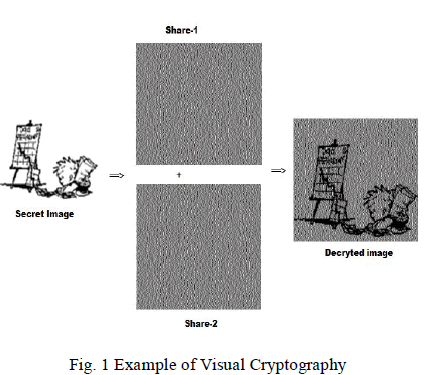 |
| In figure 1 a secret image that has to be sent is divided into shares. When these two shares are stacked together and put into a Human Visual System the resultant image is revealed.In the visual secret sharing model [1], a secret picture must be shared among n participants. The picture is divided into n shares so that if m transparencies (shares) are placed together the picture is visible. When there are fewer m transparencies it is invisible. This ensures that the secret picture is viewed as a set of black and white pixels with each pixel being handled separately. |
RELATED WORK |
| 2.1 Basic (2,2) Scheme |
| The (2, 2) VC scheme divides the secret image into two shares so that reconstruction of an image from a share is impossible. Each share is printed in transparency. A share is a random noise. Encryption is performed for each pixel. Fig.2 shows the 2 different shares for black and white pixels. The figure shows how a pixel in a image in divided into two sub pixels depending on whether the pixel is black or white. By doing so the width of the share increases. This is termed as Pixel Expansion. |
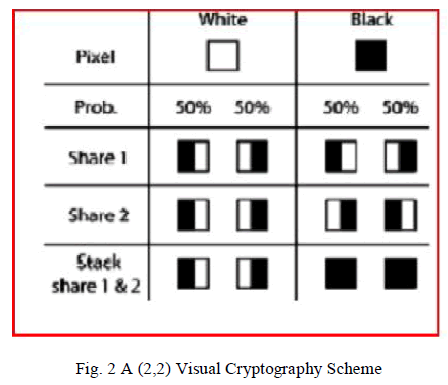 |
| Figure 2 shows the problem of Pixel expansion where a Pixel in the image is divided into 2 sub pixels which increase the width of the entire image and thus there will be increase in bandwidth required and so increase in the power consumption. |
| 2.2 Pseudo Randomized Visual Cryptography Scheme |
| Figure 3 shows how the shares are generated by pixel reversal and using pseudo random technique. Each pixel is being handled separately. The input is a secret image and the output is the shares. Here there is no pixel expansion. The decoded image and the original secret image are of the same sizes. But the secret image which is decoded had a darker resolution than the original image. Pre-processing technique was used to overcome this problem. |
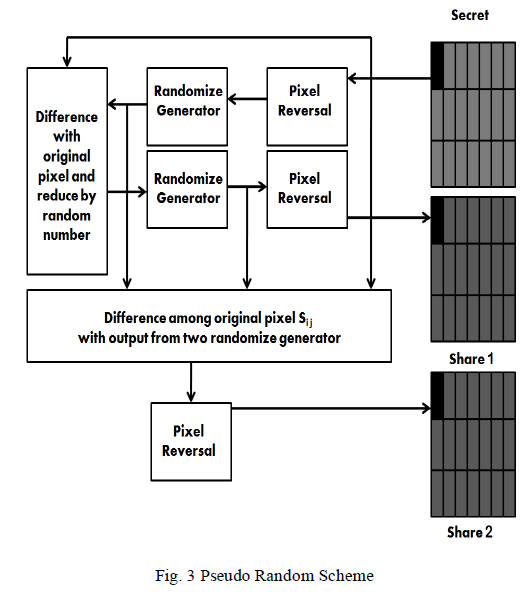 |
| Figure 3 shows the elimination of problem of pixel expansion and the generation of share 1 and share 2 for a gray image. |
PROPOSED WORK |
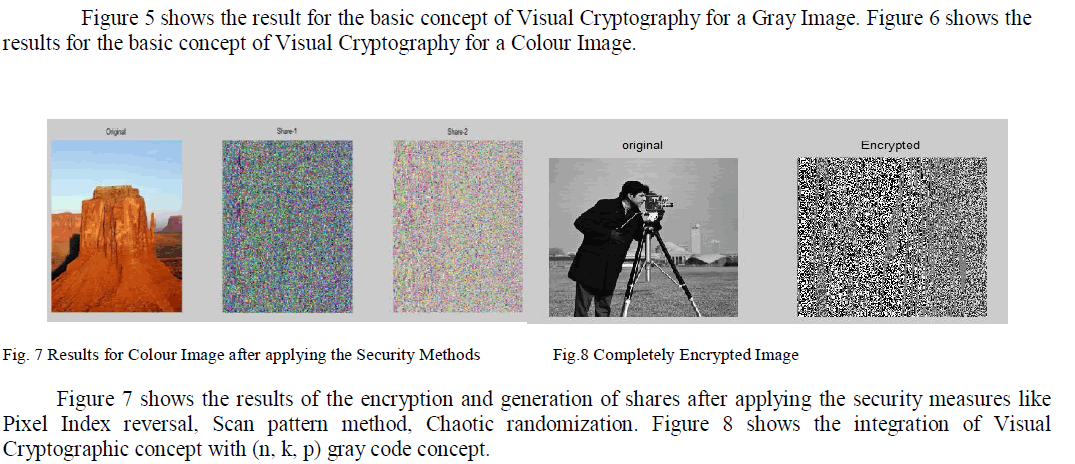
| In this paper, the problem of pixel expansion is eliminated and also a method is proposed for color image usage and thus the degradation of the resultant image is reduced. A secret image is taken and is split into RGB components. Each component is handled separately. Each pixel is decomposed using Bit Plane Decomposition technique. ATMF and De – noising is done to eliminate the presence of noise. This result is then encrypted using Chaotic Random Number Generator and the bit planes are re – ordered and Re – combined. Pixel Index Reversal is done to reverse the index of the pixel to improve the Security. At this stage Zigzag Scan Pattern is applied to increase the scrambling, thus increasing the Security. The output after the Scan is then applied to Pseudo Random Scheme as shown in Figure 3. |
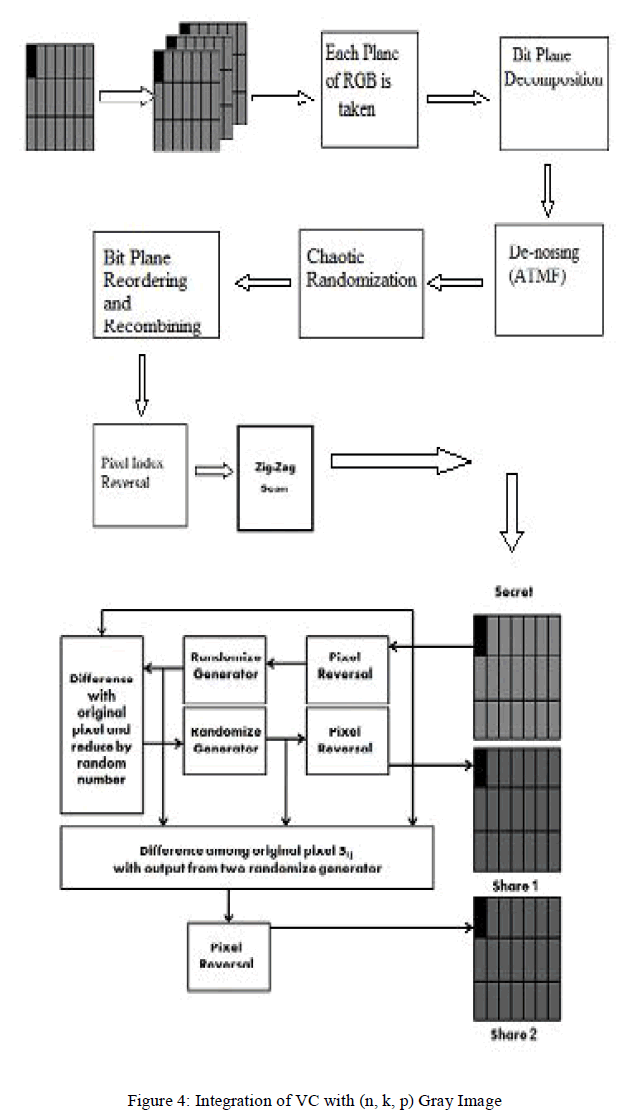 |
| Figure 4 shows the integration of concept of Visual Cryptography with pixel index reversal, Zigzag Scan of the image for a colour image with its integration with (n, k, p) gray codes. |
| 3.1Simulations and Results |
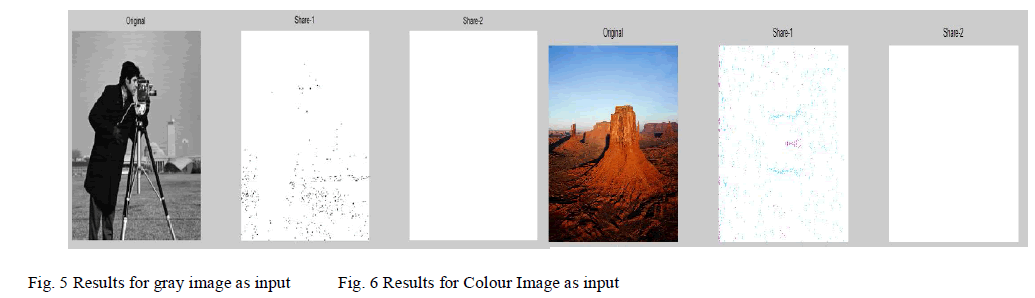
| The algorithm is implemented in MATLAB. Figure 5 shows the experiment results for the gray image. |
 |
 |
| 3.2 Comparison of the Algorithms |
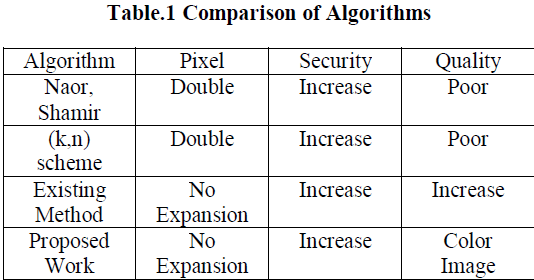 |
| The above table shows the comparison of the existing and proposed techniques of Visual Cryptography. |
CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK |
| The security increases as the scrambling is more. The time consumption is also in terms of Nano seconds and hence this method can be applicable in most of the fields. The problem of pixel expansion is also eliminated. Future work can include the application of this technique for 3D images. Some technique can be made to improve the quality of resultant image and also to reduce the power consumption. Video Encryption using the same method can be worked out. |
References |
|