ISSN ONLINE(2278-8875) PRINT (2320-3765)
ISSN ONLINE(2278-8875) PRINT (2320-3765)
B.Jagadeesh1, D.Praveen Kumar2
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Copyright protection of digital content is of great importance in present day scenario as manipulation of digital data is very simple.This can be offered by watermarking techniques. Many proposed watermarking of digital images throughout the years, in this paper a novel digital image watermarking algorithm is proposed based on artificial neural networks. As neural networks are good at pattern recognition, they can be used as a medium to store the frequency domain components of the image and these can be used at the extraction of watermark. The input to the network is given from the HVS model. Care should be taken such that the host image is not distorted, this information can be given by HVS model. The proposed model gives a better PSNR value and it is robust to many image processing attacks like compression, resizing, filtering etc.
Keywords |
| Digital Image Watermarking, Human Visual System, Discrete Cosine Transform, Back Propagation Neural Network. |
INTRODUCTION |
| Copyright protection is much needed for digital information because the internet has become most used resource as the people have unlimited access to share the digital contents such as images, videos, etc. Digital image watermarking has become very popular in recent years as a good solution for these cases [1]. In this field many have proposed good algorithms for the problems existing before. In digital image watermarking the watermark is embedded into the host image, and it is extracted when needed. There are three kinds of detection types at the receiver, first it is blind method where the receiver do not know any information about the host image, second it is the semi blind method in this the receiver has some information about the host image and last it is the non-blind method where the receiver need the host image to extract the watermark. In this paper semi blind method is used. |
| Embedding of the watermark into a host image can be done in three ways, first by directly placing the watermark into the host image as we are embedding the watermark into the pixels directly this method is called as spatial domain method. Second we can transform the host image values into its frequency domain coefficients and embed the watermark into the coefficients this method is called as transform domain method, third type of method make use of both the approachesfor embedding watermark this is called as hybrid domain method. Each method has its own merits and demerits based on the application embedding method is chosen. |
| This paper is organized as following: Section 2 explains about the related work. Section 3 describes the basic model of Human Visual System and Back Propagation Neural Networks. This is followed by Section 4 that explains the embedding and extraction of digital image watermarking. In Section 5, the experimental results are given for various image processing attacks. The conclusions are specified in section 6. |
RELATED WORK |
| Image watermarking algorithms which are based on the artificial intelligence techniques [2-13] are available in the literature.Through the years many have developed algorithms for watermarking some of them areCharu Agrawal et al. [2] proposed an algorithm based on Human Visual System (HVS) and Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) using Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT).Qiao Baoming et al. [3] proposed a watermarking method using Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN) and Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT). 2-level DWT is applied to host image. Blocks are selected based on standard deviation values. Block values fed to network as input and target vectors. Trained network and extra information is used in extracting the watermark. |
| Nallagarla et al. [4] proposed a watermarking method using Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN) and Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT). 2-level DWT is applied to host image. Trained network and extra information is used in extracting the watermark.Sameh Oueslatiet al. [5] proposed a HVS (Human Visual System) based watermarking method using Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN) and Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT).Sameh Oueslati et al. [6] proposed an adaptive watermarking algorithm performed in the wavelet domain which exploits Human Visual System (HVS) and a Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) for medical images. |
| In the proposed method, three coefficients from the low frequency, mid frequency and high frequency bands of the transformed 8x8 sub-image, and watermarked bits are placed in these coefficients. When extraction of the watermark these three coefficient values are added and compared with a threshold value and based on the output the extracted bit is determined either 0 or 1. |
PRELIMINARIES |
A. Discrete Cosine Transform: |
| The DCT transforms a signal from a time domain representation to frequency domain representation. Embedding watermark into lower frequency coefficients will cause imperceptibility problems, embedding into higher frequency coefficients will not sustain to attacks such as compression etc, so to make algorithm more robust to known and unknown image processing attacks in this paper middle frequency coefficients are considered. By [2] Two dimensional DCT used in digital image processing for a given image A of size N*N is defined as |
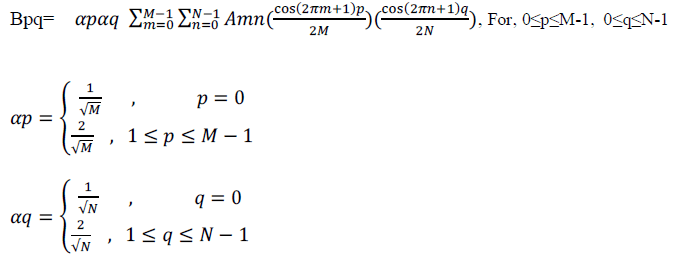 |
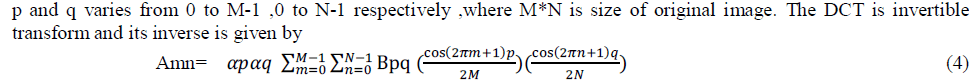 |
B. Human Visual System: |
| The sensitivity of human eye to various spatial frequencies is determined by the frequency sensitivity. The effect of the imperceptibility to noise on a constant background is calculated by luminance sensitivity. We focus here on the sensitivity of brightness, frequency and edge. The HVS model used in this work has been suggested in [1]. This model is also used in many insertion algorithm and detection of the watermark. |
1. Luminance sensitivity ( Lk): |
| Brightness masking proves the effects of detectable noise thresholds on a constant background. The brighter the background is, the larger the embedded signal could be. The luminance sensitivity is estimated by the following formula: |
| Where XDC,k, is theDCcoefficient of the DCT of the kthblock,XDCis the mean value of all DC coefficients of a specific image. |
2. Frequency sensitivity ( Fk): |
| If we divide the image into 8x8 blocks and DCT is applied to each block, there will be 8x8 matrix of DCT coefficients for each block. This matrix is divided into three areas of high frequency (H), low frequency (L), and medium frequency (M). The 2D DCT matrix's top left comer represents lowest frequency coefficient while the bottom right comer is the highest frequency. The Energy content of image is placed in low frequency DCT coefficients. It has been proved that watermark embedding in low frequency, places the water-mark perceptibly in the image [28]. On the other hand embedding the watermark in high frequency coefficients causes the watermark to be removed from the image after the image compression, since compression process causes the DCT coefficients to be removed in high frequencies. So the medium frequencies are used to embed the watermark. |
3. The Edge Sensitivity (Ek): |
| As the edge is detected within the image using threshold operation, edge sensitivity can be quantified as a natural corollary to the computation of the block threshold T. The Matlab image processing toolbox implements graythresh( ) routine which computes the block threshold using histogram – based [13]. The implementation of this routine is as follows: |
| Ek = graythresh(f) (6) |
| where f is the host sub-image (block) in question and T is the computed threshold value. |
C. Back Propagation Neural Network: |
| For simulation of biology neural computation neural networks are introduced. It has self-learning, self-organizing, association of ideas, etc. and has great compatibility with human visual system. Therefore, the selected NN in this paper is a feed-forward NN. There are five layers including an input layer, hidden layers and an output layer. The desired outputs of NN are the maximum watermarking strength. Figure shows the architecture of this network. The first layer is to present the input variables of network. Each HVS parameter is a input variables to the network, i.e. The sensitivity value of luminance, edge respectively. These inputs are then fed to a hidden layer using tan sigmoid activation functions (output in the range frequency sensitivity values); this is then fed to the output layer. During training samples, information is propagated back through the network and used to update connection weights. It repeats learning many times for every example in the training set until it has minimized the output errors. This system does not fully replace humans; they are still needed to generate the training data and should check the results periodically to ensure the neural network is working at peak performance. |
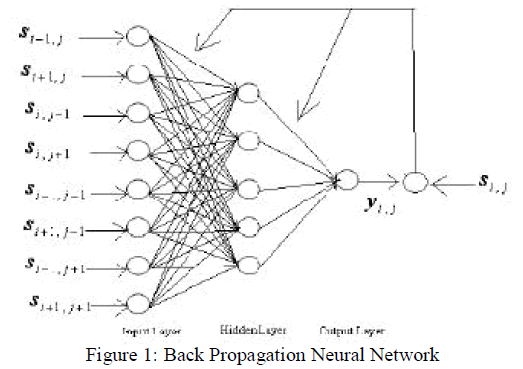 |
PROPOSED METHOD |
| Divide the host image into non overlapping blocks and apply DCT to each block, calculate HVS parameters and train the neural network. Training the neural network to frequency sensitivity values, these values are used inembedding process by doing so the frequency domain coefficients of the sub image are not varied by an unknown quantity instead replaced by one of the coefficient values, thus the block values remain unchanged even after inverseDCT is applied. At the extraction side the trained neural network is used so as to obtain a similar set of data which is used to embed the watermark into the host image and by performing the inverse operation the watermark is extracted from the watermarked image. |
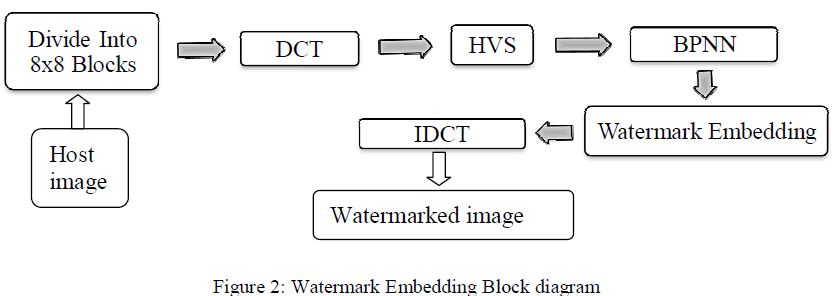 |
A. Embedding Algorithm |
| 1: Divide the input image into 8x8 non overlapping sub images and take DCT for each sub-image |
| 2: Calculate HVS parameters for each sub image. |
| 3: For calculated HVS parameters as input to the neural network train it for the frequency sensitivity values |
| 4: Calculate mean for each sub image and arrange them in descending order take the first 1024 blocks as key1 |
| 5: Embed the watermark into the image by taking key1 using the embedding formula. |
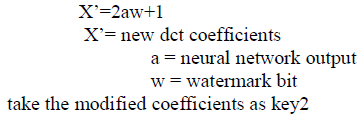 |
| 6: Take inverse DCT for each sub image and recombine them all to form the original image. |
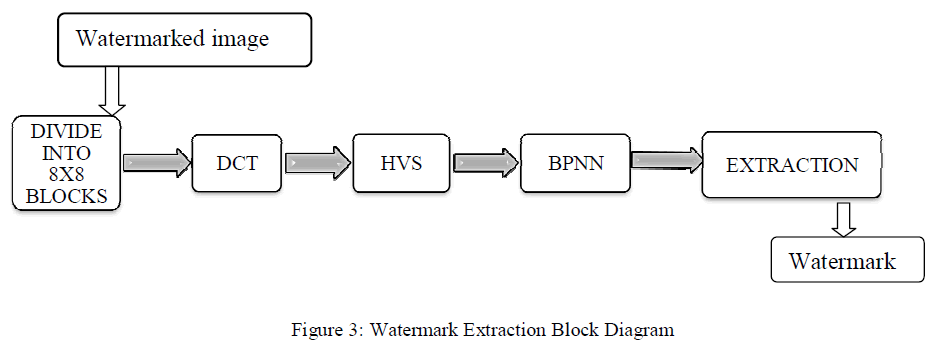 |
B. Extraction Algorithm: |
| 1: For the input noisy image split it into 8x8 non overlapping sub images and apply DCT for each block. |
| 2: Calculate HVS parameters for each sub image |
| 3: Train the neural network for the frequency sensitivity values |
| 4: Making use of key1 and key2 calculate the watermark bits by |
| W=X’-1/2a |
| X’=DCT coefficients |
| a= neural network output |
| 5: Rearrange the watermark bits into32x32 image. |
EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS |
| Experiments are performed to evaluate the effectiveness of the method on host 512x512 pixels grey-scale image ‘LENA’, shown in Figure 4. |
 |
| The watermark image is 32x32, a logo having the letters ‘ECE’ as shown in Figure 5. The watermark is a monochrome image having only single color either black or white and while considering the pixel values for embedding black pixels are considered as 0 and white pixels are considered as 1. |
 |
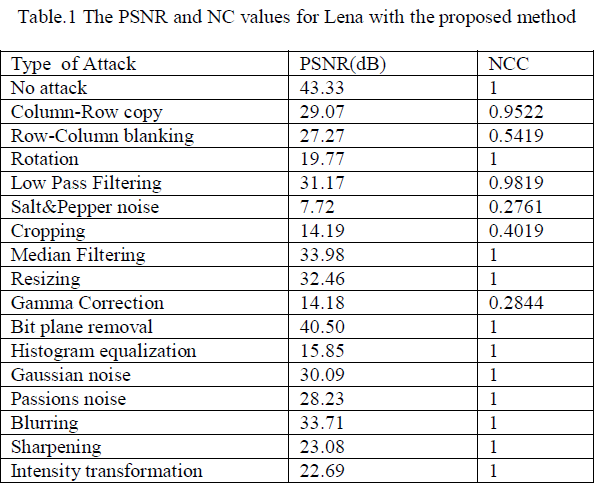
| Different image processing attacks are applied to the watermarked image and watermak is extracted from the watermarked image.Image processing attacks applied, include row column blanking where random rows/columns are made zero, in the presentresult rows 302,128,510,columns 290,512,110 are made zero.In the rotation attack the watermarked image is rotated by an angle 10 degrees. In sharpening attack all the edges in the image are enhanced. In resizing attack the watermarked image is first resized to 256x256 pixels and then again resized to 512x512 pixels. In histogram eqilisation attack the watermarked image is enhanced using histogram equilization methodamd watermark is retrived from the enhanced image.For filtering attacks low pass filter, median filter are applied to the watermarked image by doing so a smoothend image is formed, and from this image watermark is extracted. The Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) and the Normalized Cross correlation (NC) are used as a metric to compare the imperceptibility and robustness respectively are summarized in Table 1. |
 |
CONCLUSION |
| In this paper, a Back Propagation Neural Network and HVS based Digital Image Watermarking scheme is proposed. The watermarks bits are embedded into the mid frequency band of the DCTcoefficients suchthat the host image is not distorted and yields a better PSNR value.In the embedding process the neural network is used to remember the original un-watermarked sub image coefficients, this network is used at the extraction process to get back the watermark bits. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is robust to many image processing attacks and for imperceptibility it yields good PSNR value. |
References |
|