Page 53
conferenceseries
.com
RRJOMS | Volume 5 | Issue 4 | July, 2017
July 27-29, 2017 Vancouver, Canada
10
th
International Conference on
Emerging Materials and Nanotechnology
Suspension thermal sprayed nanocomposite WC-Co coatings: Nano-indentation assessment
Matheus (Theo) F A Goosen
1
, Omar Ali
2
, Rehan Ahmed
1
, Nadimul H Faisal
1
, Nayef M Al-Anazi
1
and
Youssef O Elakwah
1
1
Alfaisal University, KSA
2
Heriot-Watt University, UK
Statement of the Problem:
Nanoindentation of WC-12Co thermal spray coatings has been used to evaluate the elastic
modulus and hardness of coating on the polished surface of the coatings. While there has been much progress overall, limited
research has been reported on the deposition and evaluation of WC-cermet coatings. The aim of this study was to evaluate the
microstructural and nanohardness characteristics of tungsten carbide-cobalt (WC-Co) cermet coatings deposited by liquid
suspension spraying.
Methodology:
Commercially available WC-Co coating powder was milled and water based suspension was produced as
feedstock for the thermal spray coating process. Microstructural evaluations of WC-Co cermet coatings included XRD (X-Ray
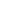
Diffraction) and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy). Post spraying nanomechanical evaluations were conducted using a
Berkovich nanoindenter.
Findings:
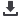
Results indicated relatively higher modulus but lower hardness of suspension coatings. The load displacement curves
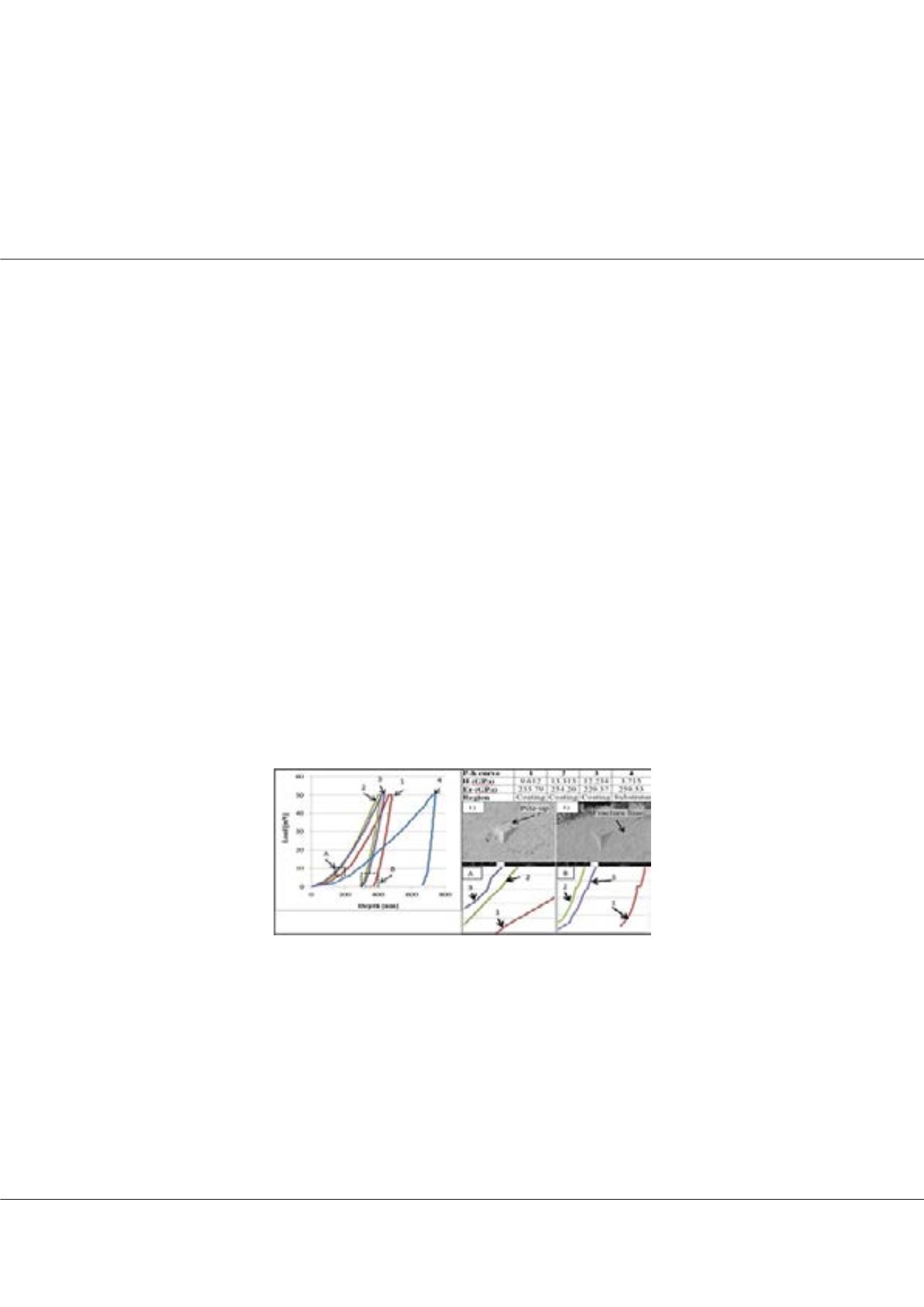
during nanoindentation were characteristic of the complex coating microstructure showing signs of microcracking and pile-
up. The load displacement (P-h) curves along with the SEM images of indents for S-HVOF (suspension high velocity oxyfuel)
coating illustrated evidence of sink-in and pile-up of material around the indent contact residual impression during the nano-
indentation process. There was some indication of microcracking during indentation as well.
Conclusions:
A comparison of S-HVOF and conventional HVOF coatings points toward phase transformations occurring in
the suspension spraying which led to nanocrystalline or amorphous phases. The elastic modulus of S-HVOF coatings was on
average higher than the conventional HVOF coating. The load displacement curves show features which are consistent with
the complex coating microstructure with evidence of micro-cracking and pile-up.
Biography
Mattheus (Theo) F A Goosen has played key roles in the development of new start up academic institutions. For the past nine years he has held the position of
founding Associate Vice President for Research & Graduate Studies at Alfaisal University a private start-up non-profit institution in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. He has
obtained a Doctoral degree in Chemical & Biomedical Engineering from University of Toronto, Canada in 1981. He has more than 180 publications to his credit
including over 133 refereed journal papers, 45 conference papers, 10 edited books and 10 patents. His H-index is over 47 and has over 8000 citations on Google
Scholar. On Scopus he has 133 publications with over 4000 citations. His research interests are in the areas of renewable energy, desalination, sustainable
development, membrane separations, spray coating technology and biomaterials.
mgoosen@alfaisal.eduMatheus (Theo) F A Goosen et al., Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2017
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C1-002