Page 63
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
November 13-15, 2017 | Las Vegas, USA
14
th
International Conference and Exhibition on
Materials Science and Engineering
RRJOMS | Volume 5 | Issue 7 | November, 2017
Characterization and analysis of phosphor condition with electrode of perovskite solar cells
Hyung Wook Choi
and
Jeong Hun Ma
Gachon University, Republic of Korea
N
owadays, solar cells of silicon have reached efficiencies of up to 25% for single crystal Si. But, the production of such material
requires energetically demanding processes and relatively expensive production. Recently, a new class of perovskite was
introduced as light harvesting material, showing strong absorption in a broad region of the visible spectrum, good electron and hole
conductivity, delivering also high open circuit voltages in photovoltaic devices. The main advantage of such an organic-inorganic
hybrid material is a high absorption coefficient, excellent long distance carriers to move the hole diffusion length. Mixed halide
perovskite materials, which electron hole diffusion length is ten times longer than those only containing iodide. Which presents
efficient charge transport, low recombination rates and also good pore filling of the TiO
2
layer enhancing device performance with
respect to Spiro-OMeTAD (HTM). Trivalent rare-earth (RE) ions activated materials have kept booming in the past decades owing
to their wonderful applications in phosphor-converted white light-emitting diodes (WLEDs), solar cells, temperature sensors, and
drug deliveries. RE ion-doped inorganic phosphors revealed intense luminescent properties and showed potential applications in
WLEDs. The conversion luminescence of a phosphor from the ultraviolet region to the visible region can enhance the light harvesting
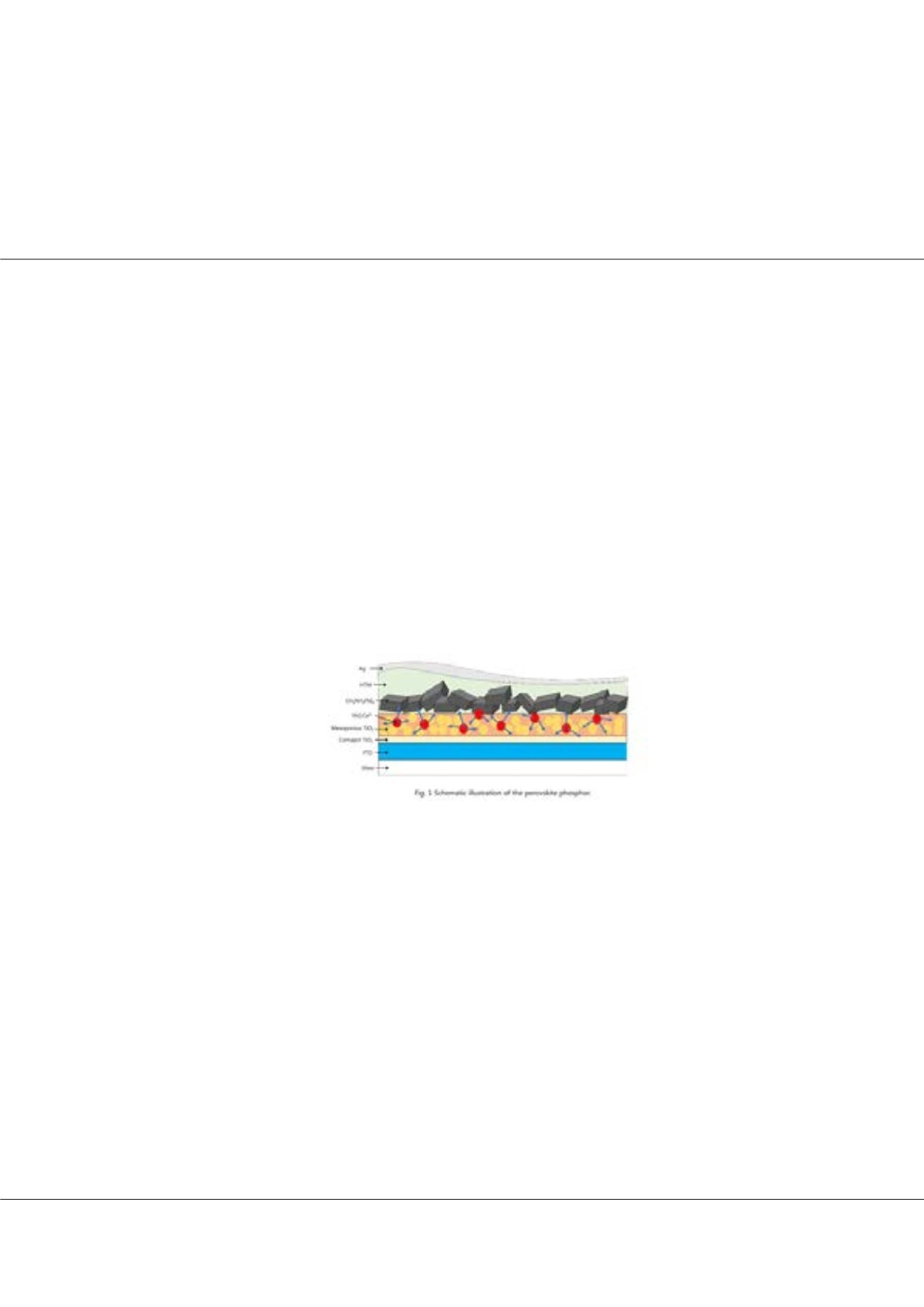
in Perovskite solar cells (PSCs), because many perovskites can only absorb visible light. In this work, to explore the influence of
phosphor additives on the conversion efficiency of PSC, we introduce the YAG:Ce
3+
phosphor layer. The samples were characterized
by XRD, SEM, UV–vis, PL and IV-curves. Photoelectrode DSSC with light-to-electric energy conversion efficiency was achieved
under a simulated solar light irradiation of 100 mW/cm
2
(AM 1.5).
Biography
Hyung Wook Choi has completed his PhD from Yonsei University, Korea and postdoctoral studies from Pennsylvania State University, USA. He has published more than
100 papers in SCI journals.
chw@gachon.ac.krHyung Wook Choi et al., Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2017, 5:7
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C1-012